1 背景相关
背景颜色 background-color = 颜色名称/rgb值/十六进制值
背景图片 background-image = url('')
背景图片平铺方式 background-repeat = repeat-x(仅水平平铺) repeat-y(仅垂直平铺) no-repeat(不平铺)
设置背景图片位置 background-position = 数字+单位/center/top/bottom/left/right 同上。 例如:50px 50px
背景图片是否滚动 background-attachment = fixed(不滚动) scroll(滚动)

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>first page</title> <style> body{ background-color: aliceblue; background-image: url('l.jpg'); background-repeat: no-repeat; background-position: right top; background-attachment: fixed; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 >hello world</h1> <p >this paragra is only used for test</p> <br> <p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> </body> </html>
2 文本相关
文本颜色: color = 颜色名称/rgb值/十六进制值
文本对齐方式:text-align = center(居中) right(右对齐) justify(两端对齐)
通过使用text-align:center; 可以将该元素中的 行内元素 居中显示,也就是图片字体都可以居中显示。
文本加工: text-decoration = underline(下划线)
文本缩进: text-indent = 十进制值+单位。例如:50px
文本大小写: text-transform = uppercase(大写) lowercase(小写) capitalize(首字母大写)
文本阴影: text-shadow = num1(左右) num2(上下) num3(粗细) color

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>first page</title> <style> .first{ color:red; text-align: center; text-transform: uppercase; text-decoration: none; } #sencend{ color:green; text-transform: capitalize; text-align: right; text-decoration: underline; text-indent: 50px; } .third{ color:yellow; text-indent: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 class="first">hello world</h1> <p id="sencend">this paragra is only used for test</p> <p class="third">this paragra is only used for test</p> <p>this paragra is only used for test</p> </body> </html>
所有文本属性:
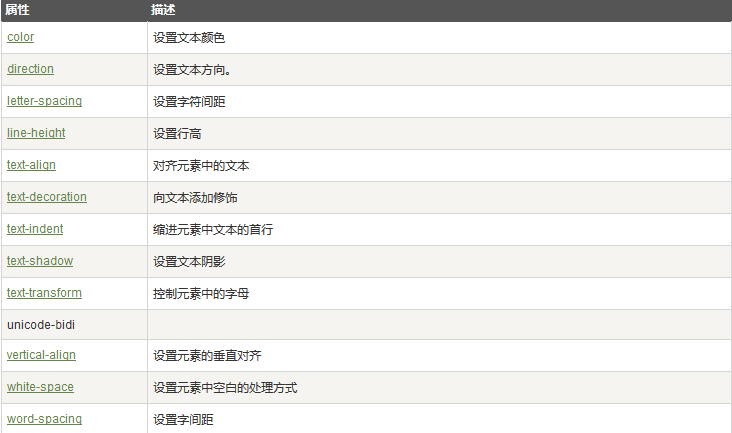
3 字体相关
字体系列 font-family 属性应该设置几个字体名称作为一种"后备"机制,如果浏览器不支持第一种字体,他将尝试下一种字体。注意: 如果字 体系列的名称超过一个字,它必须用引号,如Font Family:"宋体"。多个字体系列是用一个逗号分隔指明:
字体样式 font-style = normal(正常) italic(斜体) oblique (粗体)
字体大小 font-size = 数字+单位

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>first page</title> <style> body{ font-family: Sans-serif,Monospace; font-style: italic; font-size: 16px; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 >hello world</h1> <p >this paragra is only used for test</p> <br> <p>hello world</p> </body> </html>
4 链接
a:link {} 未访问过的链接
a:visited {} 已访问过的链接
a:hover {} 鼠标放在链接时
a:active {} 链接被点击时

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>first page</title> <style> a:link{color:mediumvioletred;font-size: 16px;text-decoration: none} a:visited{color:blue;font-size:16px;text-decoration: none} a:hover{color:darkgreen;font-size:24px;text-decoration: underline;background-color: aquamarine;padding: 4px} a:active{color:darkgoldenrod;font-size: 44px;text-decoration: overline} </style> </head> <body> <h1 >hello world</h1> <p >this paragra is only used for test</p> <a href="http://baidu.com" target="_blank">百度</a> <br> <p>hello world</p> </body> </html>
5 列表
列表项样式 list-style-type = disc(默认实心圆)/circle(空心圆)/square(方块)/decimal(数字)……
列表项图片 list-style-image = url('')

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> ul.a {list-style-type:circle;} ul.b {list-style-type:square;} ol.c {list-style-type:upper-roman;} ol.d {list-style-type:lower-alpha;} </style> </head> <body> <p>Examples of a and b:</p> <ul class="a"> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Tea</li> <li>Coca Cola</li> </ul> <ul class="b"> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Tea</li> <li>Coca Cola</li> </ul> <p>Examples of c and d </p> <ol class="c"> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Tea</li> <li>Coca Cola</li> </ol> <ol class="d"> <li>Coffee</li> <li>Tea</li> <li>Coca Cola</li> </ol> </body> </html>
6 表格
边框全面设置: border = 1px solid(实线) 颜色 后两个属性可以省略
边框颜色: border-color = 颜色
边框样式: border-style = solid(只记住这一个就可以了)
单独边框: border-top
border-top-color
border-top-style
border-top-width
详情请看:http://www.w3school.com.cn/cssref/index.asp

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> #customers { font-family:"Trebuchet MS", Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; width:100%; border-collapse:collapse; } #customers td, #customers th { font-size:1em; border:1px solid #98bf21; padding:3px 7px 2px 7px; } #customers th { font-size:1.1em; text-align:left; padding-top:5px; padding-bottom:4px; background-color:#A7C942; color:#ffffff; } #customers tr.alt td { color:#000000; background-color:#EAF2D3; } </style> </head> <body> <table id="customers"> <tr> <th>Company</th> <th>Contact</th> <th>Country</th> </tr> <tr> <td>Alfreds Futterkiste</td> <td>Maria Anders</td> <td>Germany</td> </tr> <tr class="alt"> <td>Berglunds snabbköp</td> <td>Christina Berglund</td> <td>Sweden</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Centro comercial Moctezuma</td> <td>Francisco Chang</td> <td>Mexico</td> </tr> <tr class="alt"> <td>Ernst Handel</td> <td>Roland Mendel</td> <td>Austria</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Island Trading</td> <td>Helen Bennett</td> <td>UK</td> </tr> <tr class="alt"> <td>Königlich Essen</td> <td>Philip Cramer</td> <td>Germany</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Laughing Bacchus Winecellars</td> <td>Yoshi Tannamuri</td> <td>Canada</td> </tr> <tr class="alt"> <td>Magazzini Alimentari Riuniti</td> <td>Giovanni Rovelli</td> <td>Italy</td> </tr> <tr> <td>North/South</td> <td>Simon Crowther</td> <td>UK</td> </tr> <tr class="alt"> <td>Paris spécialités</td> <td>Marie Bertrand</td> <td>France</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>
7 轮廓
轮廓(outline)是绘制于元素周围的一条线,位于边框边缘的外围,可起到突出元素的作用。
可以对轮廓指定样式,颜色和外边框的宽度。


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .b{ outline:10px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <p><span class="b">hello world</span></p> </body> </html>
8 盒子模型
边框:
-border: 2px solid red; 表示边框宽度(border-width)为2px,边框样式(border-style)为实线,边框颜色(border-color)为红色
-其中常用的边框样式有:solid 实线 dashed 虚线 dotted 点线
-可以单独设置上右下左边框:border-top/border-right/border-bottom/border-left
外边距 margin:
-若margin后面跟一个数字,则表示上右下左外边距相同,且值为该数字;若margin后面跟两个数字,第一个表示垂直,第二个表示水平;若 margin后面跟4个数字,则按照 上 右 下 左 的顺序设置。
-可以单独设置上右下左外边距:margin-top/margin-right/margin-bottom/margin-left
-使用margin:0px auto;可以将 定宽 的 块元素 设置为居中显示
内边距 padding:
同上。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .a{ padding:10px; border:1px solid red; width:100px; } p { margin:50px; width:200px } </style> </head> <body> <p class="a">hello world </p> </body> </html>
9 尺寸

vertical-align 属性设置元素的垂直对齐方式。该属性定义行内元素的基线相对于该元素所在行的基线的垂直对齐。
10 元素分类
html元素分为三类:
块元素 block:如<div>、<p>、<h1>...<h6>、<ol>、<ul>、<dl>、<table>、<address>、<blockquote> 、<form>等。
特点: 每个块级元素都从新的一行开始,其后的元素另起一行,也就是说,块级元素很霸道,要占一整行。
块级元素可以设置 宽 高 行高 顶边距 和底边距
元素宽度在不设置的情况下,是其父容器的100%
行内(内联)元素 inline:如<a>、<span>、<br>、<i>、<em>、<strong>、<label>、<q>、<var>、<cite>、<code>等
特点: 前后无换行符
元素的高 宽 顶边距和底边距不可设置
元素的宽度就是他包含的文本或者图片的宽度。
行内块元素 inline-block:如<img>、<input>
特点: 前后无换行符
元素的 高 宽 顶边距和底边距可以设置
我们可以使用css中的display属性改变元素类型:
display = inline 默认。此元素会被显示为内联元素,元素前后没有换行符。
block 此元素将显示为块级元素,此元素前后会带有换行符。
none 此元素会被隐藏,且隐藏的元素不会占用任何空间
inline-block 设置为行内块元素
css中的display属性对元素进行转换,也可以隐藏元素。

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <style> 5 6 li{ 7 display: inline; 8 background-color: #A7C942; 9 font-size: 28px; 10 } 11 12 13 14 15 </style> 16 </head> 17 18 <body> 19 20 <ul > 21 <li>a</li> 22 <li>b</li> 23 <li>c</li> 24 <li>d</li> 25 </ul> 26 27 </body> 28 </html>

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <style> 5 6 span{ 7 display: block; 8 background-color: #A7C942; 9 font-size: 28px; 10 } 11 12 13 14 15 </style> 16 </head> 17 18 <body> 19 20 <p><span>hello</span><span>world</span></p> 21 22 </body> 23 </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> span{ display: block; background-color: #A7C942; font-size: 28px; } .a{ display: none; } </style> </head> <body> <p><span class="a">hello</span><span>world</span></p> </body> </html>
11 布局模型
CSS 有三种基本的定位机制:普通流、绝对定位、浮动。
css中有三种布局模型:
1 流动模型,默认模型。在这种模型下:
1 块元素都会在所处的包含元素自上而下按照顺序垂直延伸分布,因此在默认状态下,块元素的宽度都是100%
2 内联元素则会在所处的包含元素内从左到右水平分布显示
2 浮动模型,float
使用float属性可以让两个块元素并排显示,浮动的元素脱离标准文档流中。
(1)元素在脱离文档流就是说,float使html元素脱离文档流浮动起来,导致其后面的(在文档流中的)元素占据了float元素的原位置。
(2)内容仍然在文档流就是说,虽然承载内容的元素脱离了文档流,但是其内部内容仍然在文档流中,后续的元素即使占据了我元素的位置,也要为了其中的内容留空间。
示例:


3 层模型,使用css中的position
css的position属性有四个值:
static:HTML元素的默认值,即没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中,也就是普通流。静态定位的元素不会受到top, bottom, left, right影响。
fixed:元素的位置相对于浏览器窗口是固定位置,相当于定位基准为视窗本身的绝对定位。即使窗口是滚动的它也不会移动。通过 left right top bottom 来确定元素在正常流中的偏移位置。
relative:相对定位元素的定位是相对其正常位置,也是出现在普通流。如果对一个元素进行相对定位,它将出现在它所在的位置上。然后,可以通过设置垂直或水平位置,让这个元素“相对于”它的起点进行移动,相对定位元素它原本占的空间不会改变(也就是在普通流中原来的位置仍保留)。通过 left right top bottom 来确定元素在正常流中的偏移位置。
absolute:绝对定位的元素的位置相对于最近的已定位父元素,如果元素没有已定位的父元素,那么它的位置相对于<html>。absolute定位的元素会和其他元素重叠。Absolute定位使元素的位置与文档流无关,因此不占据空间。通过 left right top bottom 来确定元素在正常流中的偏移位置。
absolute可以和relative组合使用,定位元素以某个元素作为参照物进行定位。但有几个前提条件:
1 参照元素必需是定位元素的父元素
2 参照元素必需使用position:relative
3 定位元素使用position:absolute进行定位
另外,我们可以使用z-index属性来设置元素的堆叠次序(垂直方向的前后)

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .b{ position:fixed; z-index: -1; } </style> </head> <body> <img class='b' src="l.jpg"> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .b{ position:relative; top: 30px; } </style> </head> <body> <p class="b">test test test</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> </body> </html>
注意:在relative介绍中,有这样一句话“相对定位元素它原本所占的空间不会改变(也就是在普通流中原来的位置仍保留)”。这句话在relative实例中,得到了体现。hello world并不会占用第一行,而是从第二个段落位置开始排列。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .b{ position:absolute; top: 30px; } </style> </head> <body> <p class="b">test test test</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> <p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p><p>hello world</p> </body> </html>
Absolute定位使元素的位置与文档流无关,因此不占据空间。可以和relative的实例结果进行比较。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .b{ position:absolute; z-index: -1; } </style> </head> <body> <img class='b' src="l.jpg"> <p>hello world</p> </body> </html>
浏览器显示:

另外,定位属性还有很多,贴张图:



<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p>Mouse over the words to change the cursor.</p> <span style="cursor:auto">auto</span><br> <span style="cursor:crosshair">crosshair</span><br> <span style="cursor:default">default</span><br> <span style="cursor:e-resize">e-resize</span><br> <span style="cursor:help">help</span><br> <span style="cursor:move">move</span><br> <span style="cursor:n-resize">n-resize</span><br> <span style="cursor:ne-resize">ne-resize</span><br> <span style="cursor:nw-resize">nw-resize</span><br> <span style="cursor:pointer">pointer</span><br> <span style="cursor:progress">progress</span><br> <span style="cursor:s-resize">s-resize</span><br> <span style="cursor:se-resize">se-resize</span><br> <span style="cursor:sw-resize">sw-resize</span><br> <span style="cursor:text">text</span><br> <span style="cursor:w-resize">w-resize</span><br> <span style="cursor:wait">wait</span><br> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> div.scroll { background-color:#00FFFF; width:200px; height:100px; overflow:scroll; } div.hidden { background-color:#00FF00; width:100px; height:100px; overflow:hidden; } </style> </head> <body> <p>The overflow property specifies what to do if the content of an element exceeds the size of the element's box.</p> <p>overflow:scroll</p> <div class="scroll">You can use the overflow property when you want to have better control of the layout. The default value is visible.</div> <p>overflow:hidden</p> <div class="hidden">You can use the overflow property when you want to have better control of the layout. The default value is visible.</div> </body> </html>

