This is an interactive problem. In the output section below you will see the information about flushing the output.
On Sunday Leha the hacker took Nura from the house where she lives and went with her to one of the most luxurious restaurants in Vičkopolis. Upon arrival, they left the car in a huge parking lot near the restaurant and hurried inside the building.
In the restaurant a polite waiter immediately brought the menu to Leha and Noora, consisting of n dishes. It is interesting that all dishes in the menu are numbered with integers from 1 to n. After a little thought, the girl ordered exactly k different dishes from available in the menu. To pass the waiting time while the chefs prepare ordered dishes, the girl invited the hacker to play a game that will help them get to know each other better.
The game itself is very simple: Noora wants Leha to guess any two dishes among all ordered. At the same time, she is ready to answer only one type of questions. Leha can say two numbers x and y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n). After that Noora chooses some dish a for the number xsuch that, at first, a is among the dishes Noora ordered (x can be equal to a), and, secondly, the value 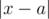 is the minimum possible. By the same rules the girl chooses dish b for y. After that Noora says «TAK» to Leha, if
is the minimum possible. By the same rules the girl chooses dish b for y. After that Noora says «TAK» to Leha, if 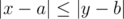 , and «NIE» otherwise. However, the restaurant is preparing quickly, so Leha has enough time to ask no more than 60 questions. After that he should name numbers of any two dishes Noora ordered.
, and «NIE» otherwise. However, the restaurant is preparing quickly, so Leha has enough time to ask no more than 60 questions. After that he should name numbers of any two dishes Noora ordered.
Help Leha to solve this problem!
There are two numbers n and k (2 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 105) in the single line of input denoting the number of dishes in the menu and the number of dishes Noora ordered.
If you want to provide an answer, output a string of the form 2 x y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n, x ≠ y), if you think the dishes x and y was among dishes ordered by Noora. After that, flush the output and terminate your program.
While helping Leha, you can ask queries to Noora no more than 60 times. Each query should be printed in it's own line and have the form 1 x y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n). You have to both print the end-of-line character and flush the output. After flushing you should read the answer for this query from input.
After each query jury's program will print one line «TAK» or «NIE» (without quotes) in input stream depending on the girl's answer.
To flush you can use (just after printing an integer and end-of-line):
- fflush(stdout) in C++;
- System.out.flush() in Java;
- stdout.flush() in Python;
- flush(output) in Pascal;
- see the documentation for other languages.
Hacking
For hacking you should write numbers n and k (2 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 105) in the first line and, for describing dishes Noora ordered, k different integers a1, a2, ..., ak (1 ≤ ai ≤ n), written in ascending order in the second line. Of course, solution you want to hack won't be able to read the numbers of ordered dishes.
3 2
NIE
TAK
NIE
TAK
TAK
TAK
1 1 2
1 2 1
1 1 3
1 3 1
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 2 3
There are three dishes in sample. Noora ordered dished numberes 2 and 3, which Leha should guess. If Noora receive requests for the first dish (x = 1), then she'll choose the second dish (a = 2) as the dish with the minimum value 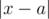 . For the second (x = 2) and the third (x = 3) dishes themselves will be optimal, because in that case
. For the second (x = 2) and the third (x = 3) dishes themselves will be optimal, because in that case 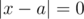 .
.
Let Leha asks Noora about the next couple of dishes:
- x = 1, y = 2, then he'll recieve «NIE» answer, because |1 - 2| > |2 - 2|
- x = 2, y = 1, then he'll recieve «TAK» answer, because |2 - 2| ≤ |1 - 2|
- x = 1, y = 3, then he'll recieve «NIE» answer, because |1 - 2| > |3 - 3|
- x = 3, y = 1, then he'll recieve «TAK» answer, because |3 - 3| ≤ |1 - 2|
- x = 2, y = 3, then he'll recieve «TAK» answer, because |2 - 2| ≤ |3 - 3|
- x = 3, y = 2, then he'll recieve «TAK» answer, because |3 - 3| ≤ |2 - 2|
According to the available information, it is possible to say that Nura ordered dishes with numbers 2 and 3.
题目大意:一个数轴上有一些数,你可以询问两个位置,交互库会回答两个位置离最近的数的距离哪个比较近(好像有点讲不清楚,你需要在60次询问中找出两个数轴上的数
60大概是19*3+3这样的分配
我们需要定义一种搜索,他接受一个区间,并且如果这个区间里有数,它会返回这个数,如果没有,他会返回一个没有意义的数
这个搜索是这样的,假设这个区间是[l,r],我们询问mid,mid+1这两个位置,这两个位置把区间分割为[l,mid]和[mid+1,r],然后可以递归做下去
于是我们对整个[1,n]进行一次搜索找到第一个数x,然后在对这个数左右各做一次搜索即可,注意搜出来的数可能不是真的,需要再做一次y x的询问,如果y确实存在那么返回一定是TAK
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <cstring> 7 #include <cmath> 8 #include <map> 9 #include <stack> 10 #include <set> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <queue> 13 #include <time.h> 14 #define eps 1e-7 15 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 16 #define MOD 1000000007 17 #define rep0(j,n) for(int j=0;j<n;++j) 18 #define rep1(j,n) for(int j=1;j<=n;++j) 19 #define pb push_back 20 #define mp make_pair 21 #define set0(n) memset(n,0,sizeof(n)) 22 #define ll long long 23 #define ull unsigned long long 24 #define iter(i,v) for(edge *i=head[v];i;i=i->nxt) 25 #define max(a,b) (a>b?a:b) 26 #define min(a,b) (a<b?a:b) 27 #define print_runtime printf("Running time:%.3lfs ",double(clock())/1000.0) 28 #define TO(j) printf(#j": %d ",j); 29 //#define OJ 30 using namespace std; 31 const int MAXINT = 100010; 32 const int MAXNODE = 100010; 33 const int MAXEDGE = 2*MAXNODE; 34 char BUF,*buf; 35 int read(){ 36 char c=getchar();int f=1,x=0; 37 while(!isdigit(c)){if(c=='-') f=-1;c=getchar();} 38 while(isdigit(c)){x=x*10+c-'0';c=getchar();} 39 return f*x; 40 } 41 char get_ch(){ 42 char c=getchar(); 43 while(c!='N'&&c!='T') c=getchar(); 44 return c; 45 } 46 //------------------- Head Files ----------------------// 47 48 int n,k; 49 int search(int l,int r){//[l,r] 50 if(r<l) return -1; 51 if(r==l) return l; 52 int midl = (l+r)/2,midr=midl+1; 53 printf("1 %d %d ",midl,midr); 54 fflush(stdout); 55 char res = get_ch(); 56 if(res=='T') return search(l,midl); else return search(midr,r); 57 } 58 void get_input(); 59 void work(); 60 int main() { 61 get_input(); 62 work(); 63 return 0; 64 } 65 void work(){ 66 int ans1 = search(1,n); 67 int ans2 = search(1,ans1-1); 68 int ans3 = search(ans1+1,n); 69 if(ans2!=-1){ 70 printf("1 %d %d ",ans2,ans1); 71 fflush(stdout); 72 char res = get_ch(); 73 if(res!='T'){ 74 printf("2 %d %d ",ans1,ans3); 75 }else{ 76 printf("2 %d %d ",ans1,ans2); 77 } 78 }else{ 79 printf("2 %d %d ",ans1,ans3); 80 } 81 } 82 void get_input(){ 83 n=read(); k=read(); 84 }