堪称明明看得见,就是写不出的一类恶心题。
通常细节颇多。
一旦方法选择合适,代码量和效率都会提升不少。
推荐:
点

struct po{ double x,y; po(){} po(double xx,double yy){ x=xx;y=yy; } po friend operator +(po a,po b){ return po(a.x+b.x,a.y+b.y); } po friend operator -(po a,po b){ return po(a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y); } };
(加减为了向量方便赋值)
两(多)点距离公式

double dis(po a,po b){ return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); }
中点
(x=(x1+x2)/2,y=(y1+y2)/2)
向量

struct vec{ double x,y; vec(){} vec(po a){ x=a.x,y=a.y; } double len(){ return sqrt(x*x+y*y); } };
向量加减和数乘略了。
len是向量的模长。
点积

double dot(vec a,vec b){ return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y; }
点积用处:可以通过两个向量的点积正负,判断向量夹角是锐角、直角、钝角
叉积

double cross(vec a,vec b){ return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; }
意义,两个向量构成的平行四边形的有向面积
AxB ,如果有A在B的逆时针方向(不超180度),那么面积是负的。否则是正的。
取绝对值就是面积。
向量旋转
https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/562549647.html
常用方法
精度控制
设置eps 1e-7~1e-10

int Fabs(double t){ if(fabs(t)<eps) return 0; if(t>0) return 1; return -1; }
点到直线距离(给出三个点)
叉积算平行四边形面积,然后除以底的长度,得到高(距离)

double hei(po p,po a,po b){ vec t1=vec(a-b),t2=vec(p-b); return fabs(cross(t1,t2))/dis(a,b); }
点到线段距离
点积判断和端点形成的角是否是钝角。是钝角,就只能是和线段两个端点的距离取min

线段是否相交
跨立实验
如果两个线段端点互相都在对方的两侧,那么相交。
点在多边形内部
上面第二篇博客有写到。
就是找一条射线,判断和多边形交点奇偶,
要枚举每条多边形上的边。(O(n))

为了排除各种和点相交,和边重合的情况,
“
为了统一起见,我们在计算射线L和多边形的交点的时候,1。对于多边形的水平边不作考虑;2。对于多边形的顶点和L相交的情况,如果该顶点是其所属的边上纵坐标较大的顶点,则计数,否则忽略;3。对于P在多边形边上的情形,直接可判断P属于多边行。 其中做射线L的方法是:设P'的纵坐标和P相同,横坐标为正无穷大(很大的一个正数),则P和P'就确定了射线L。
”
——https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35776579/article/details/54836612
求任意多边形面积
三角剖分
任意选择一个点,然后逆时针/顺时针枚举所有边,和这个点构成三角形,叉积计算有向面积,然后做和即可。
记得取绝对值,然后除以二
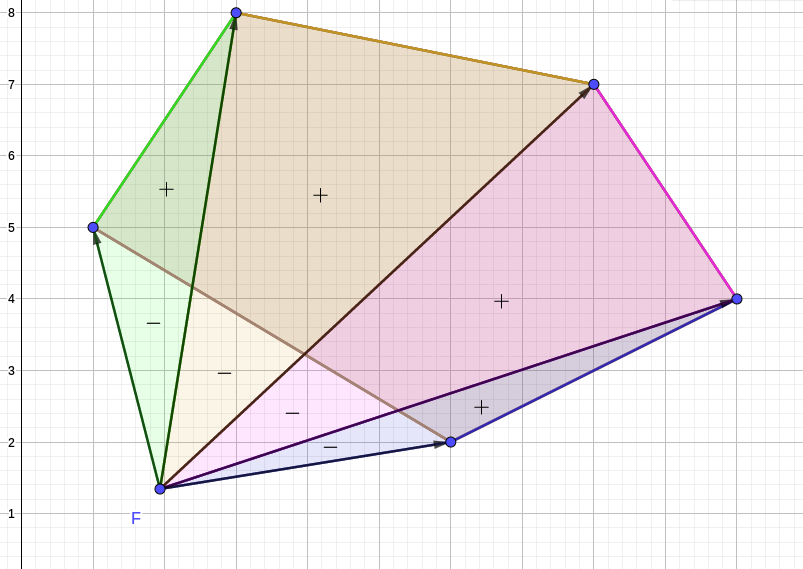
多边形重心
同样方法将多边形三角剖分
算出每个三角形的重心,套用质点组的重心公式即可
公式见上面第一篇博客。
三角形重心:
$((x1+x2+x3)/3,(y1+y2+y3)/3)$
两条直线的交点
https://blog.csdn.net/dgq8211/article/details/7952825
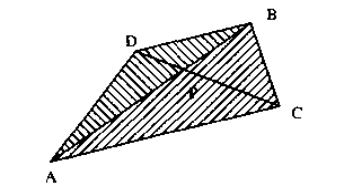
可以根据三角形相似。
得到DP和PC的比值,就可以通过D、C的坐标,算出来P的坐标。
三角形的面积必须是有向面积,因为情况不止图的这一种。
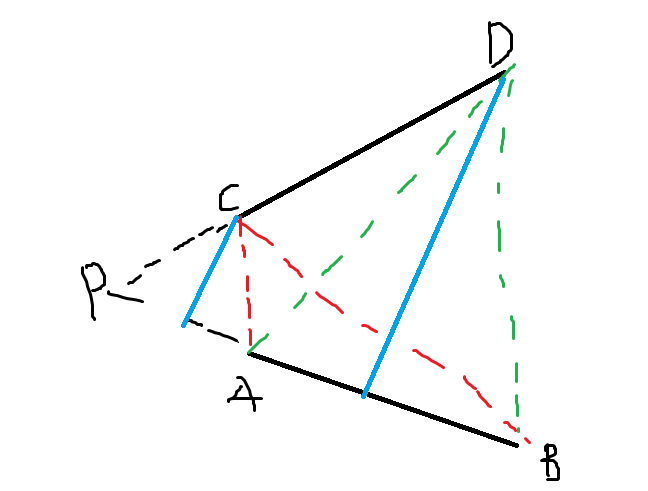
这个时候,必须求ABD,ABC的有向面积。这样正负号才是对的。
式子:
$P=frac{AB×AC*D+AD×AB*C}{AB×AC+AD×AB}$
$AB$等都是向量,从A指向B
$×$是叉乘,$*$是和点乘(横纵坐标分别相乘)
凸包
长这个样子的一个包。
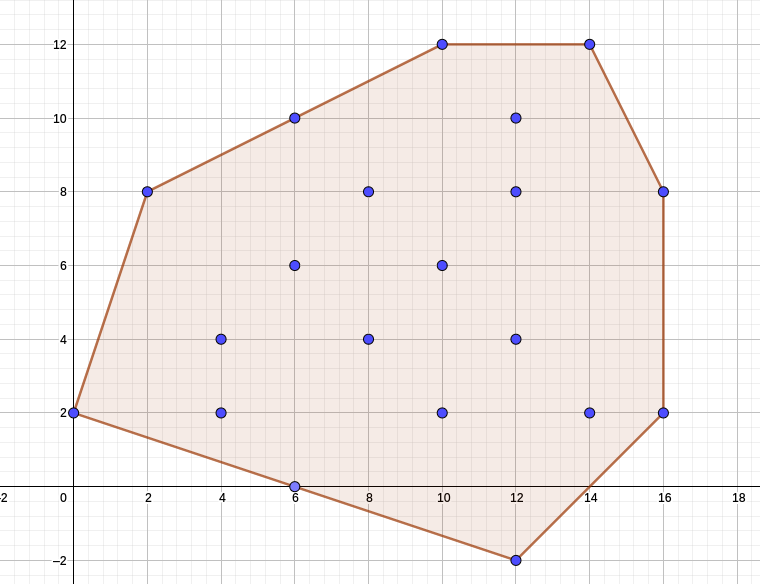
Graham 算法
①选择左下点,按极角排序,
②用一个栈维护凸包上的点,相邻的凹凸情况,用叉积判断。
由于排序,所有O(nlogn)
代码见下面模板处
旋转卡壳
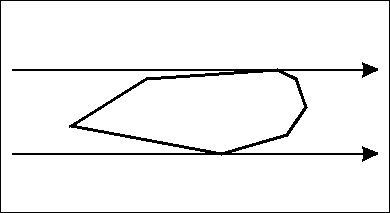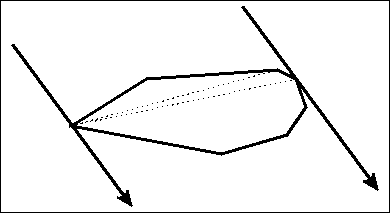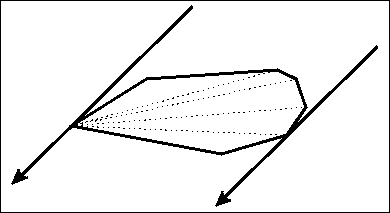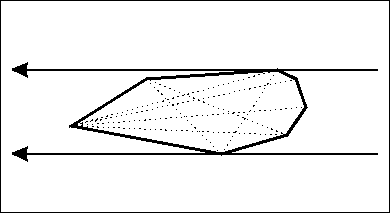
用于求凸包最大直径,或者平面最远点对。
做法:枚举一条边,然后找到和这条边平行的边在另一端的切点。(距离这个边最远的点)
具体移动点的话,可以通过叉积判断面积,找最大的位置。(当然,你也可以三分。。。)
然后这个位置和这个边的距离较大的一个,就是这次可以更新ans的值。
(证明:
只需证明,最远点对之一A,一定是和"另一个点B和与B相邻的某个点C"形成的B-C边距离最远的点。
应该可以证明因为找不出反例233333
)
发现,这个切点的位置是具有单调性的,即可O(n)解决这个问题。
(其实,Graham的排序还是O(nlogn)的)
半平面交
另一篇博客
其他
例题
【模板】二维凸包 / [USACO5.1]圈奶牛Fencing the Cows

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define reg register int #define il inline #define numb (ch^'0') using namespace std; typedef long long ll; il void rd(int &x){ char ch;x=0;bool fl=false; while(!isdigit(ch=getchar()))(ch=='-')&&(fl=true); for(x=numb;isdigit(ch=getchar());x=x*10+numb); (fl==true)&&(x=-x); } namespace Miracle{ const int N=10000+5; const double eps=1e-8; int n; struct po{ double x,y; po(){}; po(double xx,double yy){ x=xx;y=yy; } po operator +(po &b){ return po(x+b.x,y+b.y); } po operator -(po &b){ return po(x-b.x,y-b.y); } double dis(const po &b){ return sqrt((x-b.x)*(x-b.x)+(y-b.y)*(y-b.y)); } }p[N]; struct vec{ double x,y; void init(const po &b){ x=b.x,y=b.y; } double cross(const vec &b){ return x*b.y-y*b.x; } double len(){ return sqrt(x*x+y*y); } }; int Fabs(double t){ if(fabs(t)<eps) return 0; if(t>0) return 1; return -1; } bool cmp(po a,po b){ vec a1,b1; a1.init(a-p[1]);b1.init(b-p[1]); double t=a1.cross(b1); if(Fabs(t)) return t>0; return a1.len()<b1.len(); } double ans; vector<po>mem; int main(){ scanf("%d",&n); if(n==0||n==1){ printf("0.00");return 0; } for(reg i=1;i<=n;++i){ scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); }int id=1; for(reg i=2;i<=n;++i){ if(p[i].x<p[id].x||((p[i].x==p[id].x)&&(p[i].y<p[id].y))) id=i; } if(id!=1) swap(p[1],p[id]); sort(p+2,p+n+1,cmp); mem.push_back(p[1]); for(reg i=2;i<=n;++i){ while(mem.size()>2){ vec t1,t2; t1.init(p[i]-mem.back());t2.init(mem.back()-mem[mem.size()-2]); double t=t2.cross(t1); if(Fabs(t)==-1) mem.pop_back(); else break; } mem.push_back(p[i]); } for(reg i=0;i<mem.size();++i){ ans+=mem[i].dis(mem[(i+1)%mem.size()]); } if(n==2){ ans/=2.0; } printf("%.2lf",ans); return 0; } } int main(){ Miracle::main(); return 0; } /* Author: *Miracle* Date: 2018/11/24 15:03:36 */
直接处理四边形不好处理。
考虑,拼成两个三角形。
我们枚举一条四边形对角线A-B(固定A),那么三角形就是在对角线两边各选择一个点C、D,使得和A-B形成的三角形面积最大。
发现,这个C、D位置,随着B的移动,也是单调移动的。
本质是维护一个三指针,然后O(n^2)解决。

// luogu-judger-enable-o2 #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define reg register int #define il inline #define numb (ch^'0') using namespace std; typedef long long ll; il void rd(int &x){ char ch;x=0;bool fl=false; while(!isdigit(ch=getchar()))(ch=='-')&&(fl=true); for(x=numb;isdigit(ch=getchar());x=x*10+numb); (fl==true)&&(x=-x); } namespace Miracle{ const int N=2002; const double eps=1e-8; int n; struct po{ double x,y; po(){} po(double xx,double yy){ x=xx;y=yy; } po friend operator +(po a,po b){ return po(a.x+b.x,a.y+b.y); } po friend operator -(po a,po b){ return po(a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y); } }a[N]; struct vec{ double x,y; vec(){} vec(po a){ x=a.x,y=a.y; } double len(){ return sqrt(x*x+y*y); } }; double dis(po a,po b){ return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); } double cross(vec a,vec b){ return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; } int Fabs(double t){ if(fabs(t)<eps) return 0; if(t>0) return 1; return -1; } double hei(po p,po a,po b){ vec t1=vec(a-b),t2=vec(p-b); return fabs(cross(t1,t2))/dis(a,b); } bool cmp(po x,po y){ double t=cross(vec(x-a[1]),vec(y-a[1])); if(Fabs(t)) return t>0; return vec(x-a[1]).len()<vec(y-a[1]).len(); } po sta[N]; int top; double ans; int main(){ scanf("%d",&n); for(reg i=1;i<=n;++i){ scanf("%lf%lf",&a[i].x,&a[i].y); }int id=1; for(reg i=2;i<=n;++i){ if(a[i].x<a[id].x||((a[i].x==a[id].x)&&(a[i].y<a[id].y))) id=i; } if(id!=1) swap(a[1],a[id]); sort(a+2,a+n+1,cmp); sta[++top]=a[1]; for(reg i=2;i<=n;++i){ while(top>2&&cross(vec(sta[top]-sta[top-1]),vec(a[i]-sta[top]))<=0) --top; sta[++top]=a[i]; } // cout<<" top "<<top<<endl; // for(reg i=1;i<=top;++i){ // cout<<i<<" : "<<sta[i].x<<" "<<sta[i].y<<endl; // } for(reg i=1;i<=top;++i){ int p1=i,p2=i+1; for(reg j=i+1;j<=top;++j){ while(p1+1<=j&&(Fabs(hei(sta[p1+1],sta[i],sta[j])-hei(sta[p1],sta[i],sta[j]))>0)) ++p1; while(p2%top+1!=i+1&&(Fabs(hei(sta[p2%top+1],sta[i],sta[j])-hei(sta[p2],sta[i],sta[j])>0))) p2=p2%top+1; if((hei(sta[p1],sta[i],sta[j])+hei(sta[p2],sta[i],sta[j]))*dis(sta[i],sta[j])/2>ans){ //cout<<" new "<<i<<" "<<p1<<" "<<j<<" "<<p2<<endl; ans=max(ans,(hei(sta[p1],sta[i],sta[j])+hei(sta[p2],sta[i],sta[j]))*dis(sta[i],sta[j])/2); //cout<<" ans is "<<ans<<endl; } } } printf("%.3lf",ans); return 0; } } int main(){ Miracle::main(); return 0; } /* Author: *Miracle* Date: 2018/11/24 16:06:58 */
很裸的旋转卡壳求平面最远点对。

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define reg register int #define il inline #define numb (ch^'0') using namespace std; typedef long long ll; il void rd(int &x){ char ch;x=0;bool fl=false; while(!isdigit(ch=getchar()))(ch=='-')&&(fl=true); for(x=numb;isdigit(ch=getchar());x=x*10+numb); (fl==true)&&(x=-x); } namespace Miracle{ const int N=50000+5; struct po{ int x,y; po(){} po(int xx,int yy){ x=xx;y=yy; } po friend operator +(po a,po b){ return po(a.x+b.x,a.y+b.y); } po friend operator -(po a,po b){ return po(a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y); } }a[N]; struct vec{ int x,y; vec(){} vec(po a){ x=a.x,y=a.y; } int len(){ return x*x+y*y; } }; int dis(po a,po b){ return (a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y); } int cross(vec a,vec b){ return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; } bool cmp(po x,po y){ vec t1=vec(x-a[1]),t2=vec(y-a[1]); int t=cross(t1,t2); if(t) return t>0; return t1.len()<t2.len(); } po sta[N]; int top; int ans; int n; int main(){ scanf("%d",&n); for(reg i=1;i<=n;++i){ rd(a[i].x);rd(a[i].y); }int id=1; for(reg i=2;i<=n;++i){ if(a[i].x<a[id].x||((a[i].x==a[id].x)&&a[i].y<a[id].y)) id=i; } if(id!=1)swap(a[1],a[id]); sort(a+2,a+n+1,cmp); sta[++top]=a[1]; for(reg i=2;i<=n;++i){ while(top>2&&cross(vec(sta[top]-sta[top-1]),vec(a[i]-sta[top]))<=0) --top; sta[++top]=a[i]; } int T=1;int B; for(reg A=1;A<=top;++A){ B=A-1;if(B==0) B=top; while(abs(cross(vec(sta[T%top+1]-sta[A]),vec(sta[B]-sta[A])))>abs(cross(vec(sta[T]-sta[A]),vec(sta[B]-sta[A]))))T=T%top+1; ans=max(ans,max(dis(sta[T],sta[A]),dis(sta[T],sta[B]))); } printf("%d",ans); return 0; } } int main(){ Miracle::main(); return 0; } /* Author: *Miracle* Date: 2018/11/24 21:17:16 */
好题。见另一篇博客
