每个题目后面有更正后的代码(有提示更正),前面代码是自己写的,不是很准确,请参考更正后的内容
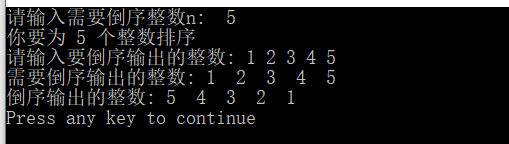
1. 将n个整数按输入顺序的逆序排列,要求应用带指针参数的函数实现
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define N 100
int tip(int num);
void addArray(int arr[], int size);
void reOrder(int *p, int num);
int main()
{
int n = 0;
int array[N] = {'�'};
n = tip(n);
addArray(array,n);
reOrder(array,n);
return 0;
}
//输入提示
int tip(int num)
{
cout<<"请输入需要倒序整数n: ";
cin>>num;
if(num<0)
{
cout<<"你输入的n值小于0
";
return 0;
}
else if(num > 100)
{
cout<<"你输入的n值大于数组的容量
";
return 0;
}
else
{
cout<<"你要为 "<<num<<" 个整数排序"<<endl;
return num;
}
}
//对数组输入值并打印输入的整数
void addArray(int arr[], int size)
{
cout<<"请输入要倒序输出的整数: ";
int i=0;
for(i; i<size; i++)
{
cin>>arr[i];
}
cout<<"需要倒序输出的整数: ";
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
{
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
//对整数进行倒序排列并输出
void reOrder(int arr[], int num)
{
cout<<"倒序输出的整数: ";
int i=0;
for(i = num-1; i>=0; i--)
{
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
运行结果:
更正:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void inverse(int *p, int n)
{
int *q=p+n-1; //指针变量q指向数组最后一个元素
int t;
while (p<q)
{
t = *p; *p = *q; *q=t; //交换*p与*q
p++;q--; //移动指针变量
}
}
int main()
{
int a[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
inverse(a,10);
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
更正运行结果:
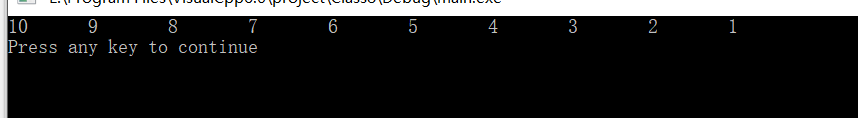
2.编程输入一行文字,找出其中的大写字母、小写字母、空格、数字以及其他字符各有多少
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
#define M 100 //预内编译命令容没分号
void number(char array[]);
int main()
{
char array[M] = {'�'};
number(array);
return 0;
}
void number(char array[])
{
int capitalNum;//大写字母个数
int lowerNum;//小写字母个数
int spaceNum;//空格个数
int digitalNum;//数字个数
int othreNum;//其他个数
capitalNum=lowerNum=spaceNum=digitalNum=othreNum = 0;
cout<<"请输入字符串:"<<endl;
gets(array);
int size = strlen(array);
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
if(array[i]>='A'&&array[i]<='Z')
capitalNum++;
else if(array[i]>='a'&&array[i]<='z')
lowerNum++;
else if(array[i]>='0'&&array[i]<'9')
digitalNum++;
else if(array[i]==' ')
spaceNum++;
else
othreNum++;
}
cout<<"字符串长度:"<<size<<endl;
cout<<"大写字母个数:"<<capitalNum<<endl;
cout<<"小写字母个数:"<<lowerNum<<endl;
cout<<"数字个数:"<<digitalNum<<endl;
cout<<"空格个数:"<<spaceNum<<endl;
cout<<"其他字符个数:"<<othreNum<<endl;
system("pause");
}
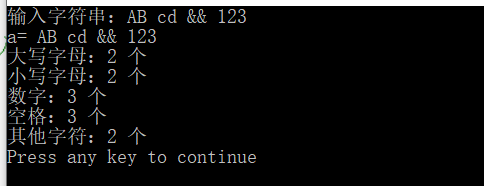
运行结果:
更正
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a[50], *p = a; //指针与数组
int i=0, j=0, m=0, n=0, k=0;
cout<<"输入字符串:";
cin.getline(a,51); //输入一段文字,自动加'�',输入最大字符个数为50
cout<<"a= "<<a<<endl;
while(*p != '�')
{
if(*p>='A'&&*p<='Z')
{i++;}
else if(*p>='a'&&*p<='z')
{j++;}
else if(*p>='0'&&*p<='9')
{m++;}
else if(*p == ' ')
{n++;}
else
{k++;}
p++; //执行完一轮后,将指针的地址指向下一个字符,继续检查
}
cout<<"大写字母:"<<i<<" 个"<<endl;
cout<<"小写字母:"<<j<<" 个"<<endl;
cout<<"数字:"<<m<<" 个"<<endl;
cout<<"空格:"<<n<<" 个"<<endl;
cout<<"其他字符:"<<k<<" 个"<<endl;
return 0;
}
更正后运行结果
3. 编写一个从n个字符串中寻找最长字符串的函数char * Longstr(char * z[],int n),其中z是指向多个字符串的指针数组,n是字符串的个数,数组返回值是最长串的首地址,并编写main函数验证程序。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
char* longstr(char* z[], int n)
{
int i;
char* p = z[0];
for(i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
if(strlen(p) < strlen(z[i]))
p = z[i];
}
return p;
}
int main()
{
char* array[ ] = {"iostream","pptx","xlsx","docx","doc","txt","c" };
char* p = longstr(array, sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]));
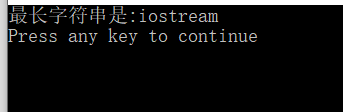
cout << "最长字符串是:" << p << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4. 编写一个将一个字符串插入到另一个字符串指定位置的函数,并编写main函数验证程序
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define X 40
#define Y 40
#define Z 40
void oderInsert(char a[],char b[],char c[])
{
int p, i, j, k;
while(1)
{
cout <<"请输入第一个字符串: "<< endl;
cin >> a;
cout <<"请输入第二个字符串: "<< endl;
cin >> b;
cout <<"请输入插入的位置: "<< endl;
cin >> p; //输入插入位置
for( i=0; i<p; i++ )
c[i] = a[i];
for( j=0; b[j] != '�'; j++ )
c[i+j] = b[j];
for( k=p; a[k] != '�'; k++ )
c[j+k] = a[k];
c[j+k] = '�';
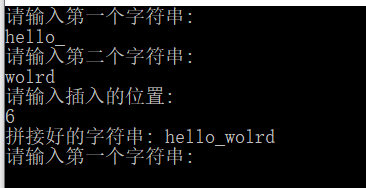
cout <<"拼接好的字符串: "<<c << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
char s1[X] = {'�'}, s2[Y] = {'�'}, s3[Z] = {'�'};
oderInsert(s1,s2,s3);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
更正:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define X 1000
int myStrlen(const char *str) //指向常量的指针,指向的数据为常量(str指向的常量)
{
int len = 0;
while(*str++)
len++;
return len;
}
//拼接函数
void myStrcat(char *str1,char *str2)
{
int len1 = strlen(str1);
int len2 = strlen(str2);
for(int i=0; i<len2; i++)
{
str1[len1 + i] = str2[i];
}
str1[len1+len2] = '�';
}
void myLink(char *str1,char *str2, int pos)
{
int len1 = myStrlen(str1);
int len2 = myStrlen(str2);
char tmp[1000];
int k = 0;
for(int i=pos; i<=len1;i++)
{
tmp[k++] = str1[i];
}
for(int j=0; j<len2; j++)
{
str1[pos + j] = *str2++;
}
str1[pos + j] = '�';
myStrcat(str1, tmp);
}
int main()
{
char str1[X], str2[X];
int n;
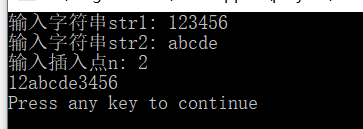
cout<<"输入字符串str1: ";
cin.getline(str1,X);
cout<<"输入字符串str2: ";
cin.getline(str2,X);
cout<<"输入插入点n: ";
cin>>n;
myLink(str1, str2, n);
cout<< str1 <<endl;
return 0;
}
更正后运行结果:

第一个方程的代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
double func (const double x);
double findRoot( double first, double last,const double e);
int main ()
{
double a,b ,c,root;
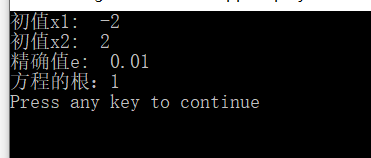
cout<<"初值x1: ";
cin>>a;
cout<<"初值x2: ";
cin>>b;
cout<<"精确值e: ";
cin>>c;
root=findRoot(a,b,c);
cout<<"方程的根:"<<root<<endl;
return 0;
}
double func(const double x)
{
double y;
y=x*x*x + x*x - 3*x +1;
return y;
}
double findRoot(double first, double last,const double e)
{
double mid,y0,y1,y2;
mid=(first+last)/2;
while((last-first)>e)
{
y0=func (mid);
y1=func(first);
y2=func(last);
if (y0==0)
return mid;
else if(y0*y1<0) last=mid;
else first=mid; /*注意这里*/
mid=(first+last)/2;
}
return mid;
}
运行结果:
第二方程的代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
double func (const double x);
double findRoot( double first, double last,const double e);
int main ()
{
double a,b ,c,root;
cout<<"初值x1: ";
cin>>a;
cout<<"初值x2: ";
cin>>b;
cout<<"精确值e: ";
cin>>c;
root=findRoot(a,b,c);
cout<<"方程的根:"<<root<<endl;
return 0;
}
double func(const double x)
{
double y;
y=x*x - 2*x -8;
return y;
}
double findRoot(double first, double last,const double e)
{
double mid,y0,y1,y2;
mid=(first+last)/2;
while((last-first)>e)
{
y0=func (mid);
y1=func(first);
y2=func(last);
if (y0==0)
return mid;
else if(y0*y1<0) last=mid;
else first=mid; /*注意这里*/
mid=(first+last)/2;
}
return mid;
}
运行结果:
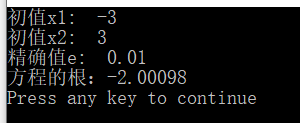
第三个方程的代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
double func (const double x);
double findRoot( double first, double last,const double e);
int main ()
{
double a,b ,c,root;
cout<<"初值x1: ";
cin>>a;
cout<<"初值x2: ";
cin>>b;
cout<<"精确值e: ";
cin>>c;
root=findRoot(a,b,c);
cout<<"方程的根:"<<root<<endl;
return 0;
}
double func(const double x)
{
double y;
y=x*x*x + 2*x*x + 2*x + 1;
return y;
}
double findRoot(double first, double last,const double e)
{
double mid,y0,y1,y2;
mid=(first+last)/2;
while((last-first)>e)
{
y0=func (mid);
y1=func(first);
y2=func(last);
if (y0==0)
return mid;
else if(y0*y1<0) last=mid;
else first=mid; /*注意这里*/
mid=(first+last)/2;
}
return mid;
}
运行结果:
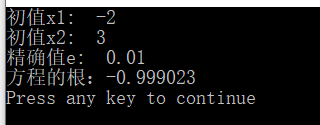
更正:
#include <cmath>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
float f1(float x)
{
return x*x*x + x*x - 3*x + 1;
}
float f2(float x)
{
return x*x - 2*x - 8;
}
float f3(float x)
{
return x*x*x + 2*x*x + 2*x + 1;
}
//二分法计算方程的解
float divide(float(*p)(float),float x1,float x2)
{
float x0;
do
{
x0=(x1+x2)/2;
if(p(x1)*p(x0)>0)
x1=x0;
else
x2=x0;
}while (fabs(p(x0))>1e-6);
return x0;
}
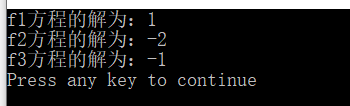
int main()
{
cout<<"f1方程的解为:"<<divide(f1,-2,2)<<endl;
cout<<"f2方程的解为:"<<divide(f2,-3,3)<<endl;
cout<<"f3方程的解为:"<<divide(f3,-2,3)<<endl;
return 0;
}
更正后的运行结果: