//==================================================================
// 《剑指Offer——名企面试官精讲典型编程题》代码
// 作者:何海涛
//==================================================================
// 面试题7:重建二叉树
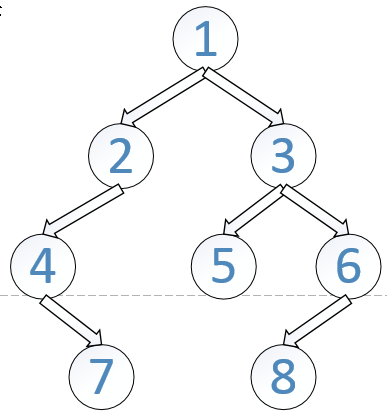
// 题目:输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输
// 入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,
// 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 8}和中序遍历序列{4, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 8, 6},则重建出
// 图中所示的二叉树并输出它的头结点。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include "..UtilitiesBinaryTree.h"
using namespace std;
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
int m_nValue;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;
};
BinaryTreeNode* ConstructCore(int* startPreorder, int* endPreorder,
int* startInorder, int* endInorder) {
// 前序遍历的第一个数字是根结点的值
// 获得根结点并初始化
int rootValue = startPreorder[0];
BinaryTreeNode* root = new BinaryTreeNode();
root->m_nValue = rootValue;
root->m_pLeft = root->m_pRight = nullptr;
// 当前序遍历和中序遍历的两个数组的两端的指针都指向同一个元素,
// 并且这个元素的值还相等时,表示递归结束
if (startPreorder == endPreorder) {
if (startInorder == endInorder && *startPreorder == *startInorder){
return root;
} else {
throw std::exception();
}
}
// 在中序遍历中定位到根节点,直到*rootInorder == rootValue
int* rootInorder = startInorder; // 从划分出的头开始
while(rootInorder <= endInorder && *rootInorder != rootValue) {
++rootInorder; // 不是就指针+1,向后移动继续查找
}
if (rootInorder == endInorder && *rootInorder != rootValue) {
throw std::exception();
}
// 利用指针的减法算出相对于当前根结点的左子树的数量
int leftLength = rootInorder - startInorder;
// 得到在前序遍历中指向最后一个左子树的元素的指针
int* leftPreorderEnd = startPreorder + leftLength;
if (leftLength > 0) {
// 构建左子树,前序遍历数组头部指针往右移,中序遍历数组根节点指针往左移,两个数组均排除一个定位好的节点
root->m_pLeft = ConstructCore(startPreorder + 1, leftPreorderEnd, startInorder, rootInorder - 1);
}
// endPreorder - startPreorder的值就是下一层元素的总个数,
// 当leftLength = endPreorder - startPreorder时,就表明下一层只有左子树
// 当他小于这个值时,就说明下一层有右子树
// 当然,他不可能大于这个值,因为他是中序遍历中 根结点左边元素的个数
if (leftLength < endPreorder - startPreorder) {
// 构建右子树,最后一个左子树的元素的指针往右移指向右子树数组的第一个元素,中序遍历数组根结点指针往右移,两个数组均排除一个定位好的节点
root->m_pRight = ConstructCore(leftPreorderEnd + 1, endPreorder, rootInorder + 1, endInorder);
}
return root;
}
BinaryTreeNode* Construct(int *preorder, int* inorder, int length) {
if (preorder == nullptr || inorder == nullptr || length <= 0) {
return nullptr;
}
return ConstructCore(preorder, preorder + length -1,
inorder, inorder + length -1);
}
部分分析过程:
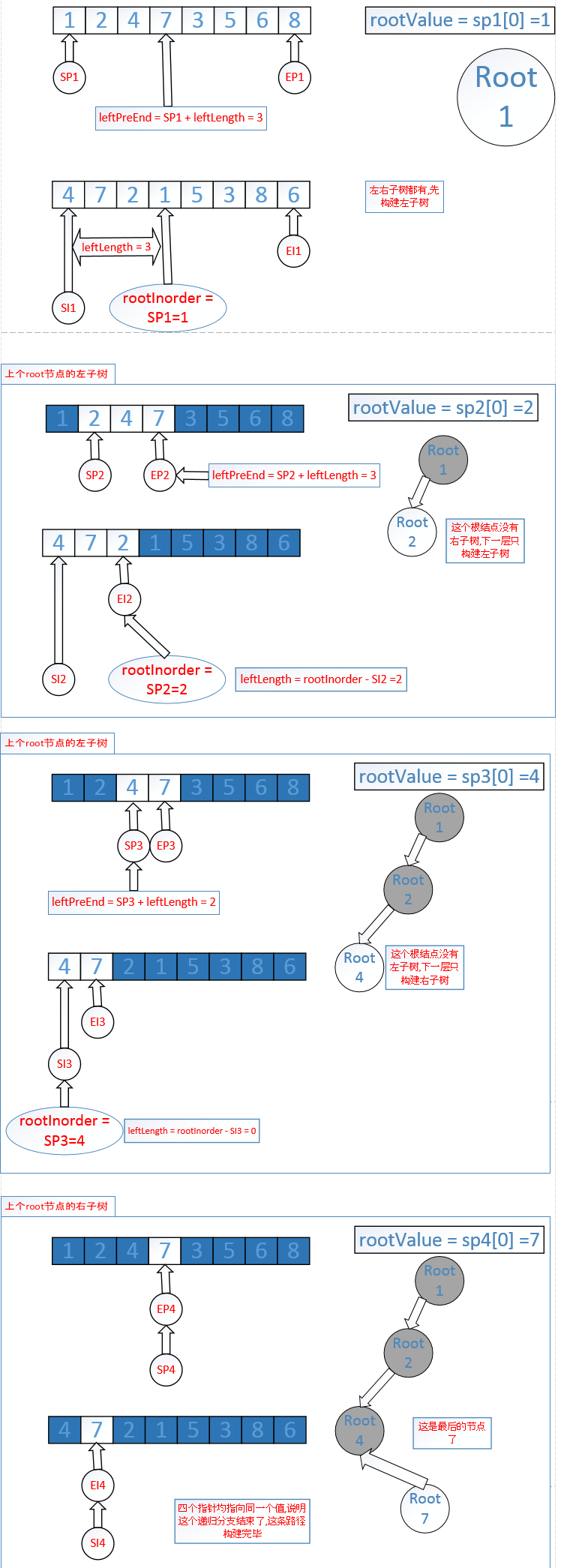
由此可以总结出:
二叉树的前序遍历中,第一个数字总是树的根结点的值
二叉树的中序遍历中,根结点的值在序列的中间,左子树的值位于根结点的左边,右子树的值位于根结点的右边
根据这两个特点,这道题的解法就是从根结点出发递归的划分左右子树
1. 根据前序遍历找到根结点
2. 根据根结点的值,在中序遍历中定位到根结点
3. 根据中序遍历中定位到的根结点,计算出左子树的长度
4. 根据左子树的长度判断是否能构建左右子树
5. 构建子树时,根据划分出的左右子树范围,移动指针,两组指针始终位于要构建的左右子树的两端,然后递归
6. 根据4个指针是否都指向同一个值作为递归的终止条件