共享内存的本质:
多个进程访问同一个逻辑内存
字节访问内存,不用read()/write()非常方便
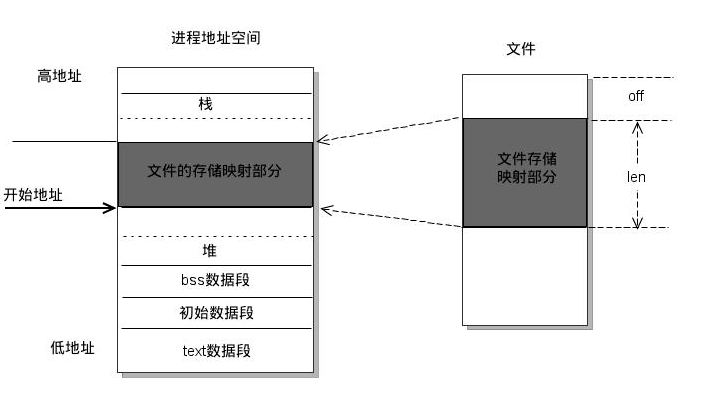
1. POSIX 共享内存
1.1分类
(1)分类
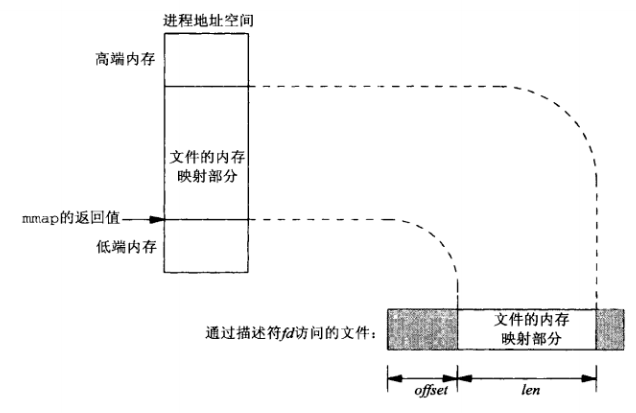
注意:共享内存的大小 = 文件大小
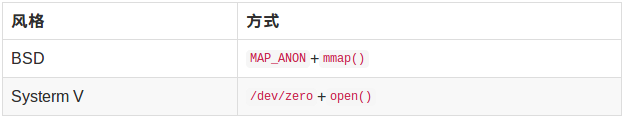
(2)匿名内存映射(亲缘进程)
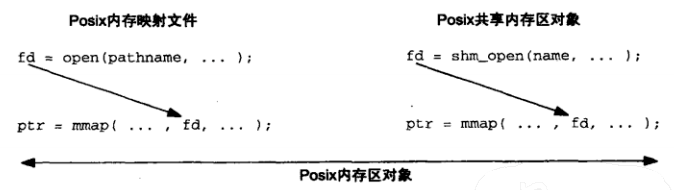
(3)共享内存区对象(非亲缘进程)
1.2 接口
头文件: #include <sys/mman.h>
库: rt
1.3函数
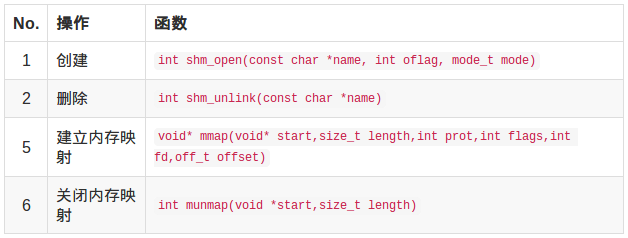
POSIX 共享内存有5个函数。
此外,在使用内存映射文件,经常要用到以下两个文件操作函数。
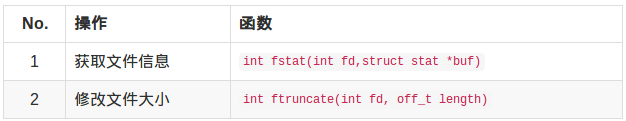
获取文件信息:
int fstat(int fd,struct stat *buf)
参数:
1 fd: 文件描述符 2 buf:struct stat 3 struct stat 4 st_mode: 权限 5 st_size: 大小 6 st_uid: 属性ID 7 st_guid: 组ID
返回值:
出错: -1 成功: 0
实例:
获取共享内存的大小
1 stat(fd, &stat) 2 stat.st_size
【示例】
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <sys/stat.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <iostream> 8 using namespace std; 9 //命令行程序,获取一个文件的大小 10 int main(int argc, char * argv[]) 11 { 12 int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY, 0644);//打开一个文件 13 14 struct stat file_stat; 15 //获取文件信息 16 fstat(fd, &file_stat); 17 18 cout << "file : " << argv[1] << " size : " << file_stat.st_size << endl; 19 20 return 0; 21 }
修改文件大小:
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length)
参数:
fd: 文件描述符
length:文件大小,如果原来的文件大小比参数length大, 超过的部分将会被删除
返回值:
成功: 0 失败: -1
实例:
设置共享内存的大小:
ftruncate(fd,len)
【示例】
命令行程序, 实现对文件的大小缩放
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <sys/types.h> 7 #include <fcntl.h> 8 #include <iostream> 9 using namespace std; 10 11 int main(int argc, char * argv[]) 12 { 13 int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR, 0644);//打开一个文件 14 15 struct stat file_stat; 16 //获取文件信息 17 fstat(fd, &file_stat); 18 cout << "file : " << argv[1] << " size : " << file_stat.st_size << endl; 19 //定义新的文件大小 20 int new_size= atoi(argv[2]); 21 ftruncate(fd, new_size);//更新文件大小 22 fstat(fd, &file_stat); 23 cout << "new size : " << file_stat.st_size << endl; 24 25 return 0; 26 }
问题
- 文件扩大后,新增文件内容是什么?
- 文件缩小后,文件内容是否会被截取?
- 文件大小是否可以变为0?
1.3.1 创建
int shm_open(const char *name, int oflag, mode_t mode)
参数:
name:POSIX IPC名字,格式为/somename
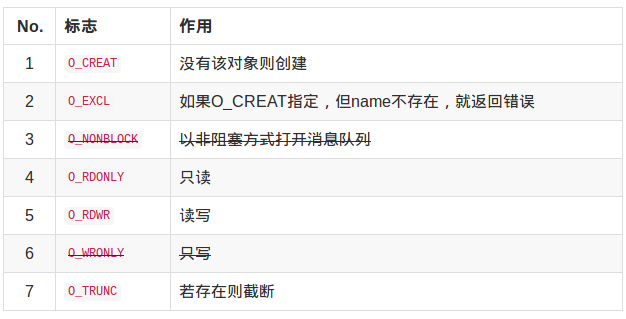
oflag: 标志
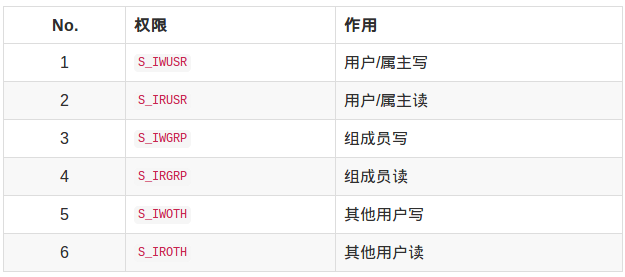
mode:权限
返回值:
出错: -1 共享内存描述符:其他
【示例】
1 //共享内存的创建 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/mman.h> 6 #include <sys/types.h> 7 #include <sys/stat.h> 8 #include <fcntl.h> 9 #include <string.h> 10 #include <iostream> 11 using namespace std; 12 13 int main(int argc, char * argv[]) 14 { 15 int fd = shm_open(argv[1], O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0644); 16 17 ftruncate(fd, atoi(argv[2])); 18 19 void * buf = NULL; 20 if((buf = mmap(NULL, BUFSIZ, PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0)) == MAP_FAILED) 21 { 22 perror("mmap error "); 23 return 1; 24 } 25 return 0; 26 }
1.3.2 删除
int shm_unlink(const char *name)
参数:
name: POSIX IPC名字
返回值:
成功: 0 出错: -1
【示例】
1 //共享内存的删除 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/mman.h> 6 #include <sys/types.h> 7 #include <sys/stat.h> 8 #include <fcntl.h> 9 #include <string.h> 10 #include <iostream> 11 using namespace std; 12 13 int main(int argc, char * argv[]) 14 { 15 shm_unlink(argv[1]); 16 return 0; 17 }
1.3.3 建立内存映射
1 void* mmap(void* start,size_t length,int prot,int flags,int fd,off_t offset)
参数:

内存保护标志:
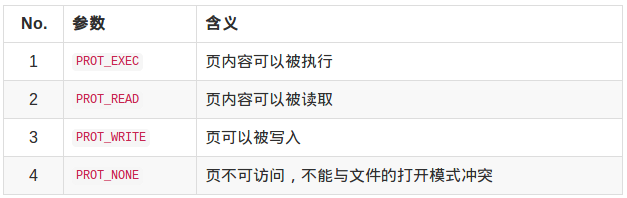
映射对象的类型:
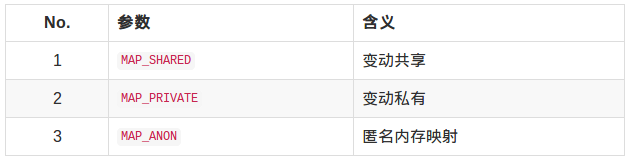
返回值:

【示例】
写共享内存
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <sys/mman.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 #include <iostream> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 int main(int argc, char * argv[]) 13 { 14 int fd = shm_open(argv[1], O_RDWR, 0); 15 void * buf = NULL; 16 17 if((buf = mmap(NULL, BUFSIZ, PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0)) == MAP_FAILED) 18 { 19 perror("mmap error "); 20 return -1; 21 } 22 memcpy(buf, argv[2]); 23 munmap(buf, BUFSIZ); 24 25 return 0; 26 }
读共享内存
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <sys/mman.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 #include <iostream> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 int main(int argc, char * argv[]) 13 { 14 int fd = shm_open(argv[1], O_RDONLY, 0); 15 void * buf = NULL; 16 17 if((buf = mmap(NULL, BUFSIZ, PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0)) == MAP_FAILED) 18 { 19 perror("mmap error "); 20 return -1; 21 } 22 cout << buf << endl; 23 munmap(buf, BUFSIZ); 24 25 return 0; 26 }
1.3.4 关闭内存映射
int munmap(void *start,size_t length)
参数:
start:映射内存起始地址
length:内存大小
返回值:
成功: 0 失败:-1
注意
关闭mmap中的文件描述符不能删除内存映射。
1.4 示例
(1)内存映射文件
创建文件并且写入数据
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <sys/mman.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 #include <iostream> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 int main() 12 { 13 int fd = open("./mmap.txt",O_CREAT|O_RDWR,0644); 14 char str[] = "hello mmap "; 15 ftruncate(fd,sizeof(str));//改变共享内存大小 16 void* buf = NULL; 17 struct stat file_stat; 18 fstat(fd, &file_stat);//获取文件大小信息 19 if(( buf = mmap(NULL,sizeof(str),PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED,fd,0)) == MAP_FAILED) 20 { 21 perror("mmap error "); 22 return 1; 23 } 24 memcpy(buf, str, file_stat.st_size); 25 munmap(buf,sizeof(str));//关闭内存映射 26 close(fd); 27 }
读取数据并且重新写入数据
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <sys/mman.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 #include <iostream> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 13 { 14 int fd = open("./mmap.txt",O_RDWR); 15 void* buf = NULL; 16 struct stat file_stat; 17 fstat(fd, &file_stat); 18 if(( buf = mmap(NULL,BUFSIZ,PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,MAP_SHARED,fd,0)) == MAP_FAILED) 19 { 20 perror("mmap error "); 21 return 1; 22 } 23 cout << buf << endl; 24 memcpy(buf, "this sdfdsfdsfdsfdsfdsfdsfdsfdsfdsf ", file_stat.st_size); 25 munmap(buf,BUFSIZ); 26 close(fd); 27 }
亲缘进程读写数据
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <sys/mman.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 #include <iostream> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 13 { 14 int fd = open("./mmap.txt",O_CREAT|O_RDWR,0644); 15 void* buf = NULL; 16 struct stat file_stat; 17 fstat(fd, &file_stat); 18 if(( buf = mmap(NULL,BUFSIZ,PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED,fd,0)) == MAP_FAILED) 19 { 20 perror("mmap error "); 21 return 1; 22 } 23 if(fork()) 24 { 25 memcpy(buf,argv[1],file_stat.st_size); 26 } 27 else 28 { 29 printf("%s ",buf); 30 } 31 munmap(buf,BUFSIZ); 32 close(fd); 33 }
非亲缘进程读写进程
写
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <sys/mman.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 #include <iostream> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 13 { 14 int fd = open("./mmap.txt",O_CREAT|O_RDWR,0644); 15 void* buf = NULL; 16 struct stat file_stat; 17 fstat(fd, &file_stat); 18 if(( buf = mmap(NULL,BUFSIZ,PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED,fd,0)) == MAP_FAILED) 19 { 20 perror("mmap error "); 21 return 1; 22 } 23 memcpy(buf,argv[1],file_stat.st_size); 24 munmap(buf,BUFSIZ); 25 close(fd); 26 }
读
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <sys/mman.h> 5 #include <fcntl.h> 6 #include <string.h> 7 #include <iostream> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 12 { 13 int fd = open("./mmap.txt",O_CREAT|O_RDWR,0644); 14 void* buf = NULL; 15 if(( buf = mmap(NULL,BUFSIZ,PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED,fd,0)) == MAP_FAILED) 16 { 17 perror("mmap error "); 18 return 1; 19 } 20 cout << buf << endl; 21 munmap(buf,BUFSIZ); 22 close(fd); 23 }
(2)匿名内存映射(亲缘进程)
Systerm V风格
1 //Systerm V风格 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/mman.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 #include <iostream> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 13 { 14 int fd = open("/dev/zero",O_RDWR); 15 void* buf = NULL; 16 struct stat file_stat; 17 fstat(fd, &file_stat); 18 if(( buf = mmap(NULL,BUFSIZ,PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED,fd,0)) == MAP_FAILED) 19 { 20 perror("mmap error "); 21 return 1; 22 } 23 if(fork()) 24 { 25 memcpy(buf,argv[1],file_stat.st_size); 26 } 27 else 28 { 29 printf("%s ",buf); 30 } 31 munmap(buf,BUFSIZ); 32 close(fd); 33 }
BSD风格
1 //BSD风格 2 //Systerm V风格 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <unistd.h> 6 #include <sys/mman.h> 7 #include <fcntl.h> 8 #include <string.h> 9 #include <iostream> 10 11 using namespace std; 12 13 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 14 { 15 int fd = open("/dev/zero",O_RDWR); 16 void* buf = NULL; 17 struct stat file_stat; 18 fstat(fd, &file_stat); 19 if(( buf = mmap(NULL,BUFSIZ,PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED|MAP_ANON,-1,0)) == MAP_FAILED 20 { 21 perror("mmap error "); 22 return 1; 23 } 24 if(fork()) 25 { 26 memcpy(buf,argv[1],file_stat.st_size); 27 } 28 else 29 { 30 printf("%s ",buf); 31 } 32 munmap(buf,BUFSIZ); 33 close(fd); 34 }
非亲缘进程
写
1 //Systerm V风格 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/mman.h> 6 #include <sys/stat.h> 7 #include <fcntl.h> 8 #include <string.h> 9 #include <iostream> 10 11 using namespace std; 12 13 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 14 { 15 int fd = open(argv[1],O_RDWR); 16 void* buf = NULL; 17 struct stat file_stat; 18 fstat(fd, &file_stat); 19 if(( buf = mmap(NULL,BUFSIZ,PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED,fd,0)) == MAP_FAILED) 20 { 21 perror("mmap error "); 22 return 1; 23 } 24 int i; 25 for(i = 2; i < argc; i++) 26 { 27 memcpy(buf, argv[1], file_stat.st_size); 28 sleep(3); 29 } 30 31 munmap(buf,BUFSIZ); 32 close(fd); 33 }
读
1 //Systerm V风格 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/mman.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <string.h> 8 #include <iostream> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 int main(int argc,char* argv[]) 13 { 14 int fd = open(argv[1],O_RDWR); 15 void* buf = NULL; 16 17 if(( buf = mmap(NULL,BUFSIZ,PROT_WRITE|PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED,fd,0)) == MAP_FAILED) 18 { 19 perror("mmap error "); 20 return 1; 21 } 22 sleep(1); 23 for(;;) 24 { 25 cout << buf << endl; 26 sleep(3); 27 } 28 29 munmap(buf,BUFSIZ); 30 close(fd); 31 }
3. 使用mmap容易出现的问题
- 现象:总线错误Bus Error
原因:映射文件的大小为0
解决:使用ftruncate()扩展文件的大小,stat.st_size。 - 现象:段错误
原因:munmap()释放内存的大小大于申请内存大小
解决:释放内存大小与申请内存大小保持一直 - 现象:Permisstion denied
原因:文件打开权限与文件映射对象访问权限不一致。
解决:只读PROT_READ的文件映射对象使用O_RDONLY打开文件;读写PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE的文件映射对象使用O_RDWR打开文件