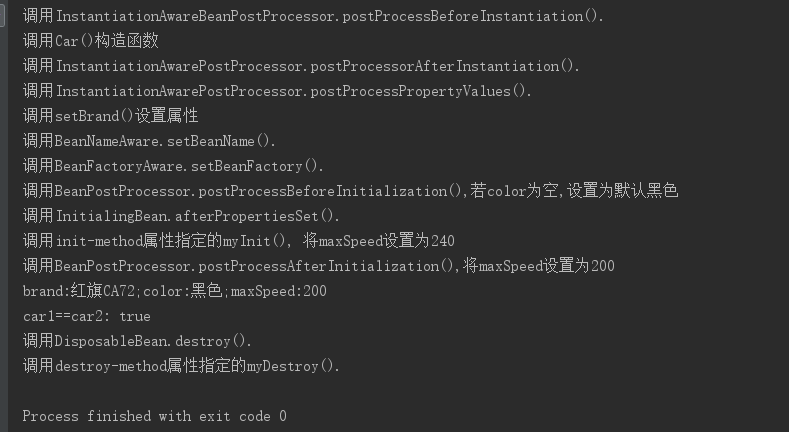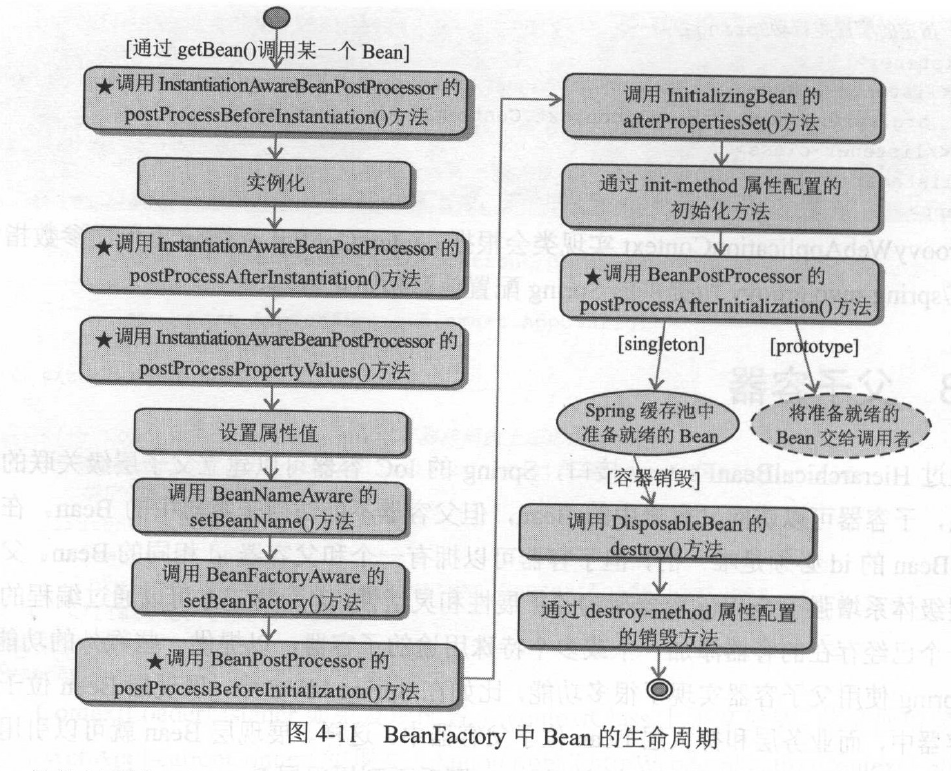






package com.smart; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.*; public class Car implements BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean{ private String brand; private String color; private int maxSpeed; private BeanFactory beanFactory; private String beanName; //默认构造函数 public Car(){System.out.println("调用Car()构造函数");} //带参构造函数 public Car(String brand, String color, int maxSpeed) { this.brand = brand; this.color = color; this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed; } //未带参方法 public void introduce() { System.out.println("brand:" + brand + ";color:" + color + ";maxSpeed:" + maxSpeed); } public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { System.out.println("调用setBrand()设置属性"); this.brand = brand; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public int getMaxSpeed() { return maxSpeed; } public void setMaxSpeed(int maxSpeed) { this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed; } // BeanFactoryAware接口方法 public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()."); this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } // BeanNameAware接口方法 public void setBeanName(String s) { System.out.println("调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()."); this.beanName = s; } // DisposableBean接口方法 public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("调用DisposableBean.destroy()."); } // InitializingBean接口方法 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("调用InitialingBean.afterPropertiesSet()."); } // 通过<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始方法 public void myInit() { System.out.println("调用init-method属性指定的myInit(), 将maxSpeed设置为240"); this.maxSpeed = 240; } //同过<bean>的destroy-method属性指定的销毁方法 public void myDestroy() { System.out.println("调用destroy-method属性指定的myDestroy()."); } }

package com.smart.beanfactory; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter; import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor; public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter { @Override // 1.接口方法,在实例化Bean前调用 public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException { // 1-1. 仅对容器中的car Bean进行处理 if ("car".equals(beanName)) { System.out.println("调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation()."); } return null; } @Override // 2.接口方法,在实例化Bean后调用 public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if ("car".equals(beanName)) { System.out.println("调用InstantiationAwarePostProcessor.postProcessorAfterInstantiation()."); } return true; } @Override // 3.接口方法,在设置某个属性时调用 public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // 3-1. 仅对容器中的car Bean进行处理, 还可以同过pds入参进行过滤 if ("car".equals(beanName)) { System.out.println("调用InstantiationAwarePostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues()."); } return pvs; } }

package com.smart.beanfactory; import com.smart.Car; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if ("car".equals(beanName)) { Car car = (Car) bean; if (car.getColor() == null) { System.out.println("调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()," + "若color为空,设置为默认黑色"); car.setColor("黑色"); } } return bean; } public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if ("car".equals(beanName)) { Car car = (Car) bean; if (car.getMaxSpeed() >= 200) { System.out.println("调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization()," + "将maxSpeed设置为200"); car.setMaxSpeed(200); } } return bean; } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.smart.Car" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestroy" p:brand="红旗CA72" p:maxSpeed="200"/> </beans>


package com.smart.beanfactory; import com.smart.Car; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; public class BeanLifeCycle { public static void lifeCycleInBeanFactory() { // 1. 装载配置文件并启动容器 Resource res = new ClassPathResource("beans.xml"); BeanFactory bf = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((DefaultListableBeanFactory) bf); reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res); //后处理器的实际调用顺序与注册顺序无关,在具有多个后处理器的情况下,必须通过实现 //org.springframework.core.Ordered接口来确定调用顺序 // 2. 向容器中注册MyBeanPostProcessor后处理器 ((ConfigurableBeanFactory) bf).addBeanPostProcessor(new MyBeanPostProcessor()); // 3. 向容器中注册MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后处理器 ((ConfigurableBeanFactory) bf).addBeanPostProcessor(new MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor()); // 4. 第一次从容器中获得car, 将触发容器实例化该Bean,这将引发Bean生命周期方法的调用 Car car1 = (Car) bf.getBean("car"); car1.introduce(); car1.setColor("红色"); // 5. 第二次从容器中获取car, 直接从缓存池中获取 Car car2 = (Car) bf.getBean("car"); // 6. 查看car1和car2是否指向同一引用 System.out.println("car1==car2: " + (car1 == car2)); // 7. 关闭容器 ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) bf).destroySingleton("car"); } public static void main(String[] args) { lifeCycleInBeanFactory(); } }