@
@article{das2011differential,
title={Differential Evolution: A Survey of the State-of-the-Art},
author={Das, Swagatam and Suganthan, P N},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation},
volume={15},
number={1},
pages={4--31},
year={2011}}
概
这是一篇关于Differential Evolution (DE) 的综述, 由于对这类方法并不熟悉, 只能简单地做个记录.
主要内容
考虑如下问题,
其中(X=(x_1,ldots,x_D)).
我所知的, 如梯度下降方法, 贝叶斯优化可以用来处理这类问题, 但是还有诸如 evolutionary algorithm (EA), evolutionary programming (EP), evolution strategies(ESs), genetic algorithm (GA), 以及本文介绍的 DE (后面的基本都不了解).
DE/rand/1/bin
先给出最初的形式, 称之为DE/rand/1/bin:
Input: scale factor (F), crossover rate (Cr), population size (NP).
1: 令(G=0), 并随机初始化(P_G={ X_{1,G},ldots, X_{NP,G}}).
2: While the stopping criterion is not satisfied Do:
- For (i=1,ldots, NP) do:
- Mutation step:
- Crossover step: 按照如下方式生成(U_{i,G}=(u_{1,i,G},ldots, u_{D,i,G}))
- Selection step:
- End For.
- (G=G+1).
End While.
其中(X_{i,G}=(x_{j,i,G}, ldots, x_{D,i,G})), (j_{rand})是预先随机生成的一个属于([1,D])的整数, 以保证(U)相对于(X)至少有些许变化产生, (X_{r_1^i,G}, X_{r_2^i,G},X_{r_3^i,G})是从(P_G)中随机抽取且互异的.
在接下来我们可以发现很多变种, 而这些变种往往是Mutation step 和 Crossover step的变体.
DE/?/?/?
DE/rand/1/exp
这是crossover step步的的一个变种:
随机从([1, D])中抽取整数(n)和(L), 然后
(L)可以通过下面的步骤生成
- (L=0)
- while (mathrm{rand}[0,1] le Cr) and (Lle D):
DE/best/1
其中(X_{best,G})是(P_{G})中的最优的点.
DE/best/2
DE/rand/2
超参数的选择
真的没有细看, 文中粗略地介绍了几处, 还有很多需要查原文.
(F)的选择
有的推荐([0.4, 1])(最佳0.5), 有的推荐(0.6), 有的推荐([0.4, 0.95])(最佳0.9).
还有一些自适应的选择, 如
我比较疑惑的是难道(|frac{f_{max}}{f_{min}}|)不是大于等于1吗?
其中(F_l), (F_u)分别为(F)取值的下界和上界.
(NP)的选择
有的推荐([5D,10D]), 有的推荐([3D, 8D]).
(Cr)的选择
有的推荐([0.3, 0.9]).
还有
一些连续变体
A
如果(mathrm{rand}[0,1] < Gamma)((Gamma)是给定的):
否则
B
其中(k_i)给定, (F'=k_i cdot F).
C
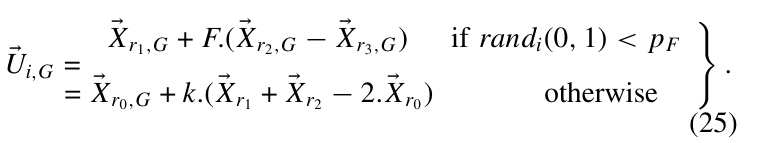
D
即在考虑(x)的时候, 还需要考虑其反(a+b-x), 假定(x in [a, b]), ([a,b])为我们给定范围, (X)的反类似的构造.
E
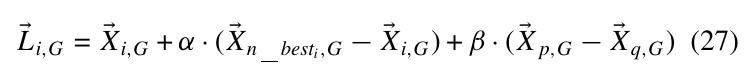
其中(X_{n_{best},G})表示在(X_{i,G})的(n)的近邻中的最优点, (p, qin [i-k,i+k]).
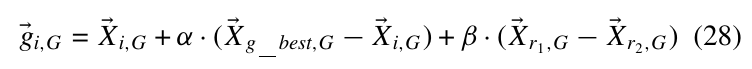
其中(X_{g_{best},G})为(P_G)中的最优点.
G
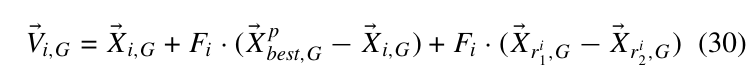
剩下的在复杂环境下的应用就不记录了(只是单纯讲了该怎么做).
一些缺点
- 高维问题不易处理;
- 容易被一些问题欺骗, 而现如局部最优解;
- 对不能分解的函数效果不是很好;
- 路径往往不会太大(即探索不充分);
- 缺少收敛性的理论的保证.
代码
(f(x,y)=x^2+50y^2).
{
"dim": 2,
"F": 0.5,
"NP": 5,
"Cr": 0.35
}
"""
de.py
"""
import numpy as np
from scipy import stats
import random
class Parameter:
def __init__(self, dim, xmin, xmax):
self.dim = dim
self.xmin = xmin
self.xmax = xmax
self.initial()
def initial(self):
self.para = stats.uniform.rvs(
self.xmin, self.xmax - self.xmin
)
@property
def data(self):
return self.para
def __getitem__(self, item):
return self.para[item]
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
self.para[key] = value
def __len__(self):
return len(self.para)
def __add__(self, other):
return self.para + other
def __mul__(self, other):
return self.para * other
def __pow__(self, power):
return self.para ** power
def __neg__(self):
return -self.para
def __sub__(self, other):
return self.para - other
def __truediv__(self, other):
return self.para / other
class DE:
def __init__(self, func, dim ,F=0.5, NP=50,
Cr=0.35, xmin=-10, xmax=10,
require_history=True):
self.func = func
self.dim = dim
self.F = F
self.NP = NP
self.Cr = Cr
self.xmin = np.array(xmin)
self.xmax = np.array(xmax)
assert all(self.xmin <= self.xmax), "Invalid xmin or xmax"
self.require_history = require_history
self.init_x()
if self.require_history:
self.build_history()
def init_x(self):
self.paras = [Parameter(self.dim, self.xmin, self.xmax)
for i in range(self.NP)]
@property
def data(self):
return [para.data for para in self.paras]
def build_history(self):
self.paras_history = [self.data]
def add_history(self):
self.paras_history.append(self.data)
def choose(self, size=3):
return random.sample(self.paras, k=size)
def mutation(self):
x1, x2, x3 = self.choose(3)
return x1 + self.F * (x2 - x3)
def crossover(self, v, x):
u = np.zeros_like(v)
for i, _ in enumerate(v):
jrand = random.randint(0, self.dim)
if np.random.rand() < self.Cr or i is jrand:
u[i] = v[i]
else:
u[i] = x[i]
u[i] = v[i] if np.random.rand() < self.Cr else x[i]
return u
def selection(self, u, x):
if self.func(u) < self.func(x):
x.para = u
else:
pass
def step(self):
donors = [self.mutation()
for i in range(self.NP)]
for i, donor in enumerate(donors):
x = self.paras[i]
u = self.crossover(donor, x)
self.selection(u, x)
if self.require_history:
self.add_history()
def multi_steps(self, times):
for i in range(times):
self.step()
class DEbest1(DE):
def bestone(self):
y = np.array([self.func(para)
for para in self.paras])
return self.paras[np.argmax(y)]
def mutation(self, bestone):
x1, x2 = self.choose(2)
return bestone + self.F * (x1 - x2)
def step(self):
bestone = self.bestone()
donors = [self.mutation(bestone)
for i in range(self.NP)]
for i, donor in enumerate(donors):
x = self.paras[i]
u = self.crossover(donor, x)
self.selection(u, x)
if self.require_history:
self.add_history()
class DEbest2(DEbest1):
def mutation(self, bestone):
x1, x2, x3, x4 = self.choose(4)
return bestone + self.F * (x1 - x2)
+ self.F * (x3 - x4)
class DErand2(DE):
def mutation(self):
x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 = self.choose(5)
return x1 + self.F * (x2 - x3)
+ self.F * (x4 - x5)
class DErandTM(DE):
def mutation(self):
x = self.choose(3)
y = np.array(list(map(self.func, x)))
p = y / y.sum()
part1 = (x[0] + x[1] + x[2]) / 3
part2 = (p[1] - p[0]) * (x[0] - x[1])
part3 = (p[2] - p[1]) * (x[2] - x[1])
part4 = (p[0] - p[2]) * (x[2] - x[0])
return part1 + part2 + part3 + part4