29 | 定义仓储:使用EF Core实现仓储层
首先定义仓储层的接口,以及仓储层实现的基类,抽象类
仓储层的接口
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure.Core
{
/// <summary>
/// 包含普通实体的仓储
/// 约束 TEntity 必须是继承 Entity 的基类,必须实现聚合根 IAggregateRoot
/// 也就是说仓储里面存储的对象必须是一个聚合根对象
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TEntity"></typeparam>
public interface IRepository<TEntity> where TEntity : Entity, IAggregateRoot
{
IUnitOfWork UnitOfWork { get; }
TEntity Add(TEntity entity);
Task<TEntity> AddAsync(TEntity entity, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
TEntity Update(TEntity entity);
Task<TEntity> UpdateAsync(TEntity entity, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
bool Remove(Entity entity);// 由于没有指定主键,只能根据当前实体进行删除操作
Task<bool> RemoveAsync(Entity entity);
}
/// <summary>
/// 包含指定主键的类型的实体的仓储
/// 继承了上面的接口 IRepository<TEntity>,也就是说拥有了上面定义的所有方法
/// 另外一个,它实现了几个跟 Id 相关的操作的方法
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TEntity"></typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="TKey"></typeparam>
public interface IRepository<TEntity, TKey> : IRepository<TEntity> where TEntity : Entity<TKey>, IAggregateRoot
{
bool Delete(TKey id);
Task<bool> DeleteAsync(TKey id, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
TEntity Get(TKey id);
Task<TEntity> GetAsync(TKey id, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
}
具体抽象类的实现
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure.Core
{
/// <summary>
/// 定义普通实体的仓储
/// 定义约束 TDbContext 必须是 EFContext,也就是仓储必须依赖于 EFContext 及其子类
/// 将来就可以把自己定义的比如 DomainContext 作为泛型参数传入 Repository,就可以很快捷地定义出来自己的仓储
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TEntity"></typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="TDbContext"></typeparam>
public abstract class Repository<TEntity, TDbContext> : IRepository<TEntity> where TEntity : Entity, IAggregateRoot where TDbContext : EFContext
{
// 具体实现需要依赖 DbContext
protected virtual TDbContext DbContext { get; set; }
public Repository(TDbContext context)
{
this.DbContext = context;
}
public virtual IUnitOfWork UnitOfWork => DbContext;// 因为 DbContext, EFContext 实际上实现了 IUnitOfWork,所以直接返回
// 下面这些方法都是 EntityFramework 提供的能力,所以就能通过简单的几行代码来实现基本的仓储操作
public virtual TEntity Add(TEntity entity)
{
return DbContext.Add(entity).Entity;
}
public virtual Task<TEntity> AddAsync(TEntity entity, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
return Task.FromResult(Add(entity));
}
public virtual TEntity Update(TEntity entity)
{
return DbContext.Update(entity).Entity;
}
public virtual Task<TEntity> UpdateAsync(TEntity entity, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
return Task.FromResult(Update(entity));
}
public virtual bool Remove(Entity entity)
{
DbContext.Remove(entity);
return true;
}
public virtual Task<bool> RemoveAsync(Entity entity)
{
return Task.FromResult(Remove(entity));
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 定义主键的实体的仓储
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TEntity"></typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="TKey"></typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="TDbContext"></typeparam>
public abstract class Repository<TEntity, TKey, TDbContext> : Repository<TEntity, TDbContext>, IRepository<TEntity, TKey> where TEntity : Entity<TKey>, IAggregateRoot where TDbContext : EFContext
{
public Repository(TDbContext context) : base(context)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据 Id 从 DbContext 获取 Entity,然后再 Remove
/// 这样的好处是可以跟踪对象的状态
/// 坏处是任意的删除都需要先去数据库里面做查询
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual bool Delete(TKey id)
{
var entity = DbContext.Find<TEntity>(id);
if (entity == null)
{
return false;
}
DbContext.Remove(entity);
return true;
}
public virtual async Task<bool> DeleteAsync(TKey id, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
var entity = await DbContext.FindAsync<TEntity>(id, cancellationToken);
if (entity == null)
{
return false;
}
DbContext.Remove(entity);
return true;
}
public virtual TEntity Get(TKey id)
{
return DbContext.Find<TEntity>(id);
}
public virtual async Task<TEntity> GetAsync(TKey id, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
return await DbContext.FindAsync<TEntity>(id, cancellationToken);
}
}
}
实现自己的 DbContext
DomainContext
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure
{
public class DomainContext : EFContext
{
public DomainContext(DbContextOptions options, IMediator mediator, ICapPublisher capBus) : base(options, mediator, capBus)
{
}
public DbSet<Order> Orders { get; set; }
public DbSet<User> Users { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
#region 注册领域模型与数据库的映射关系
modelBuilder.ApplyConfiguration(new OrderEntityTypeConfiguration());
modelBuilder.ApplyConfiguration(new UserEntityTypeConfiguration());
#endregion
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
}
}
映射关系,针对每一个领域模型创建一个 EntityTypeConfiguration
OrderEntityTypeConfiguration
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure.EntityConfigurations
{
class OrderEntityTypeConfiguration : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Order>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Order> builder)
{
// 定义主键
builder.HasKey(p => p.Id);
//builder.ToTable("order");
//builder.Property(p => p.UserId).HasMaxLength(20);
//builder.Property(p => p.UserName).HasMaxLength(30);
// 定义导航属性
builder.OwnsOne(o => o.Address, a =>
{
a.WithOwner();
//a.Property(p => p.City).HasMaxLength(20);
//a.Property(p => p.Street).HasMaxLength(50);
//a.Property(p => p.ZipCode).HasMaxLength(10);
});
}
}
}
UserEntityTypeConfiguration
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure.EntityConfigurations
{
class UserEntityTypeConfiguration : IEntityTypeConfiguration<User>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<User> builder)
{
builder.HasKey(p => p.Id);
}
}
}
事务处理
要实现对 DomainContext 的事务处理的话,仅仅需要创建一个类 DomainContextTransactionBehavior
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure
{
public class DomainContextTransactionBehavior<TRequest, TResponse> : TransactionBehavior<DomainContext, TRequest, TResponse>
{
public DomainContextTransactionBehavior(DomainContext dbContext, ICapPublisher capBus, ILogger<DomainContextTransactionBehavior<TRequest, TResponse>> logger) : base(dbContext, capBus, logger)
{
}
}
}
为了演示效果,在应用程序启动时,添加一行代码
Startup
// 这一行代码的作用是创建一个 Scope,在这个范围内创建 DomainContext
using (var scope = app.ApplicationServices.CreateScope())
{
var dc = scope.ServiceProvider.GetService<DomainContext>();
// 确定数据库已经创建,如果数据库没有创建,这个时候会执行数据库的自动创建过程,根据模型创建数据库
dc.Database.EnsureCreated();
}
数据库的注册部分
ServiceCollectionExtensions
/// <summary>
/// 这个定义就是将连接字符串配置到 dDomainContext
/// </summary>
/// <param name="services"></param>
/// <param name="connectionString"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static IServiceCollection AddMySqlDomainContext(this IServiceCollection services, string connectionString)
{
return services.AddDomainContext(builder =>
{
builder.UseMySql(connectionString);
});
}
这一行代码的调用位置是在 ConfigureServices 里面
// 从配置中获取字符串
services.AddMySqlDomainContext(Configuration.GetValue<string>("Mysql"));
启动程序,运行过程中 EF 框架会根据定义的实体映射关系生成数据库,可在 Mysql 数据库中查看生成结果
接着丰富一下 Order 的映射关系
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure.EntityConfigurations
{
class OrderEntityTypeConfiguration : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Order>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Order> builder)
{
// 定义主键
builder.HasKey(p => p.Id);
builder.ToTable("order");// 修改表名为 order,不带 s
builder.Property(p => p.UserId).HasMaxLength(20);// 修改字段长度
builder.Property(p => p.UserName).HasMaxLength(30);
// 定义导航属性
// OwnsOne 的方式可以将 Address 这个值类型作为同一个表的字段来设置
builder.OwnsOne(o => o.Address, a =>
{
a.WithOwner();
a.Property(p => p.City).HasMaxLength(20);
a.Property(p => p.Street).HasMaxLength(50);
a.Property(p => p.ZipCode).HasMaxLength(10);
});
}
}
}
启动程序,可以看到数据库修改结果
这说明可以在仓储层定义领域模型与数据库的映射关系,这个映射关系可以组织为一个目录,为每一个领域模型设置一个类型来定义,并且这个过程是强类型的,这样的结构,便于后期维护
另外仓储层的话,定义了一个 IOrderRepository,仅仅实现了 IRepository 泛型接口,引进 Order,由于 Order 实际上有一个主键是 long,所以这里把主键类型也传给 IRepository
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure.Repositories
{
public interface IOrderRepository : IRepository<Order, long>
{
}
}
Order
public class Order : Entity<long>, IAggregateRoot
这样子,Order 的仓储就定义完毕
那么 Order 仓储的实现也非常简单,仅仅需要继承 Repository,把 Order,long,DomainContext 传入泛型 Repository 即可,这里还实现了 IOrderRepository
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure.Repositories
{
public class OrderRepository : Repository<Order, long, DomainContext>, IOrderRepository
{
public OrderRepository(DomainContext context) : base(context)
{
}
}
}
通过这样简单的继承,可以复用之前定义的代码,快速实现仓储层的定义
可以通过代码提升看到仓储层是有 Add,Update,Remove,Delete 方法,还有 UnitOfWork 的属性
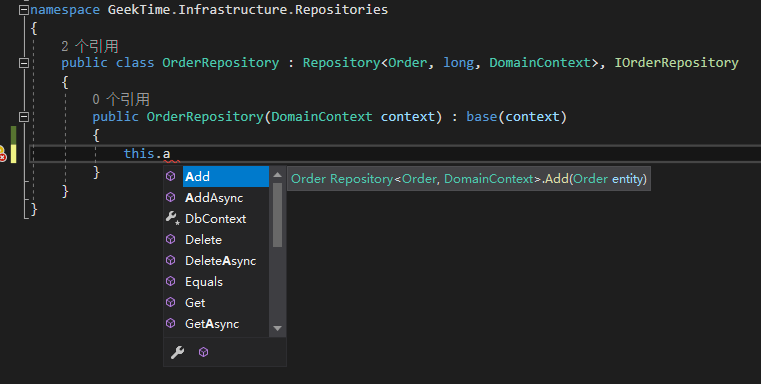
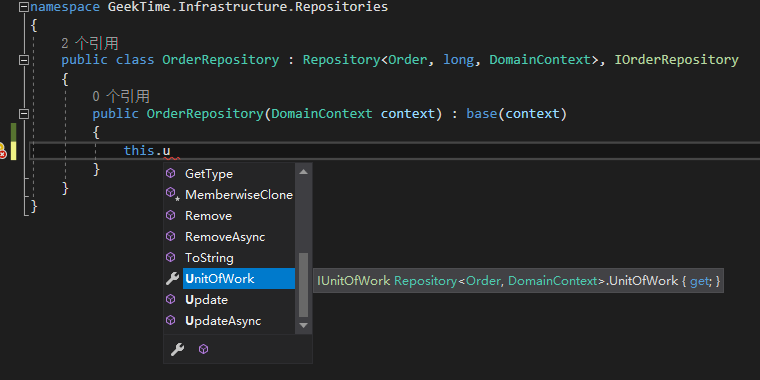
这样一来就完成了仓储层的定义,可以看到仓储层的代码非常的薄,仅仅包含了一些接口的定义和类的继承,需要自定义一些方法的时候,可以在仓储层定义一些特殊方法,比如 AddABC 等特殊的逻辑都可以在这里去实现
namespace GeekTime.Infrastructure.Repositories
{
public class OrderRepository : Repository<Order, long, DomainContext>, IOrderRepository
{
public OrderRepository(DomainContext context) : base(context)
{
}
}
public void AddABC()
{
}
}
另外一个在组织领域模型和数据库的关系的时候,可以很清晰的看到,是在 EntityConfiguration 这个目录下面,为每一个模型定义一个映射类,当领域模型越来越复杂,数据库的结构越来越复杂的时候,这样的组织结构会非常的清晰
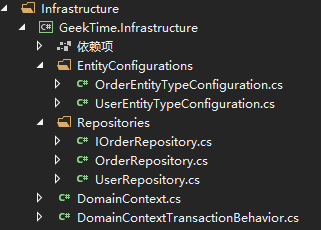


本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。
欢迎转载、使用、重新发布,但务必保留文章署名 郑子铭 (包含链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/MingsonZheng/ ),不得用于商业目的,基于本文修改后的作品务必以相同的许可发布。
如有任何疑问,请与我联系 (MingsonZheng@outlook.com) 。
