一、DDT(数据驱动)简介
Data-Driven Tests(DDT)即数据驱动测试,可以实现不同数据运行同一个测试用例(通过数据的不同来驱动测试结果的不同)。
ddt本质其实就是装饰器,一组数据一个场景。
ddt模块包含了一个类的装饰器ddt(@ddt)和三个方法的装饰器(@data、@unpack、@file_data),其中:
@data:包含多个你想要传给测试用例的参数,可以为列表、元组、字典等;
@file_data:会从json或yaml中加载数据;
(注意,如果文件以”.yml”或者”.yaml”结尾,ddt会作为yaml类型处理,其他所有文件都会作为json文件处理。如txt文件)
@unpack:分割元素。
(需要搭配unittest测试框架使用,实现数据驱动测试)
数据驱动测试:
1、避免编写重复代码
2、数据与测试脚本分离
3、通过使用数据驱动测试,来验证多组数据测试场景
通常来说,多用于单元测试和接口测试
二、python中使用ddt传递参数
前提:需要安装ddt包
1、传递列表、字典等数据
# get_ddt.py import unittest from ddt import ddt, data, unpack, file_data # 声明了ddt类装饰器 @ddt class MyddtTest(unittest.TestCase): # @data方法装饰器 # 单组元素 @data(1,2,3) def test_01(self, value): # value用来接受data的数据 print(value) # 多组数据,未拆分 @data([1,2],[3,4]) def test_02(self, value): print(value) # 多组数据,拆分 # @unpac拆分,相当于把数据的最外层结构去掉 @data([5,6],[7,8]) @unpack def test_03(self, value1, value2): print(value1, value2) # 单个列表字典,未拆分 @data([{"name": "peter", "age": 15, "addr": "chengdu"}]) def test_04(self, value): print(value) # 多个列表字典,拆分 @data([{"name":"peter","age":16,"addr":"chengdu"},{"name":"lily","age":17,"addr":"chengdu"}]) @unpack def test_05(self, value1, value2): print(value1, value2) # 单个字典,拆分 # @data里的数据key必须与字典的key保持一致 @data({"name":"jack","age":20}) @unpack def test_06(self, name, age): print(name, age) # 多个字典, 拆分 @data({"name":"peter","age":18,"addr":"chengdu"},{"name":"lily","age":19,"addr":"chengdu"}) @unpack def test_07(self, name, age, addr): print(name, age, addr) # 多个列表字典,引用数据 testdata = [{"name": "peter", "age": 21, "addr": "chengdu"}, {"name": "lily", "age": 22, "addr": "chengdu"}] @data(testdata) @unpack def test_08(self, value1, value2): print(value1, value2) # @data(*testdata):*号意为解包,ddt会按逗号分隔,将数据拆分(不需要@unpack方法装饰器了) testdata = [{"name":"peter","age":23,"addr":"chengdu"},{"name":"lily","age":24,"addr":"chengdu"}] @data(*testdata) def test_09(self, value): print(value)
if __name__ == "__main__": unittest.main()
运行结果: ................... ---------------------------------------------------------------------- Ran 19 tests in 0.000s OK 1 2 3 [1, 2] [3, 4] 5 6 7 8 [{'name': 'peter', 'age': 15, 'addr': 'chengdu'}] {'name': 'peter', 'age': 16, 'addr': 'chengdu'} {'name': 'lily', 'age': 17, 'addr': 'chengdu'} jack 20 peter 18 chengdu lily 19 chengdu {'name': 'peter', 'age': 21, 'addr': 'chengdu'} {'name': 'lily', 'age': 22, 'addr': 'chengdu'} {'name': 'peter', 'age': 23, 'addr': 'chengdu'} {'name': 'lily', 'age': 24, 'addr': 'chengdu'}
2、传递json、yaml文件
# config.json { "stu1": { "name": "Peter", "age": 29, "addr": "BeiJing" }, "stu2": { "name": "Jack", "age": 30, "addr": "ShenZhen" } }
# config.yaml # 使用-分隔用例,则yaml读取到的数据类型为列表 - model: 注册模块 title: 注册成功 url: http://api.nnzhp.cn/api/user/user_reg method: POST data: username: yingcr10 pwd: Ace123456 cpwd: Ace123456 check: error_code: 0 msg: 注册成功! - model: 注册模块 title: 用户名长度小于6位,注册失败 url: http://api.nnzhp.cn/api/user/user_reg method: POST data: username: yingc pwd: Ace123456 cpwd: Ace123456 check: error_code: 3002
# get_ddt.py
import unittest from ddt import ddt, data, unpack, file_data # 声明了ddt类装饰器 @ddt class MyddtTest(unittest.TestCase): # @file_data加载json文件 # **testdata:将提取到的数据存放在空字典testdata中 @file_data("config.json") def test_10(self, **testdata): # 再从字典testdata中单独提取参数 name = testdata['name'] age = testdata['age'] addr = testdata['addr'] print(testdata) print(name, age, addr) # 直接提取参数, test()方法中的参数必须与json文件中的键保持一致 @file_data("config.json") def test_11(self,name, age, addr): name = name age = age addr = addr print(name, age, addr) # @file_data加载yaml文件 @file_data("config.yaml") def test_12(self, model, title, url, method, data, check): username = data['username'] pwd = data['pwd'] cpwd = data['pwd'] print(model, title, url, method, data, check) print(username, pwd, cpwd) # **testdata:将提取到的数据存放在空字典testdata中 @file_data("config.yaml") def test_13(self, **testdata): # 再从字典testdata中单独提取参数 model = testdata['model'] title = testdata['title'] print(testdata) print(model, title) if __name__ == "__main__": unittest.main()
运行结果: ........ ---------------------------------------------------------------------- Ran 8 tests in 0.000s OK {'name': 'Peter', 'age': 29, 'addr': 'BeiJing'} Peter 29 BeiJing {'name': 'Jack', 'age': 30, 'addr': 'ShenZhen'} Jack 30 ShenZhen Peter 29 BeiJing Jack 30 ShenZhen 注册模块 注册成功 http://api.nnzhp.cn/api/user/user_reg POST {'username': 'yingcr10', 'pwd': 'Ace123456', 'cpwd': 'Ace123456'} {'error_code': 0, 'msg': '注册成功!'} yingcr10 Ace123456 Ace123456 注册模块 用户名长度小于6位,注册失败 http://api.nnzhp.cn/api/user/user_reg POST {'username': 'yingc', 'pwd': 'Ace123456', 'cpwd': 'Ace123456'} {'error_code': 3002} yingc Ace123456 Ace123456 {'model': '注册模块', 'title': '注册成功', 'url': 'http://api.nnzhp.cn/api/user/user_reg', 'method': 'POST', 'data': {'username': 'yingcr10', 'pwd': 'Ace123456', 'cpwd': 'Ace123456'}, 'check': {'error_code': 0, 'msg': '注册成功!'}} 注册模块 注册成功 {'model': '注册模块', 'title': '用户名长度小于6位,注册失败', 'url': 'http://api.nnzhp.cn/api/user/user_reg', 'method': 'POST', 'data': {'username': 'yingc', 'pwd': 'Ace123456', 'cpwd': 'Ace123456'}, 'check': {'error_code': 3002}} 注册模块 用户名长度小于6位,注册失败
三、通过ddt读取yaml测试数据
config.yaml数据文件与上文的一致。
# get_ddt.py import requests import unittest import json from ddt import ddt, data, unpack, file_data @ddt class SignTest(unittest.TestCase): # 使用ddt加载yaml中的测试数据 @file_data("config.yaml") def test_get_yaml(self,model,title,url,method,data,check): # 提取分离各参数 model = model title = title url = url method = method data = data check = check self.sign_test(model,title,url,method,data,check) def sign_test(self,model,title,url,method,data,check): print("模块: ", model) print("用例标题: ", title) response = requests.request(url=url, method=method, data=data).text response = json.loads(response) try: # 通过断言,判断测试是否通过 assert check['error_code'] == response['error_code'] print("测试通过") except Exception as e: print("测试失败") raise e if __name__ == "__main__": unittest.main()
运行结果: 模块: 注册模块 用例标题: 注册成功 测试通过 模块: 注册模块 用例标题: 用户名长度小于6位,注册失败 测试通过 .. ---------------------------------------------------------------------- Ran 2 tests in 0.188s OK
四、python中使用ddt+excel读取测试数据
大体思路:先从excel文件中读取数据,然后再用ddt加载已读取的数据。
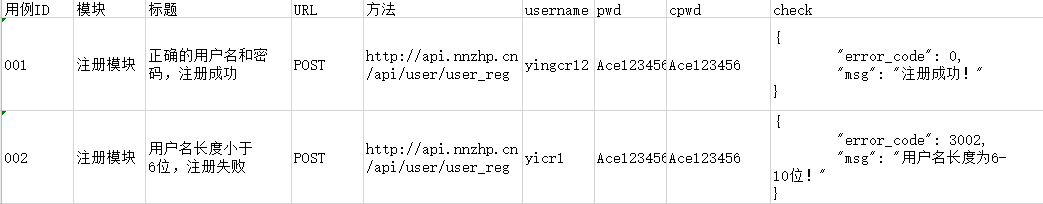
# get_excel.py from openpyxl import load_workbook class ExcelData(): def __init__(self, file="config.xlsx"): ''' 初始化Excel对象 ''' self.file = file self.wb = load_workbook(self.file) def get_row_value(self, row, sheet_name="Sheet1"): ''' 获取Excel中某一行的数据 ''' sh = self.wb[sheet_name] max_col = sh.max_column row_value = [] for col in range(1, max_col+1): value = sh.cell(row, col).value row_value.append(value) return row_value def get_all_row(self, sheet_name="Sheet1"): ''' 获取Excel中所有行的数据,并存放在列表中 ''' sh = self.wb[sheet_name] max_row = sh.max_row row_value = [] for row in range(2, max_row+1): value = self.get_row_value(row) row_value.append(value) return row_value if __name__ == "__main__": excel = ExcelData() testdata = excel.get_all_row() print(testdata)
# get_ddt.py import requests import unittest from ddt import ddt, data, unpack, file_data from get_excel import ExcelData @ddt class SignTest(unittest.TestCase): # 从get_excel.py中读取测试数据 excel = ExcelData() testdata = excel.get_all_row() @data(*testdata) def test_sign(self, datas): # 由于从excel中读取到的数据为列表形式,所以采用下标来提取各参数 ID = datas[0] model = datas[1] title = datas[2] method = datas[3] url = datas[4] username = datas[5] pwd = datas[6] cpwd = datas[7] check = datas[8] body = { "username": username, "pwd": pwd, "cpwd": cpwd } self.sign_test(ID,model,title,url,method,body,check) def sign_test(self,ID,model,title,url,method,body,check): print("用例ID:", ID) print("模块:", model) print("用例标题:", title) response = requests.request(url=url, method=method, data=body).text try: # 通过断言,比较实际结果是否与预期结果一致 # 由于从excel中读取到的check为str类型,所以response不用转换为dict,直接断言比较是否相等 assert check == response print("测试通过") except Exception as e: print("测试失败") raise e if __name__ == "__main__": unittest.main()
运行结果: 用例ID: 001 模块: 注册模块 用例标题: 正确的用户名和密码,注册成功 .测试通过 用例ID: 002 模块: 注册模块 用例标题: 用户名长度小于6位,注册失败 .测试通过 OK ---------------------------------------------------------------------- Ran 2 tests in 0.190s Process finished with exit code 0
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/78998bcf3e05
参考:http://www.manongjc.com/detail/18-eosubecmlglohgb.html