模式定义
状态模式(State Pattern) :允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变它的行为,对象看起来似乎修改了它的类。
UML类图
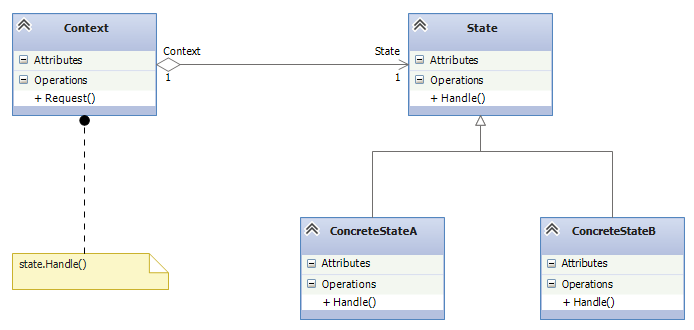
- 环境类(Context): 在环境类中维护一个抽象状态类型State的字段,一调用状态的处理行为和状态切换业务逻辑。
- 抽象状态类(State):用于定义一个接口以封装与环境类的一个特定状态相关的行为。
- 具体状态类(ConcreteState):是抽象状态类的子类,实现特定状态的行为,每一个子类实现一个与环境类的一个状态相关的行为。
代码结构
public class StateApp
{
public void Run()
{
Context c = new Context(new ConcreteStateA());
c.Request();
c.Request();
c.Request();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
abstract class State
{
public abstract void Handle(Context context);
}
class ConcreteStateA : State
{
public override void Handle(Context context)
{
context.State = new ConcreteStateB();
}
}
class ConcreteStateB : State
{
public override void Handle(Context context)
{
context.State = new ConcreteStateA();
}
}
class Context
{
public State State { get; set; }
public Context(State state)
{
this.State = state;
}
public void Request()
{
this.State.Handle(this);
}
}
情景案例
有一款比较火的微信小游戏“头脑王者”,不同的等级,需要不同的”星“才可以晋级
public class StateRealWorldApp
{
public void Run()
{
Player player = new Player("小王");
player.Display();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
player.Win();
}
player.Display();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
abstract class Grade
{
protected int Score = 0;
public string Name = string.Empty;
public Player Player { get; set; }
public abstract void Win();
public abstract void Lose();
}
class New : Grade
{
public New(Player player)
{
this.Player = player;
this.Name = "入手新门";
}
public override void Win()
{
this.Score = this.Score + 1;
if(this.Score == 5)
{
this.Player.State = new Skilled(this);
this.Score = 0;
}
}
public override void Lose()
{
if(this.Score != 0)
{
this.Score = this.Score - 1;
}
}
}
class Skilled : Grade
{
public Skilled(Grade state)
{
this.Player = state.Player;
this.Name = "起步熟手";
}
public override void Win()
{
this.Score = this.Score + 1;
if (this.Score == 7)
{
this.Player.State = new BlackIron(this);
this.Score = 0;
}
}
public override void Lose()
{
if (this.Score != 0)
{
this.Score = this.Score - 1;
}
}
}
class BlackIron : Grade
{
public BlackIron(Grade state)
{
this.Player = state.Player;
this.Name = "坚韧黑铁";
}
public override void Win()
{
this.Score = this.Score + 1;
if (this.Score == 7)
{
this.Score = 0;
}
}
public override void Lose()
{
if (this.Score != 0)
{
this.Score = this.Score - 1;
}
}
}
class Player
{
public Grade State { get; set; }
private string Name;
public Player(string name)
{
this.State = new New(this);
this.Name = name;
}
public void Win()
{
this.State.Win();
}
public void Lose()
{
this.State.Lose();
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("用户:{0},等级为:{1}",this.Name,this.State.Name);
}
}