摘自:https://blog.csdn.net/xuancbm/article/details/81436681
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/hazir/p/instruction_to_readline.html
参考:https://tiswww.case.edu/php/chet/readline/rltop.html
readline库的简单使用
这周要实现一个简单的 shell, 平时使用bash, zsh这些shell的时候, 如果文件名或命令太长,又或者要频繁执行几条命令的话,最常用的应该就是tab键补全和上下键切换历史命令了。
想要在自己的shell里面实现这两个功能很困难,但有一个C语言库集成了这些功能,只需要调用几个函数就可以实现这两个功能。
可以在这里找到有关 readline 库的相关资料和下载地址,软件包里面也提供了很多手册和示例。
实现shell用到的函数不是很多,tab键补全,上下键切换历史命令,添加历史命令等等
readline()
在 readline.h 里可以找到关于他的定义:
1 /* Readline functions. */ 2 /* Read a line of input. Prompt with PROMPT. A NULL PROMPT means none. */ 3 extern char *readline PARAMS((const char *));
readline() 的参数是一个字符串,调用函数的时候会在屏幕上输出,这个函数会读取一行输入,然后返回一个指向输入字符串的指针,readline 会为输入的字符串动态分配内存,所以使用完之后需要free掉。
下面举一个简单的例子
1 #include <stdlib.h> 2 #include <readline/readline.h> 3 4 int main(void) 5 { 6 while (1) 7 { 8 char * str = readline("Myshell $ "); 9 free(str); 10 } 11 }
由于readline是一个动态库,编译的时候需要加上 -lreadline,不然会找不到相关的函数
当我们按下tab键之后发现就可以实现bash里面的补全功能了。

用惯了zsh后发现黑白的提示符好难看,于是也想着给里面的参数加上颜色。C语言中输出有颜色的字符printf就可以实现,模板类似这样 printf("�33[47;31m string �33[0m");
47是背景色,31是字符的颜色,string 是要输出的字符串,�33[5m是ANSI控制码,意思是关闭输出的属性,不然以后的输出都会是之前设置的颜色。相关的内容网上有很多可以自行查阅。
为了方便使用,加上了这些宏定义
1 #define CLOSE "�33[0m" // 关闭所有属性 2 #define BLOD "�33[1m" // 强调、加粗、高亮 3 #define BEGIN(x,y) "�33["#x";"#y"m" // x: 背景,y: 前景
在修改一下readline()这个函数
char * str = readline(BEGIN(49, 34)"Myshell $ "CLOSE);
然后编译运行:

似乎一切完美,但当我们输入很长很长的字符串之后:

emmmm……………输入太多会导致提示符被输入覆盖,写个shell出现这种状况岂不是贼尴尬
查资料查了很久才找到解决方法:
这个bug需要在非打印字符前后加上 �01 和 �02 才能解决
其实头文件就有提到
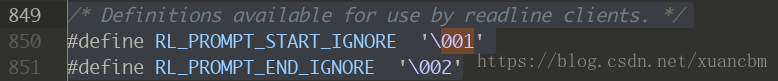
在之前定义的宏里面加上这两个字符之后终于解决了
最后的代码为:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <readline/readline.h> 4 5 #define CLOSE "�01�33[0m�02" // 关闭所有属性 6 #define BLOD "�01�33[1m�02" // 强调、加粗、高亮 7 #define BEGIN(x,y) "�01�33["#x";"#y"m�02" // x: 背景,y: 前景 8 9 int main(void) 10 { 11 while (1) 12 { 13 char * str = readline(BEGIN(49, 34)"Myshell $ "CLOSE); 14 free(str); 15 } 16 }
readline使用的时候默认了tab补全,但是我们平时用到的shell不但可以补全文件名,还可以补全命令。readline库当然也提供了这个功能,具体如何使用可以看这篇博客。
单独的使用readline()并没有上下键切换补全的功能,实现这个需要用到另一个函数 - add_history()
history.h
上下键切换需要我们把输入的字符串加入到历史命令中,需要调用
/* Place STRING at the end of the history list. The associated data field (if any) is set to NULL. */ extern void add_history PARAMS((const char *));
函数接受一个字符串作为参数存入到历史文件中,函数的定义在history.h中,使用的时候需要包含头文件
char * str = readline(BEGIN(49, 34)"Myshell $ "CLOSE); add_history(str); free(str);
编译后测试了一下发现功能完美运行。
但是关掉程序在尝试一下发现,诶?我不能切换到上一次运行程序的历史命令,只能记录本次运行中输入的命令。然后开始查看头文件的内容,发现了不少和history有关的函数。
其中有两个正好用的上
1 /* Add the contents of FILENAME to the history list, a line at a time. 2 If FILENAME is NULL, then read from ~/.history. Returns 0 if 3 successful, or errno if not. */ 4 extern int read_history PARAMS((const char *)); 5 /* Write the current history to FILENAME. If FILENAME is NULL, 6 then write the history list to ~/.history. Values returned 7 are as in read_history (). */ 8 extern int write_history PARAMS((const char *));
read_history() 和 write_history() 都接受一个字符串做参数,成功返回0,错误则把相应的错误码赋值给errno。
两个函数接受的参数都是一个文件名,read_history() 从指定的文件中读取历史记录,write_history() 将历史记录存入指定的文件。如果参数为NULL默认的文件是:~/.history
有了这个函数,我们只要在程序最开处加上read_history(NULL), add_history(str)之后加上 write_history() 就可以了。
这样下次运行程序的时候我们就可以找到上次运行的历史命令了。
shell 的内置命令不多,cd 是一个, history也是一个shell内置的命令。
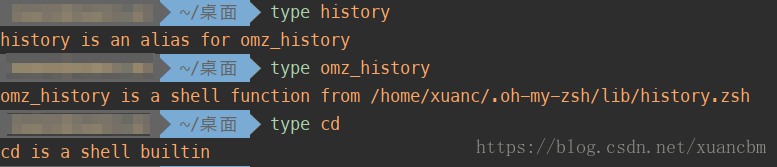
readline既然可以把输入加入历史,读入和写进历史,那么自然可以读取历史文件列表,头文件中我们可以找到这样一个函数:
/* Return a NULL terminated array of HIST_ENTRY which is the current input history. Element 0 of this list is the beginning of time. If there is no history, return NULL. */ extern HIST_ENTRY **history_list PARAMS((void));
这个函数可以查看存储的 history 列表,HIST_ENTRY 是一个结构体类型,存储了很多信息:
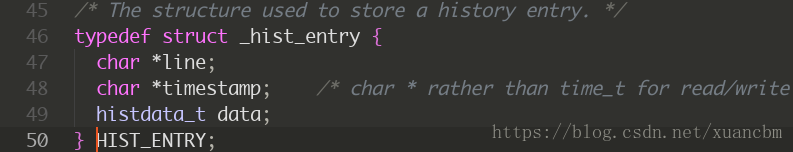
我们要的历史内容就存储在 data 元素里面。
这个函数返回一个数组,以空指针为结束标志,我们简单封装一下就可以实现一个自己 shell 内置的 history 函数了。
1 void ShowHistory() 2 { 3 int i = 0; 4 HIST_ENTRY **his; 5 his = history_list(); 6 while (his[i] != NULL) 7 { 8 printf("%s ", his[i]->line); 9 i++; 10 } 11 }
history.h 里面提供了很多函数,我们的要实现一个简单的shell用到的函数上面都提到过,更多的函数可以在官方文档里面查看。
realine 这个库很强大,现在只是发现了他的冰山一角,提供的功能远远超过上述所说的。