题目

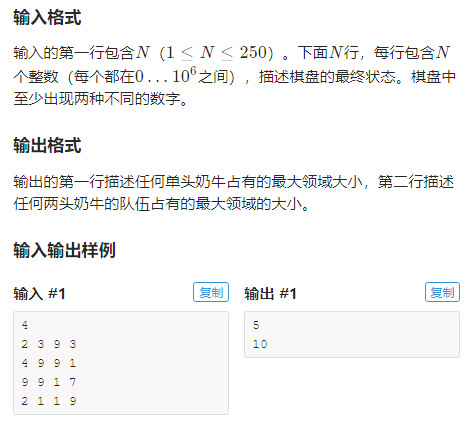

注:题目来源luogu4380
分析
Part 1 写在前面
看到题解里好多大佬用STL,蒟蒻瑟瑟发抖,打了两遍BFS,过了。
这道题本身是刷并查集时刷到的,然而发现自己用并查集想不到第二问该怎么做……
(不过luogu题解里有大佬是用的并查集)
果断放弃了并查集的思路重新思考后,发现这道题到是用BFS染色可以做。
Part 2 BFS ?
第一问倒是好想,标记连通块,统计连通块的大小,最后输出最大值就好。
void bfs1(int sx,int sy){ ++tot;//连通块的编号 color[tot] = a[sx][sy];//记下连通块的颜色 queue<Node>q; q.push((Node){sx,sy}); vis[sx][sy] = tot;//标记起点 while(!q.empty()){ Node u = q.front(); q.pop(); cnt[tot]++;//记连通块的数量 for(int i = 0;i < 4; ++ i){ int nx = u.x + dx[i]; int ny = u.y + dy[i]; if(nx <= 0 || ny <= 0 || nx > n || ny > n) continue; if(!vis[nx][ny] && a[nx][ny] == a[sx][sy]){ q.push((Node){nx,ny}); vis[nx][ny] = tot;//保证只进一次队 continue; } if(vis[nx][ny] && vis[nx][ny] < tot){ eadd(tot,vis[nx][ny]); eadd(vis[nx][ny],tot); //连双向边 } } } ans = max(ans,cnt[tot]); }
第一问主模块:
//-----------------第一问 for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++ i) for(int j = 1;j <= n; ++ j){ if(!vis[i][j]) bfs1(i,j); } put(ans);puts("");
关键是第二问。
看题:
同一队的两头奶牛像之前一样可以创建一个领域,但是现在领域中的格子可以属于队伍中的任一头奶牛。
两头奶牛占有的领域必须要同时包含队伍中两头奶牛的编号,不能仅仅包含一头。
也就是只包含两个颜色的最大连通块
我们可以思考:
最后得到的答案连通块,一定是由某个单色连通块和另一个相连的不同颜色的连通块扩展所得。
这样,
我们就可以在第一问寻找连通块的时候,为每个连通块编号,将这个连通块跟与之相邻的联通块之间加一条无向边,这样可以保证每一条边的两端颜色都是不同的。
在第二问时,按顺序遍历每一个联通快,并将其跟与它相连的连通块组成组合,一起扩展,求出最大的组合连通块即可
void bfs2(int s1,int s2){ queue<int>q; num++;//num是方案的编号 (双色连通块的编号) int tmp = 0; q.push(s2); q.push(s1); used[s1] = num; used[s2] = num; //不在同一方案中走环 while(!q.empty()){ int u = q.front(); q.pop(); tmp += cnt[u]; for(int i = first[u];i;i = edge[i].nt){ int v = edge[i].v; if(used[v] == num) continue; if(color[v]!=color[s1] && color[v]!=color[s2]) continue; used[v] = num; q.push(v); } } ans = max(ans,tmp); }
直接将这样的代码交上去,超时,不过有90分
但是我们有优化:
Part 3 优化
优化 1 遍历边优化
还记得我再将第二问的时候特别强调了一句话:
这样可以保证每一条边的两端颜色都是不同的
题目中的第二问要求:包含且仅包含两头牛
所以,一条边(u,v),确定了包含u,v的方案,注意不是包含u,v的颜色的方案
因为有可能有与u,v颜色相同的方案,只是和u,v不连通
所以 一条边就代表一个方案
这样,我们在遍历到有标记的边时,可以直接跳过,因为已经遍历过这种方案了
这样可以保证每条边只遍历一次
if(usededge[j]) continue; usededge[j] = 1;usededge[j^1] = 1;
(标记边和反向边)
但是其实有些地方还是不必要遍历的,因为连通块是一个图,有环,在便历时因为标记点、不走环的原因,不一定把连通块中所有的边都遍历了,所以不一定都标记完,下一次可能还会走到这些没标记的边,不过还没想好怎么优化,只有用标记点稍微优化一下。
优化 2 遍历点优化
跟边优化其实有一点重合,没有边优化强大,但我还是要说(蚊子肉也是肉)。
因为我们是按顺序来的,遍历完一个点后,就是把这个点的所有方案都遍历完了。
所以遇到比自己小的点,一定是已经遍历过的,那么这个方案也被遍历过了,就可以直接跳过
if(v<u) continue;
优化 3 答案优化
如果答案大于了面积的一半,就可以直接输出了
if(ans>n*n/2) break;
至此,就可以过掉这道题啦
代码
/************************* User:Mandy.H.Y Language:c++ Problem:luogu 4380 *************************/ #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = 62505; int q,n,cnt[maxn],size = 1,first[maxn]; //size = 1,便于找到反向边 int color[maxn],num; int a[255][255]; int vis[255][255]; int used[maxn]; bool usededge[maxn<<2]; int ans = 0,tot; int dx[5] = {0,0,1,-1}; int dy[5] = {1,-1,0,0}; struct Edge{ int v,nt; }edge[maxn << 2]; struct Node{ int x,y; }; template<class T>inline void read(T&x){ x = 0;char ch = getchar();bool flag = 0; while(!isdigit(ch)) flag |= ch == '-',ch = getchar(); while(isdigit(ch)) x = (x << 1) + (x <<3) + (ch ^ 48),ch = getchar(); if(flag) x = -x; } template<class T>void putch(const T x){ if(x > 9) putch(x / 10); putchar(x % 10 | 48); } template<class T>void put(const T x){ if(x < 0) putchar('-'),putch(-x); else putch(x); } void file(){ freopen("4380.in","r",stdin); // freopen("4380.out","w",stdout); } void readdata(){ read(n); for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++ i) for(int j = 1;j <= n; ++ j) read(a[i][j]); } void eadd(int u,int v){ edge[++size].v = v; edge[size].nt = first[u]; first[u] = size; } void bfs1(int sx,int sy){ ++tot;//连通块的编号 color[tot] = a[sx][sy];//记下连通块的颜色 queue<Node>q; q.push((Node){sx,sy}); vis[sx][sy] = tot;//标记起点 while(!q.empty()){ Node u = q.front(); q.pop(); cnt[tot]++;//记连通块的数量 for(int i = 0;i < 4; ++ i){ int nx = u.x + dx[i]; int ny = u.y + dy[i]; if(nx <= 0 || ny <= 0 || nx > n || ny > n) continue; if(!vis[nx][ny] && a[nx][ny] == a[sx][sy]){ q.push((Node){nx,ny}); vis[nx][ny] = tot;//保证只进一次队 continue; } if(vis[nx][ny] && vis[nx][ny] < tot){ eadd(tot,vis[nx][ny]); eadd(vis[nx][ny],tot); //连双向边 } } } ans = max(ans,cnt[tot]); } void bfs2(int s1,int s2){ queue<int>q; num++;//num是方案的编号 (双色连通块的编号) int tmp = 0; q.push(s2); q.push(s1); used[s1] = num; used[s2] = num; //不在同一方案中走环 while(!q.empty()){ int u = q.front(); q.pop(); tmp += cnt[u]; for(int i = first[u];i;i = edge[i].nt){ int v = edge[i].v; if(used[v] == num || v < s1) continue;//优化2 if(color[v]!=color[s1] && color[v]!=color[s2]) continue; if(usededge[i]) return;//优化1 //这里直接return,因为是一个方案都遍历过 //这里也要加上这个剪枝, 因为有可能是上一次双色连通块判断点的时候就返回了,就没有标记边 //主程序里边没剪完 usededge[i] = 1;usededge[i^1] = 1;//标记边与反向边 used[v] = num; q.push(v); } } ans = max(ans,tmp); } void work(){ //-----------------第一问 for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++ i) for(int j = 1;j <= n; ++ j){ if(!vis[i][j]) bfs1(i,j); } put(ans);puts(""); //-----------------第二问 ans = 0; int maxans = (n*n)>>1; for(int i = 1;i <= tot; ++ i){//按序遍历单色连通块 for(int j = first[i];j;j = edge[j].nt){ int v = edge[j].v; if(v <= i) continue;//优化2 if(color[v] == color[i]) continue; if(usededge[j]) continue; //这里先剪一部分边,前面遍历过的双色连通块里的边不一定都标记完了 usededge[j] = 1;usededge[j^1] = 1;//优化1 bfs2(i,v); if(ans > maxans) break; //优化3 } } put(ans); } int main(){ // file(); readdata(); work(); return 0; }