OOP
Q1: Vending Machine
In this question you'll create a vending machine that only outputs a single product and provides change when needed.
Create a class called
VendingMachinethat represents a vending machine for some product. AVendingMachineobject returns strings describing its interactions. Remember to match exactly the strings in the doctests -- including punctuation and spacing!Fill in the
VendingMachineclass, adding attributes and methods as appropriate, such that its behavior matches the following doctests:
According to the wiki, a vending machine is an automated machine that provides items to consumers after cash, or other forms of payment are inserted into the machine or otherwise made
这里说的 vending machine 其实也就是常见的自动售货机, 我们要为其写一个类实现应该有的功能. 这里的要求更为简单, 因为我们要实现的自动售货机只有一样东西可以卖, 而且每次只会买一件. 注意下面要实现函数的逻辑即可:
restock, 补充商品, 这个比较简单add_funds- 商品有库存的时候才会记住你付了多少钱
- 商品没有库存的时候直接退款给你
vend- 商品有库存的时候
- 你支付的钱如果足够就可以买
- 不够的话会告诉你还差多少钱
- 不要忘记购买成功后库存要 - 1
- 商品没有库存
- 提示要补充货物
- 商品有库存的时候
class VendingMachine:
"""A vending machine that vends some product for some price.
"""
def __init__(self, product, price):
self.product = product
self.price = price
self.balance = 0
self.stocks = 0
def restock(self, num):
"""Restock num items to our vending machine"""
self.stocks += num
return f"Current {self.product} stock: {self.stocks}"
def add_funds(self, fund):
"""Add funds to balance, return funds if no stocks"""
if self.stocks != 0:
self.balance += fund
return f"Current balance: ${self.balance}"
else:
return f"Nothing left to vend. Please restock. Here is your ${fund}."
def vend(self):
"""Vend a product"""
if self.stocks == 0:
return 'Nothing left to vend. Please restock.'
else:
if self.balance < self.price:
return f"You must add ${self.price - self.balance} more funds."
else:
change = self.balance - self.price
self.balance = 0
self.stocks -= 1
if change == 0:
return f"Here is your {self.product}."
else:
return f"Here is your {self.product} and ${change} change."
Q2: Mint
A mint is a place where coins are made. In this question, you'll implement a
Mintclass that can output aCoinwith the correct year and worth.
- Each
Mintinstance has ayearstamp. Theupdatemethod sets theyearstamp to thepresent_yearclass attribute of theMintclass.- The
createmethod takes a subclass ofCoinand returns an instance of that class stamped with themint's year (which may be different fromMint.present_yearif it has not been updated.)- A
Coin'sworthmethod returns thecentsvalue of the coin plus one extra cent for each year of age beyond 50. A coin's age can be determined by subtracting the coin's year from thepresent_yearclass attribute of theMintclass.
这一题要我们实现铸币厂的类, 可以制造出年份和面值都正确的硬币.
class Mint:
"""A mint creates coins by stamping on years.
"""
present_year = 2021
def __init__(self):
self.update()
def create(self, kind):
return kind(self.year)
def update(self):
self.year = Mint.present_year
class Coin:
def __init__(self, year):
self.year = year
def worth(self):
age = Mint.present_year - self.year
if age > 50:
return self.cents + (age - 50)
else:
return self.cents
Linked Lists
Q3: Store Digits
Write a function
store_digitsthat takes in an integernand returns a linked list where each element of the list is a digit ofn.Important: Do not use any string manipulation functions like
strandreversed
简单来说, 就是要把整数 n 的每一位存储到链表里面. 这个用迭代的方法做就很简单, 我们可以每次 %10 来获得最后一位, 采用链表的头插法来构建链表, 头插法就是每次我们都新建结点插入到链表的开头. 这里用了哨兵结点.
def store_digits(n):
"""Stores the digits of a positive number n in a linked list.
"""
sentinel = Link(0)
while n > 0:
all_but_last, last = n // 10, n % 10
# every time we insert node in the front of the linklist
new_node = Link(n % 10, sentinel.rest)
sentinel.rest = new_node
n = all_but_last
return sentinel.rest
Q4: Mutable Mapping
Implement
deep_map_mut(fn, link), which applies a functionfnonto all elements in the given linked listlink. If an element is itself a linked list, applyfnto each of its elements, and so on.Your implementation should mutate the original linked list. Do not create any new linked lists.
Hint: The built-in
isinstancefunction may be useful.>>> s = Link(1, Link(2, Link(3, Link(4)))) >>> isinstance(s, Link) True >>> isinstance(s, int) False
对嵌套链表的每个元素应用 fn 函数, 显然这个要用递归方法来解决. 具体解题思路可以看下面的代码
def deep_map_mut(fn, link):
"""Mutates a deep link by replacing each item found with the
result of calling fn on the item. Does NOT create new Links (so
no use of Link's constructor)
"""
# base case 1. do thing if it is empty
if link is Link.empty:
return
# base case 2. if it is an integer
if isinstance(link, int):
link = fn(link)
if isinstance(link.first, int):
link.first = fn(link.first)
else:
deep_map_mut(fn, link.first)
deep_map_mut(fn, link.rest)
Q5: Two List
Implement a function
two_listthat takes in two lists and returns a linked list. The first list contains the values that we want to put in the linked list, and the second list contains the number of each corresponding value. Assume both lists are the same size and have a length of 1 or greater. Assume all elements in the second list are greater than 0.
有两个列表: 一个表示值, 一个表示这个值应该重复插入几次. 用这种方式构建一个链表, 用链表的尾插法即可(每次把新的节点插入到链表末尾). 这里同样用了哨兵结点
def two_list(vals, amounts):
"""
Returns a linked list according to the two lists that were passed in. Assume
vals and amounts are the same size. Elements in vals represent the value, and the
corresponding element in amounts represents the number of this value desired in the
final linked list. Assume all elements in amounts are greater than 0. Assume both
lists have at least one element.
"""
idx = 0
sentinel = Link(0)
pos = sentinel
while idx < len(vals):
val, amount = vals[idx], amounts[idx]
for _ in range(amount):
new_node = Link(val)
pos.rest = new_node
pos = pos.rest
idx += 1
return sentinel.rest
Extra Questions
Q6: Next Virahanka Fibonacci Object
Implement the
nextmethod of theVirFibclass. For this class, thevalueattribute is a Fibonacci number. Thenextmethod returns aVirFibinstance whosevalueis the next Fibonacci number. Thenextmethod should take only constant time.Note that in the doctests, nothing is being printed out. Rather, each call to
.next()returns aVirFibinstance. The way eachVirFibinstance is displayed is determined by the return value of its__repr__method.Hint: Keep track of the previous number by setting a new instance attribute inside
next. You can create new instance attributes for objects at any point, even outside the__init__method.
这题要求我们写一个类, 每次调用它的方法就可以算出下一个斐波那契数
Q7: Is BST
Write a function
is_bst, which takes a Treetand returnsTrueif, and only if,tis a valid binary search tree, which means that:
- Each node has at most two children (a leaf is automatically a valid binary search tree)
- The children are valid binary search trees
- For every node, the entries in that node's left child are less than or equal to the label of the node
- For every node, the entries in that node's right child are greater than the label of the node
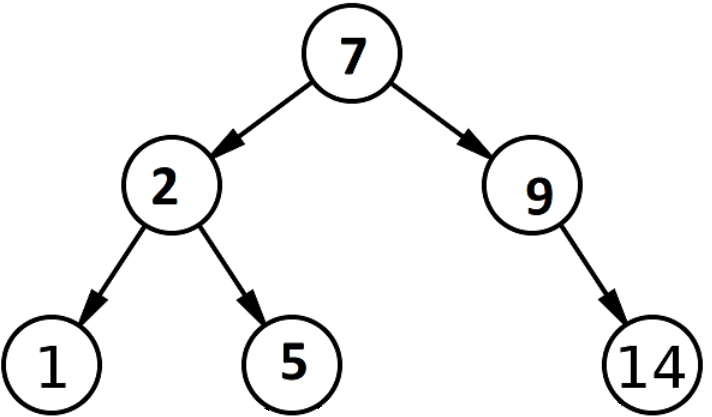
An example of a BST is:
Note that, if a node has only one child, that child could be considered either the left or right child. You should take this into consideration.
Hint: It may be helpful to write helper functions
bst_minandbst_maxthat return the minimum and maximum, respectively, of a Tree if it is a valid binary search tree.
写一个函数判断输入是否为二叉搜索树, 根据提示我们需要先实现两个辅助函数: bst_min 和 bst_max, 返回输入的树的最小和最大值
写代码要注意下面几点:
- 左子树最小值 <= 当前节点. 而不是 <
- 当前节点如果只有一个子树, 那么在那边都可以, 这里要做两种情况的判定
def is_bst(t):
"""Returns True if the Tree t has the structure of a valid BST.
"""
def bst_min(t):
"""Return the min value of the tree t"""
if t.is_leaf():
return t.label
sub_branch_min = min([bst_min(b) for b in t.branches])
return min(t.label, sub_branch_min)
def bst_max(t):
"""Return the max value of the tree t"""
if t.is_leaf():
return t.label
sub_branch_max = max([bst_max(b) for b in t.branches])
return max(t.label, sub_branch_max)
# base case 1. a leaf node is a BST
if t.is_leaf():
return True
# base case 2. each node has at most 2 children
if len(t.branches) > 2:
return False
# base case 3. a node with a single child
# it can be considered either the left or the right
if len(t.branches) == 1:
return (bst_max(t.branches[0]) < t.label or bst_min(t.branches[0]) > t.label) \
and is_bst(t.branches[0])
left_max = bst_max(t.branches[0])
right_min = bst_min(t.branches[1])
return left_max <= t.label < right_min and is_bst(t.branches[0]) and is_bst(t.branches[1])