目录
- 引入
- 组合模式
- 源码
引入
在上一篇执行 _connectionDelegate 之后,HttpConnectionMiddleware 处理请求
return connection.ProcessRequestsAsync(_application);
在 HttpConnection 中调用 IRequestProcessor 的 ProcessRequestsAsync 方法
await requestProcessor.ProcessRequestsAsync(httpApplication);
跳转到 IRequestProcessor 的实现类 HttpProtocol 的 ProcessRequests 方法
private async Task ProcessRequests<TContext>(IHttpApplication<TContext> application) where TContext : notnull
这里会创建 MessageBody
var messageBody = CreateMessageBody();
然后创建一个真正的 context,这个时候 context 就被转换成一个可读的 HTTPContext
var context = application.CreateContext(this);
接着开始真正的调用 HTTPApplication,走到 Host 里面,接着执行 startup 里面写的管道
// Run the application code for this request
await application.ProcessRequestAsync(context);
那么接下来的 controller,api 如何出来呢?
通过 routing 和 endpoints,每个请求会 map 到一个 endpoint
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
});

调用 UseRouting 之后会添加一个 EndpointRoutingMiddleware,用于匹配路由,会将一个 URL 匹配到一个 Endpoint
MapControllers 会扫描所有 api 上面的路由,添加到 DataSource 中,它被 EndpointDataSource 所使用
由于 DataSource 的存在,可以找到匹配,匹配之后会将 SelectEndpoint 挂到 HttpContext
而 Endpoint 中是一个 RequestDelegate
如果不使用 Route 和 Endpoint,可以使用这样的形式
app.Run(async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("aaa"); });
在匹配的时候我们用到了组合的设计模式
组合模式
将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构,使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性
组合模式(Composite)经常用于树形结构,为了简化代码,使用Composite可以把一个叶子节点与一个父节点统一起来处理
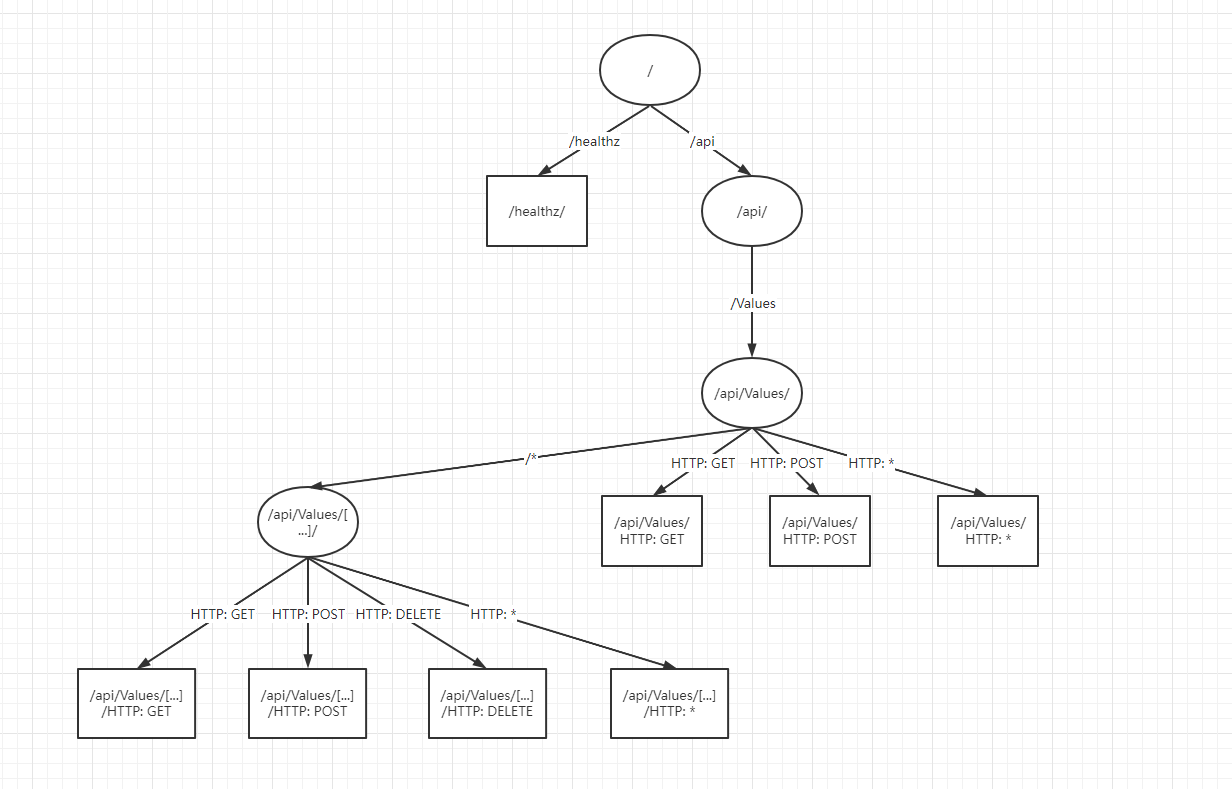
Route DfaNode:通过遍历的形式,当一个 url 进来的时候,会把所有的路由进行分割,从上到下进行匹配
源码
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/
在目录 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Routing.Matching 下面有一个 DfaMatcher,它继承自 Matcher
internal sealed partial class DfaMatcher : Matcher
DfaMatcher 有一个 MatchAsync 方法
public sealed override Task MatchAsync(HttpContext httpContext)
在 MatchAsync 方法里面首先拿到 path,接着查找候选集
var path = httpContext.Request.Path.Value!;
var (candidates, policies) = FindCandidateSet(httpContext, path, segments);
FindCandidateSet 方法里面有已经构造好的 DfaState,包含了路由分割信息
private readonly DfaState[] _states;
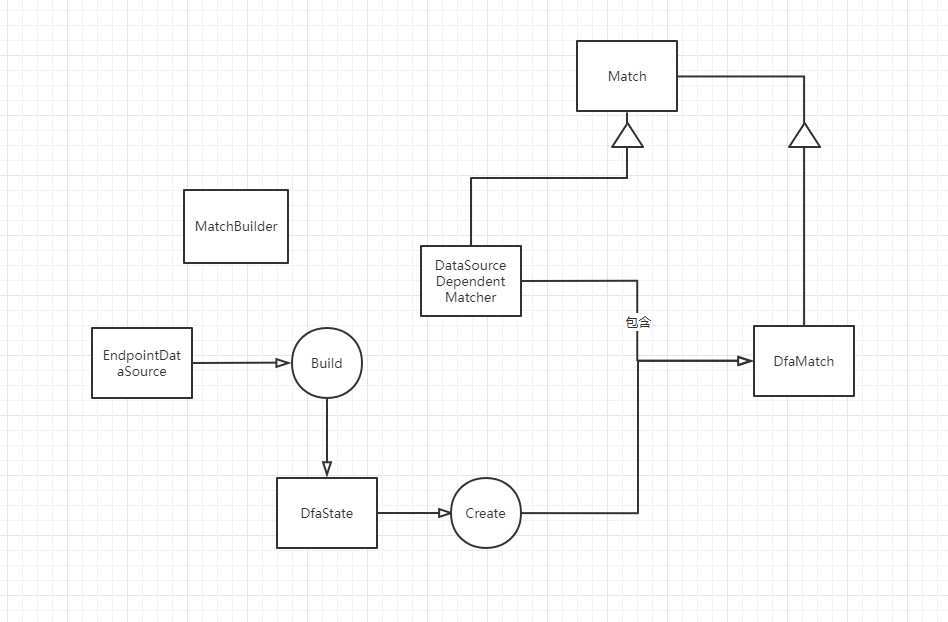
在进行 Match 之前需要有一个 DfaTree,可以在 DfaMatcherBuilder 中找到
DfaMatcherBuilder 有一个 Build 方法
public override Matcher Build()
在 Build 方法里面 BuildDfaTree
var root = BuildDfaTree(includeLabel);
BuildDfaTree 由很多个 Node 组成
AddNode(root, states, exitDestination);
然后构建 DfaState
states[exitDestination] = new DfaState(
Array.Empty<Candidate>(),
Array.Empty<IEndpointSelectorPolicy>(),
JumpTableBuilder.Build(exitDestination, exitDestination, null),
null);
再把 DfaState 传给 DfaMatcher
return new DfaMatcher(_loggerFactory.CreateLogger<DfaMatcher>(), _selector, states, maxSegmentCount);
由于这个过程比较复杂,所以将这个过程包装在 DataSourceDependentMatcher,但是它不是一个 Matcher
DataSourceDependentMatcher 的 MatchAsync 方法直接调用了 CurrentMatcher 的 MatchAsync 方法
public override Task MatchAsync(HttpContext httpContext)
{
return CurrentMatcher.MatchAsync(httpContext);
}
所以 DataSourceDependentMatcher 的主要功能是构造一个 Matcher,就是一个 DfaMatcher
private Matcher CreateMatcher(IReadOnlyList<Endpoint> endpoints)
对外部来讲只是一个 Matcher,然后它需要实现对内部的封装,把所有细节隐藏在 DataSourceDependentMatcher 中
DataSourceDependentMatcher 只是一个对 DfaMatcher 叶子节点的组合
课程链接
https://appsqsyiqlk5791.h5.xiaoeknow.com/v1/course/video/v_5f39bdb8e4b01187873136cf?type=2
本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。
欢迎转载、使用、重新发布,但务必保留文章署名 郑子铭 (包含链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/MingsonZheng/ ),不得用于商业目的,基于本文修改后的作品务必以相同的许可发布。
如有任何疑问,请与我联系 (MingsonZheng@outlook.com) 。
