使用邻接矩阵进行存储
原图
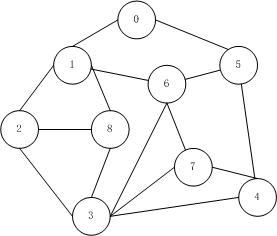
调整后

package graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class BFSTraverse {
private static ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 邻接矩阵存储;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始数据;
int[] vertexs = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
int[][] edges = { { 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1 }, { 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 }, { 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
BFSTraverse(vertexs, edges);
System.out.println("深度遍历结果:" + list);
}
private static void BFSTraverse(int[] vertexs,int[][] edges) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[vertexs.length];
for(int i=0;i<visited.length;i++) {
visited[i]=false;
}
LinkedList<Integer> helper=new LinkedList<Integer>();//辅助队列;
helper.offerLast(vertexs[0]);//将第一个放入访问队列;
visited[0]=true;
BFS(vertexs,edges,visited,helper);
}
private static void BFS(int[] vertexs,int[][] edges,boolean[] visited,LinkedList<Integer> helper) {
while(!helper.isEmpty()) {
int i = helper.pollFirst();
list.add(i);
for(int j=0;j<vertexs.length;j++) {
if(edges[i][j]==1&&!visited[j]) {
visited[j]= true; //注意这个放置的位置,应该是将顶点放入到队列的时候进行设置,不能再将顶点从队列取出的时候再设置;
helper.offerLast(vertexs[j]);
}
}
}
}
}