1、介绍
Logging组件是微软实现的日志记录组件包括控制台(Console)、调试(Debug)、事件日志(EventLog)和TraceSource,但是没有实现最常用用的文件记录日志功能(可以用其他第三方的如NLog、Log4Net。之前写过NLog使用的文章)。
2、默认配置
新建.Net Core Web Api项目,添加下面代码。
[Route("api/[controller]")] public class ValuesController : Controller { ILogger<ValuesController> logger;
//构造函数注入Logger public ValuesController(ILogger<ValuesController> logger) { this.logger = logger; } [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<string> Get() { logger.LogWarning("Warning"); return new string[] { "value1", "value2" }; } }
运行结果如下:
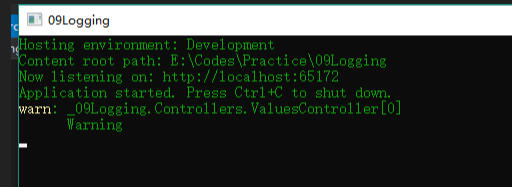
我刚开始接触的时候,我就有一个疑问我根本没有配置关于Logger的任何代码,仅仅写了注入,为什么会起作用呢?最后我发现其实是在Program类中使用了微软默认的配置。
public class Program { public static void Main(string[] args) { BuildWebHost(args).Run(); } public static IWebHost BuildWebHost(string[] args) => WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)//在这里使用了默认配置 .UseStartup<Startup>() .Build(); }
下面为CreateDefaultBuilder方法的部分源码,整个源码在 https://github.com/aspnet/MetaPackages,可以看出在使用模板创建项目的时候,默认添加了控制台和调试日志组件,并从appsettings.json中读取配置。
builder.UseKestrel((builderContext, options) => { options.Configure(builderContext.Configuration.GetSection("Kestrel")); }) .ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, config) => { var env = hostingContext.HostingEnvironment; //加载appsettings.json文件 使用模板创建的项目,会生成一个配置文件,配置文件中包含Logging的配置项 config.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true) .AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true); ....... }) .ConfigureLogging((hostingContext, logging) => {
//从appsettings.json中获取Logging的配置 logging.AddConfiguration(hostingContext.Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
//添加控制台输出 logging.AddConsole();
//添加调试输出 logging.AddDebug(); })
3、建立自己的Logging配置
首先修改Program类
public class Program { public static void Main(string[] args) { //指定配置文件路径 var config = new ConfigurationBuilder() .SetBasePath(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())//设置基础路径 .AddJsonFile($"appsettings.json", true, true)//加载配置文件 .AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{EnvironmentName.Development}.json", true, true) .Build(); var host = new WebHostBuilder() .UseKestrel() .UseStartup<Startup>() .UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()) .UseConfiguration(config)//使用配置 .UseUrls(config["AppSettings:Url"])//从配置中读取 程序监听的端口号 .UseEnvironment(EnvironmentName.Development)//如果加载了多个环境配置,可以设置使用哪个配置 一般有测试环境、正式环境
//.ConfigureLogging((hostingCotext, logging) => //第一种配置方法 直接在webHostBuilder建立时配置 不需要修改下面的Startup代码
//{
// logging.AddConfiguration(hostingCotext.Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
// logging.AddConsole();
//})
.Build();
host.Run();
}
}
修改Startup类如下面,此类的执行顺序为 Startup构造函数 > ConfigureServices > Configure
public class Startup { public IConfiguration Configuration { get; private set; } public IHostingEnvironment HostingEnvironment { get; private set; } //在构造函数中注入 IHostingEnvironment和IConfiguration,配置已经在Program中设置了,注入后就可以获取配置文件的数据 public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env, IConfiguration config) { HostingEnvironment = env; Configuration = config; } public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
services.AddMvc();
//第二种配置 也可以这样加上日志功能,不用下面的注入
//services.AddLogging(builder =>
//{
// builder.AddConfiguration(Configuration.GetSection("Logging"))
// .AddConsole();
//});
} //注入ILoggerFactory public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); }
//第三种配置 注入ILogggerFactory,然后配置参数 //添加控制台输出 loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
//添加调试输出 loggerFactory.AddDebug(); app.UseMvc(); } }
这种结构就比较清晰明了。
4、Logging源码解析
三种配置其实都是为了注入日志相关的服务,但是调用的方法稍有不同。现在我们以第二种配置来详细看看其注入过程。首先调用AddLogging方法,其实现源码如下:
public static IServiceCollection AddLogging(this IServiceCollection services, Action<ILoggingBuilder> configure) { services.AddOptions();//这里会注入最基础的5个服务 option相关服务只要是跟配置文件相关,通过Option服务获取相关配置文件参数参数 services.TryAdd(ServiceDescriptor.Singleton<ILoggerFactory, LoggerFactory>()); services.TryAdd(ServiceDescriptor.Singleton(typeof(ILogger<>), typeof(Logger<>))); services.TryAddEnumerable(ServiceDescriptor.Singleton<IConfigureOptions<LoggerFilterOptions>>(new DefaultLoggerLevelConfigureOptions(LogLevel.Information))); configure(new LoggingBuilder(services)); return services; }
接着会调用AddConfiguration
public static ILoggingBuilder AddConfiguration(this ILoggingBuilder builder, IConfiguration configuration) { builder.AddConfiguration();
//下面为AddConfiguration的实现
public static void AddConfiguration(this ILoggingBuilder builder)
{
builder.Services.TryAddSingleton<ILoggerProviderConfigurationFactory, LoggerProviderConfigurationFactory>();
builder.Services.TryAddSingleton(typeof(ILoggerProviderConfiguration<>), typeof(LoggerProviderConfiguration<>));
}
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IConfigureOptions<LoggerFilterOptions>>(new LoggerFilterConfigureOptions(configuration)); builder.Services.AddSingleton<IOptionsChangeTokenSource<LoggerFilterOptions>>(new ConfigurationChangeTokenSource<LoggerFilterOptions>(configuration)); builder.Services.AddSingleton(new LoggingConfiguration(configuration)); return builder; }
下面来看打印日志的具体实现:
public void Log<TState>(LogLevel logLevel, EventId eventId, TState state, Exception exception, Func<TState, Exception, string> formatter)
{
var loggers = Loggers; List<Exception> exceptions = null;
//loggers为LoggerInformation数组,如果你在Startup中添加了Console、Deubg日志功能了,那loggers数组值有2个,就是它俩。 foreach (var loggerInfo in loggers) { //循环遍历每一种日志打印,如果满足些日子的条件,才执行打印log方法。比如某一个日志等级为Info,
//但是Console配置的最低打印等级为Warning,Debug配置的最低打印等级为Debug
//则Console中不会打印,Debug中会被打印
if (!loggerInfo.IsEnabled(logLevel)) { continue; } try {
//每一种类型的日志,对应的打印方法不同。执行对应的打印方法 loggerInfo.Logger.Log(logLevel, eventId, state, exception, formatter); } catch (Exception ex) { if (exceptions == null) { exceptions = new List<Exception>(); } exceptions.Add(ex); } } }
下面具体看一下Console的打印实现:
首先ConsoleLogger实现了ILogger的Log方法,并在方法中调用WriteMessage方法
public void Log<TState>(LogLevel logLevel, EventId eventId, TState state, Exception exception, Func<TState, Exception, string> formatter) { //代码太多 我就省略一些判空代码 var message = formatter(state, exception); if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(message) || exception != null) { WriteMessage(logLevel, Name, eventId.Id, message, exception); } } public virtual void WriteMessage(LogLevel logLevel, string logName, int eventId, string message, Exception exception) { ....... if (logBuilder.Length > 0) { var hasLevel = !string.IsNullOrEmpty(logLevelString); //这里是主要的代码实现,可以看到,并没有写日志的代码,而是将日志打入到一个BlockingCollection<LogMessageEntry>队列中
//这里需要指出 BlockingCollection是线程安全的集合,多个线程同时访问,不会发生数据混乱。 _queueProcessor.EnqueueMessage(new LogMessageEntry() { Message = logBuilder.ToString(), MessageColor = DefaultConsoleColor, LevelString = hasLevel ? logLevelString : null, LevelBackground = hasLevel ? logLevelColors.Background : null, LevelForeground = hasLevel ? logLevelColors.Foreground : null }); }
...... }
下面看日志被放入队列后的具体实现:
public class ConsoleLoggerProcessor : IDisposable
{
private const int _maxQueuedMessages = 1024;
private readonly BlockingCollection<LogMessageEntry> _messageQueue = new BlockingCollection<LogMessageEntry>(_maxQueuedMessages);
private readonly Thread _outputThread;
public IConsole Console; public ConsoleLoggerProcessor() { //在构造函数中启动一个线程,执行ProcessLogQueue方法
//从下面ProcessLogQueue方法可以看出,是循环遍历集合,将集合中的数据打印
_outputThread = new Thread(ProcessLogQueue) { IsBackground = true, Name = "Console logger queue processing thread"public virtual void EnqueueMessage(LogMessageEntry message) { if (!_messageQueue.IsAddingCompleted) { try { _messageQueue.Add(message); return; } catch (InvalidOperationException) { } } WriteMessage(message); } internal virtual void WriteMessage(LogMessageEntry message) { if (message.LevelString != null) { Console.Write(message.LevelString, message.LevelBackground, message.LevelForeground); } Console.Write(message.Message, message.MessageColor, message.MessageColor); Console.Flush(); } private void ProcessLogQueue() {
try
{
//GetConsumingEnumerable()方法比较特殊,当集合中没有值时,会阻塞自己,一但有值了,直到集合中又有元素继续遍历
foreach (var message in _messageQueue.GetConsumingEnumerable()) { WriteMessage(message); } } catch { try { _messageQueue.CompleteAdding(); } catch { } } } }