JZOJ8月10日提高组T2 Fix
题目
Description
There are a few points on a plane, and some are fixed on the plane, some are not. We want to connect these points by some sticks so that all the points are fixed on the plane. Of course, we want to know the minimum length of the sum of the sticks.
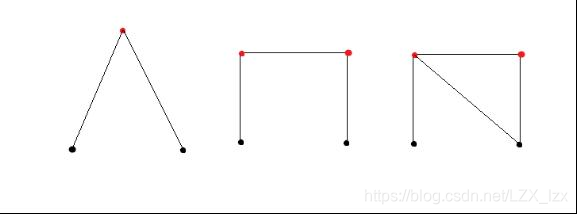
As in the images, the black points are fixed on the plane and red ones are not, which need to be fixed by sticks.
All the points in the left image have been fixed. But the middle one is not, which we need add one stick to fix those four points (the right image shows that stick). Triangle is steady, isn’t it?
Input
The input consists of multiply test cases. The first line of each test case contains one integer, n (1 <= n <= 18), which is the number of points. The next n lines, each line consists of three integers, x, y, c (0 <= x, y < 100). (x, y) indicate the coordinate of one point; c = 1 indicates this point is fixed; c = 0 indicates this point is not fixed. You can assume that no two points have the same coordinate.
The last test case is followed by a line containing one zero, which means the end of the input.
Output
Output the minimum length with six factional digits for each test case in a single line. If you cannot fix all the points, then output “No Solution”.
Sample Input
4
0 0 1
1 0 1
0 1 0
1 1 0
3
0 0 1
1 1 0
2 2 0
0
Sample Output
4.414214
No Solution
Hint
大概意思就是给你一些点,其中一些点是固定的,然后还有一些没有固定的,然后问你固定所有点所用的线段的最小长度是多少。
所谓固定,就是形如三角形的情况,就是两个固定的点向一个未固定的点连两条边,就能把未固定的点固定。
题解
题意
给出(n)个点,其中一些点是固定的,然后还有一些没有固定的,问固定所有点所用的线段的最小长度是多少。
定义固定:两个固定的点向一个未固定的点连两条边,就能把未固定的点固定。
分析
可以想到状压(DP)来维护状态
如果枚举状态、固定点和连线点的话,将会是(O(2^n*n^3))
思考优化
既然要答案优,就要使得连线点更加靠经固定点
那么排序后扫一遍就可以了
优化至(O(2^n*n^2))
Code
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#define inf 2147483646.9
using namespace std;
int n,now,fix,op,i,j,k,num,er[20];
double l,f[500005];
struct node1
{
int x,y;
}a[20];
struct node
{
double val;
int id;
}dis[20][20];
double sqr(int x)
{
return 1.0*x*x;
}
bool cmp(node x,node y)
{
return x.val<y.val;
}
int main()
{
while (true)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
if (n==0) break;
now=0;
fix=0;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y,&op);
if (op==1)
{
fix++;
now+=(1<<(i-1));
}
}
if (fix==n)
{
printf("0.000000
");
continue;
}
if (fix<2)
{
printf("No Solution
");
continue;
}
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for (j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
dis[i][j].val=sqrt(sqr(a[i].x-a[j].x)+sqr(a[i].y-a[j].y));
dis[i][j].id=j;
}
sort(dis[i]+1,dis[i]+n+1,cmp);
}
for (i=0;i<=n;i++)
er[i]=1<<i;
for (i=1;i<=(1<<n);i++)
f[i]=inf;
f[now]=0;
for (i=now;i<(1<<n);i++)
{
if (f[i]!=inf)
for (j=1;j<=n;j++)
if ((i&(1<<(j-1)))==0)
{
num=0;
l=0;
for (k=1;k<=n;k++)
if ((i&(1<<(dis[j][k].id-1)))!=0)
{
num++;
l+=dis[j][k].val;
if(num==2)
{
f[i+(1<<(j-1))]=min(f[i+(1<<(j-1))],f[i]+l);
break;
}
}
}
}
printf("%.6f
",f[(1<<n)-1]);
}
return 0;
}