摘自: https://www.cnblogs.com/zhuifeng-mayi/p/10535311.html
数据库操作
1、开启数据库
net start mysql
2、登录数据库
mysql -u用户名 -p密码
mysql -hIP地址 -P端口 -u用户名 -p
3、创建数据库
create database 数据库名称
create database 数据库名 charset=utf8; CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS dingtalkrobot DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8;
4、查看数据库,列出所有数据库的名字
show databases;
5、进入数据库
use 数据库的名字;
5、查看当前在哪个数据库中。
SELECT DATABASE();
6、修改数据库编码
alter database 数据库名称 default character set 编码方式 collate 编码方式_bin ;
7、删除数据库
drop database 数据库名称;
8、查看版本
SELECT VERSION();
9、显示当前时间:
select now();
10、查看编码
show variables like 'character%';
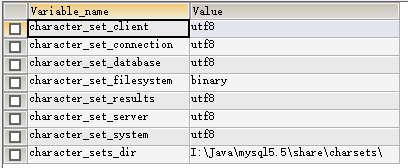
character_set_client为客户端编码方式;
character_set_connection为建立连接使用的编码;
character_set_database数据库的编码;
character_set_results结果集的编码;
character_set_server数据库服务器的编码;
只要保证以上四个采用的编码方式一样,就不会出现乱码问题。
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'collation%';

11、备份与恢复
备份
mysqldump –uroot –p 数据库名 > .备份文件.sql;
按提示输入mysql的密码
恢复
连接mysql,创建数据库 退出连接,执行如下命令 mysql -uroot –p 数据库名 < .备份文件.sql 根据提示输入mysql密码
数据库的基本表操作
8、显示所有表名
show tables;
8、创建表
create table 表名
{
字段名 1,数据类型[完整性约束条件],
字段名 2,数据类型[完整性约束条件],
...
字段名 n,数据类型[完整性约束条件],
}
例:创建学生表,字段要求如下:姓名(长度为10),年龄、身高(要求保留两位小数)
create table student2( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment, name varchar(10), age int unsigned, height decimal(5,2) )
CREATE TABLE news( id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL, username VARCHAR(100), PASSWORD VARCHAR(100), gender BIT(1) );
9、查看表结构
desc 表名字 ;

SHOW CREATE TABLE news; 显示如下: CREATE TABLE `news` ( `id` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL, `PASSWORD` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL, `gender` BIT(1) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
10、删除表
方式一: drop table 表名; 方式二: drop table if exists 表名;
10、修改表名称
rename table 原表名 to 新表名;
10、修改表(增加、删除、修改字段)
alter table 表名 add|change|drop 列名 类型;
如:ALTER TABLE news ADD isDelete BIT DEFAULT 0;
11、增加数据
添加一行数据
格式一:所有字段设置值,值的顺序与表中字段的顺序对应
说明:主键列是自动增长,插入时需要占位,通常使用0或者default或者null来占位,插入成功后以实际数据为准
insert into 表名 value(...)
例:
insert into student2 values(0,“亚瑟”,27,178.9)
若指向name里插入数据
insert into 表名(列) values(...)
例:
insert into student2(name) valuse("亚瑟2")
添加多行数据
insert into 表名(列1、列2、列3) values(...),(...),(...)
12、修改数据
update 表名 set 列1=值1,列2=值2...where 条件 例:修改id为5的学生数据,姓名改为狄仁杰,年龄改为20 update student2 set age=20,name="狄仁杰" where id=5
13、删除数据
delete from 表名 where 条件 例:删除id为6的学生数据 delete from student2 where id = 6
逻辑删除 1、设计表,给表添加一个字段isdelete,1代表删除,0代表没有删除 2、把所有的数据iadelete都改为0 3、删除某一条数据时,更新他的isdelete为1 4、当要查询数据时,只查询isdelete为0的数据
14、查询数据
创建数据表
create table students( studentNo varchar(100) primary key, name varchar(100), sex varchar(100), hometown varchar(100), age tinyint(4), class varchar(100), card varchar(100) )
准备数据
insert into students values
('001','王昭君','女','北京','20','1班','3403122123402120'),
('002','诸葛亮','男','上海','18','2班','3403122123402120'),
('003','张飞','男','南京','24','3班','3403122123402120'),
('004','白起','男','安徽','22','4班','3403122123402120'),
('005','大乔','女','天津','19','3班','3403122123402120'),
('006','孙尚香','女','河北','18','1班','3403122123402120'),
('007','百里玄策','男','山西','20','2班','3403122123402120'),
('008','小乔','女','河南','15','3班','3403122123402120')
查询所有字段 select * from 表名; 查询指定字段 在select后面的列名部分,可以使用as为列起别名,这个别名出现在结果集中 select 列1,列2,,列3... from 表名; 表名、字段名 select students.name,students.age from students 可以通过as给表起别名 select s.name,s.age from students as s 例:查询学生姓名有哪几种? select sex from students
条件查询
使用where子句对表中的数据筛选,符号条件的数据会出现在结果集中 select 字段1、字段2、字段3... from 表名 where 条件; 例: select * from students where id = 1;
where后面支持多种运算符,进行条件的处理
。比较运算
。逻辑运算
。模糊查询
。范围查询
。空判断
比较运算符
等于:=
大于:>
大于等于:>=
小于:<
小于等于:<=
不等于:!= 或 < >
例1:查询小乔的年龄 select age from students where name="小乔” 例2:查:20岁以下的学生 select * from students where age<20 例3:查询家乡不在北京的学生 select *from students where hoetown!="北京"
逻辑运算符
and
or
not
例1:查询年龄小于20的女同学 select * from students where age<20 and sex="女" 例2:查询女学生或1班的学生 select * from students where sex="女" or class="1班" 例3:查询非天津的学生 select * from students where not hometown="天津"
模糊查询
like
%表示任意多个任意字符
_表示一个任意字符
例1:查询姓孙的学生 select * from students where name like "孙%" 例2:查询姓孙且名字是一个字的学生 select * from students where name like "孙_" 例3:查询叫乔的学生 select * from students where name like "%孙" 例4:查询姓名含白的学生 select * from students where name like "%白%"
范围查询
in表示在一个非连续的范围内
where 表示 在一个连续的范围内
例1、查询家乡是北京或上海或广东的学生
select * from students where in("北京"、"上海"、"广东")
例2、查询年龄为18至20的学生
select * from students where age between 18 and 20
空判断
注意: null与""是不同的
判空is null
例1:查询没有填写身份证的学生 select * from students where card is null
判非空is not null
例2:查询填写了身份证的学生 select * from students where is not null
排序
为了方便查看数据,可以对数据进行排序
select * from 表名 order by 列1 asc|desc,列2 asc|desc...
将行数据按照列1进行排序,如果某些行列1的值相同时,则按照列2排序,以此类推
默认按照列值从小到大排列
asc从小到大排列,即升序
desc从大到小排序,即降序
例1:查询所有学生信息,按年龄从小到大排序 select * from students order by age 例2:查询所有学生信息,按年龄从大到小排序,年龄相同时,再按学号从小到大排序 select * from students order by age desc,studentNo
注:order by要写在where的后面
例:SELECT * FROM news WHERE id IN(1,3) ORDER BY id DESC;
聚合函数
为了快速得到统计数据,经常会用到如下5个聚合函数
聚合函数不能在where中使用
- count(*)表示计算总行数,括号中写星与列名,结果是相同的
- max(列)表示求此列的最大值
- min(列)表示求此列的最小值
- sum(列)表示求此列的和
- avg(列)表示求此列的平均值
例1:查询学生总数 select count(*) from students 例2:查询女生的最大年龄 select max(age) from students where sex = "女" 例3:查询1班的最小年龄 select min(age) from students where class = "1班" sum(列)表示求此列的和 例4:查询北京学生的年龄和 select sum(age) from students where hometown="北京" avg(列)表示求此列的平均值 例5:查询女生的平均年龄 select avg(age) from students where sex = "女"
分组
按照字段分组,表示此字段相同的数据会被放到一个组中
分组后,分组的依据列会显示在结果集中,其他列不会显示在结果集中
可以对分组后的数据进行统计,做聚合运算
select 列1,列2,聚合... from 表名group by 列1,2... 例1:查询各种性别的人数 select sex,count(*) from students group by sex 例2:查询各种年龄的人数 select age,count(*) from students group by age 例3:查询各个班各有多少男生女生 select class,sex,count(*) from students group by class,sex
分组后的数据筛选
select列1,列2,聚合...from表名 group by列1,列2,列3....having列1...聚合.. 例1:查询男生总人数 方案一: select count(*) from students where sex="男" 方案二: select sex,count(*) from students group by sex having sex="男" 例2:查询1班除外其他班级学生的平均年龄、最大年龄、最小年龄 select class,min(age),max(age),avg(age) from students group by class having class!="1班"
对比where与having
where是对from后面指定的表进行数据筛选,属于对原始数据的筛选
having是对group by的结果进行筛选
获取部分行
当数据量过大时,在一页中查看数据是一件非常麻烦的事情
select * from 表名 limit start(开始),count 从start开始,获取count条数据 start索引从0开始 例1:查询前3行学生信息 select * from students limit 0,3 例2:查询第4到第6行学生信息 select * from students limit 3,3
分页
- 当数据量过大时,在一页中查看数据是一件非常麻烦的事情
- 语法
select * from 表名 limit start,count
- 从start开始,获取count条数据
- start索引从0开始
示例:分页
- 已知:每页显示m条数据,当前显示第n页
- 求总页数:此段逻辑后面会在python中实现
- 查询总条数p1
- 使用p1除以m得到p2
- 如果整除则p2为总数页
- 如果不整除则p2+1为总页数
- 求第n页的数据
已知:每页显示m条数据,求:显示第n页的数据
select * from students where isdelete = 0 limit (n-1)*m,m
去重
distinct 去重,去掉重复的字段 语法: select distinct 列1,列2 from 表1 where .... 例:用一条SQL语句查询出每门课都大于80分的学生姓名 create table score( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), subject varchar(20), score int); insert into score values (null,'张三','语文',81), (null,'张三','数学',75), (null,'李四','语文',76), (null,'李四','数学',90), (null,'王五','语文',81), (null,'王五','数学',100), (null,'王五 ','英语',90); 答案: select distinct name from score where name not in (select distinct name from score where score<=80)
总结
- 完整的select语句
select distinct * from 表名 where .... group by ... having ... order by ...asc|desc 分组的目的是为了聚合,为了使用5个聚合函数 limit start,count
- 执行顺序为:
- from 表名
- where ....
- group by ...
- select distinct *
- having ...
- order by ...
- limit star,count
- 实际使用中,只是语句中某些部分的组合,而不是全部
高级
1、关系
- 创建成绩表scores,结构如下
- id
- 学生
- 科目
- 成绩
- 思考:学生列应该存什么信息呢?
- 答:学生列的数据不是在这里新建的,而应该从学生表引用过来,关系也是一条数据;根据范式要求应该存储学生的编号,而不是学生的姓名等其它信息。同理,科目表也是关系列,引用科目表中的数据

- 创建表的语句如下
create table scores( id int primary key auto_increment, stuid int, subid int, score decimal(5,2) );
外键
- 思考:怎么保证关系列数据的有效性呢?任何整数都可以吗?
- 答:必须是学生表中id列存在的数据,可以通过外键约束进行数据的有效性验证
为stuid添加外键约束
alter table scores add constraint stu_sco foreign key(stuid) references students(id);
此时插入或者修改数据时,如果stuid的值在students表中不存在则会报错
在创建表时可以直接创建约束
create table scores( id int primary key auto_increment, stuid int, subid int, score decimal(5,2), foreign key(stuid) references students(id), foreign key(subid) references subjects(id) );
外键的级联操作
- 在删除students表的数据时,如果这个id值在scores中已经存在,则会抛异常
- 推荐使用逻辑删除,还可以解决这个问题
- 可以创建表时指定级联操作,也可以在创建表后再修改外键的级联操作
语法
alter table scores add constraint stu_sco foreign key(stuid) references students(id) on delete cascade;
- 级联操作的类型包括:
- restrict(限制):默认值,抛异常
- cascade(级联):如果主表的记录删掉,则从表中相关联的记录都将被删除
- set null:将外键设置为空
- no action:什么都不做
2、连接查询
先看个问题
- 问:查询每个学生每个科目的分数
- 分析:学生姓名来源于students表,科目名称来源于subjects,分数来源于scores表,怎么将3个表放到一起查询,并将结果显示在同一个结果集中呢?
- 答:当查询结果来源于多张表时,需要使用连接查询
- 关键:找到表间的关系,当前的关系是
- students表的id---scores表的stuid
- subjects表的id---scores表的subid
- 则上面问题的答案是:
select students.sname,subjects.stitle,scores.score
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
inner join subjects on scores.subid=subjects.id;
- 结论:当需要对有关系的多张表进行查询时,需要使用连接join
连接查询
- 连接查询分类如下:
- 表A inner join 表B:表A与表B匹配的行会出现在结果中
- 表A left join 表B:表A与表B匹配的行会出现在结果中,外加表A中独有的数据,未对应的数据使用null填充
- 表A right join 表B:表A与表B匹配的行会出现在结果中,外加表B中独有的数据,未对应的数据使用null填充
- 在查询或条件中推荐使用“表名.列名”的语法
- 如果多个表中列名不重复可以省略“表名.”部分
- 如果表的名称太长,可以在表名后面使用' as 简写名'或' 简写名',为表起个临时的简写名称
练习
- 查询学生的姓名、平均分
select students.sname,avg(scores.score)
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
group by students.sname;
- 查询男生的姓名、总分
select students.sname,avg(scores.score)
from scores
inner join students on scores.stuid=students.id
where students.gender=1
group by students.sname;
- 查询科目的名称、平均分
select subjects.stitle,avg(scores.score)
from scores
inner join subjects on scores.subid=subjects.id
group by subjects.stitle;
- 查询未删除科目的名称、最高分、平均分
select subjects.stitle,avg(scores.score),max(scores.score)
from scores
inner join subjects on scores.subid=subjects.id
where subjects.isdelete=0
group by subjects.stitle;连接查询
当查询结果的列来源于多张表时,需要将多张表连接成一个大的数据集,再选择合适的列返回
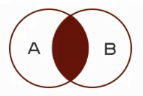
等值连接查询:查询的结果为两个表匹配到的数据
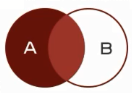
左连接查询:查询的结果为两个表匹配到的数据加左表特有的数据,对于右表中不存在的数据使用null填充
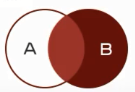
右连接查询:查询的结果为两个表匹配到的数据加右表特有的致据,对于左表中不存在的数据使用null填充
准备数据
drop table if exists courses; create table courses( courseNo int(10) unsigned primary key auto_increment, name varchar(10) )
insert into courses values
('1','数据库'),
('2','qtp'),
('3','linux'),
('4','系统测试'),
('5','单元测试'),
('6','测试过程')
drop table if exists scores; create table scares ( id int(10) unsigned primary key auto_increment, courseNo int (10), studentNo varchar(10), score tinyint(4). )
insert into scores values
('1','1','001','90'),
('2','1','002','75'),
('3','2','002','93'),
('4','3','001','86'),
('5','3','003','76'),
('6','4','004','70'),
('7','5','005','86'),
('8','6','006','97'),
等值连接
方式一 select * from 表1,表2 where 表1.列 = 表2.列 方式二(又称内连接) select *from 表1 inner join 表2 on 表1.列 = 表2.列 例1:查询学生信息及学生的成绩 select * from student as stu,scores as sc where stu.studentNo = sc.studentNo select *from student as stu inner join scores as sc on stu.studentNo = sc.studentNo 例2:查询课程信息及课程的成绩 select *from courses as cs,scores as sc where cs.courseNo=sc.courseNo select *from courses as cs inner join scores as sc on cs.courseNo = sc.courseNo 例3:查询学生生信息及学生课程对应的成绩 select *from students,courses,scores where students.studentNo = scores.courseNo and scores.courseNo = courses.courseNo select * from students inner join scores on students.studentNo = scores.studentNo inner join courses on scores.courseNo = courses.courseNo 例4:查询王昭君的成绩,要求显示姓名、课程号、成绩 select students.name,courses.courseNo,scores.score from students where students.studentNo = scores.studentNo and students.name = "王昭君" select students.name,courses.courseNo,scores.score from students
inner join scores on studnets.studentNo = scores.studnetNo inner join courses on scores.courseNo = courses.courseNo and students.name = "王昭君"
使用内连接不会产生笛卡尔积、不会产生内联表
例5:查询王昭君的数据库成绩,要求显示姓名、课程名、成绩 select students.name,courses.name,scores.score from students,courses,scores where students.studentNo = scores.studentNo and scores.courseNo =courses.courseNo and students.name = "王昭君" and courses.name = "数据库" select students.name,courses.name,scores.score from students,courses,scores
inner join scores on scores.courseNo = courses.courseNo inner join students on students.studentNo = scores.studentno where students.name = "王昭君" and courses.name = "数据库"
例6:登询所有学生的数据库成绩,要求显示姓名、课程名、成绩
select students.name,courses.name,scores.score from students,courses,scores
inner join scores on scores.courseNo = courses.courseNo
inner join students on students.studentNo = scores.studentno where courses.name = "数据库"
例7:查询男生中最高成绩,要求显示姓名、课程名、成绩 select students.name,courses.name,scores.score from students,courses,scores
inner join scores on scores.courseNo = courses.courseNo
inner join students on students.studentNo = scores.studentno where sex = "男" order by score desc limit 1
左连接
select * from 表1 left join 表2 on 表1.列=表2.列 join前边的表称为左表 例1:查询所有学生的成绩,包括没有成绩的学生 select scores.score from students left join scores on students.studengNo = scores.studentNo 例2:查询所有学生的成绩,包括没有成绩的学生,需要显示课程名 select scores.score,courses.name from students left join scores on students.studengNo = scores.studentNo left join courses on coursrs.courseNo = scores.coursrNo
右连接
select * from 表1 right join 表2 on 表1.列=表2.列 添加两门课程 insert into courses values (0,'语文'), (0,'数学') 例1:查询所有课程的成绩,包括没有成绩的课程 select * from scores right join courses on scores.courseNo=courses.courseNo 例2:查询所有课程的成绩,包括没有成绩的课程,包括学生信息 select * from scores right join courses on scores.courseNo=courses.courseNo left join student on students.studetNo= scores.scoreNo
3、自关联
设计省信息的表结构provinces
id
ptitle
设计市信息的表结构citys
id
ctitle
proid
citys表的proid表示城市所属的省,对应着provinces表的id值
问题:能不能将两个表合成一张表呢?
思考:观察两张表发现, citys表比provinces表多一个列proid,其它列的类型都是一样的
意义:存储的都是地区信息,而且每种信息的数据量有限,没必要增加一个新表,或者将来还要存储区、乡镇信息,都增加新表的开销太大
答案:定义表areas,结构如下
id
atitle
pid
因为省没有所属的省份,所以可以填写为null
城市所属的省份pid,填写省所对应的编号id
这就是自关联,表中的某一列,关联了这个表中的另外一列,但是它们的业务逻辑含义是不一样的,城市信息的pid引用的是省信息的id
在这个表中,结构不变,可以添加区县、乡销街道、村社区等信息
使用自关联前提:
1、多个表的表结构十分相似
2、业务逻辑十分相近
create table areas(
aid int primary key,
atitle varchar (28).
pid int
)
insert into areas values
('130000','河北省',NULL),
('130100','石家庄市',130000),
('130400','邯郸市',130000),
('130600','保定市',130000),
('130700','张家口市',130000),
('130800','承德市',130000),
('410000','河南省',NULL),
('410100','郑州市',410000),
('410300','洛阳市',410000),
('410500','安阳市',410000),
('410700','新乡市',410000),
('410800','焦作市',410000)
例1:查询河南省所有的城市 数据从一个表中取多次,必须取别名 select * from areas as sheng,areas as shi where sheng.aid=shi.pid and sheng.atitle = '河南省'
添加区县数据
insert into areas values
('410101','中原区','410100'),
('410102','二七区','410100'),
('410103','金水区','410100')
例2:查询郑州市的所有区县 select * from areas as sheng,areas as shi where sheng.aid = shi.pid and sheng.atitle = '郑州市' 例3:查询河南省的所有区县 select * from areas as sheng,areas as shi,areas as qu where sheng.aid = shi.pid and sheng.atitle = '河南省' and shi.aid = qu.pid
CREATE TABLE booktest_areas( id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL, aname VARCHAR(20), pid INT UNSIGNED, FOREIGN KEY(pid) REFERENCES booktest_areas(id) ); mysql -uroot -p USE mydatabase;
--导入sql文件 source D:\python\python_学习笔记\python_stu\04数据库\01mysql\areas.sql; --统计所有记录 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM booktest_areas; --列出所有省的名字 SELECT * FROM booktest_areas WHERE pid IS NULL; --列出河南省的所有市 SELECT shi.aname FROM booktest_areas AS sheng,booktest_areas AS shi WHERE shi.pid = sheng.id AND sheng.aname='河南省';
SELECT shi.aname FROM booktest_areas AS sheng INNER JOIN booktest_areas AS shi ON shi.pid = sheng.id AND sheng.aname='河南省';
--列出广州市的所有区县 SELECT shi.aname FROM booktest_areas AS sheng,booktest_areas AS shi WHERE shi.pid = sheng.id AND sheng.aname='广州市';
子查询
在一个select语句中,嵌入了另外一个select语句,那么被嵌入的select语句称之为子查询语句
主查询
主要查询的对象,第一条select语句
主查询和子查询的关系
子查询是嵌入到主查询中,
子查询是辅助主查询的,要么充当条件,要么充当数据源
子查询是可以独立存在的语句,是一条完整的select语句
子查询分类
标量子查询:子查询返回的结果是一个数据(一行一列)
列子查询:返回的结果是一列(一列多行)
行子查询:返回的结果是一行(一行多列)
表级子查询:返回的结果是多行多列
标量子查询
例1:查询班级学生的平均年龄
查询班级学生平均年龄
select avg(age) from students
查询大于平均年龄的学生
select * from students where age > 21.4167
select * from students where age > (select avg(age) from students);
例2:查询王昭君的成绩,要求显示成绩
select score from scores where studentNo=(select studentNo from students where name = '王昭君')
列级子查询
例3:查询18岁的学生的成绩,要求显示成绩
学生表中查询18岁的学生的学号
select studentNo from students where age=18
成绩表中根据学号查询成绩
select * from scores where studentNo in ('002','006'.)
select * from scores where studentNo in (select studentNo from students where age=18)
行级子查询
例4:查询男生中年龄最大的学生信息
select * from students where sex='男'
select * from students where (sex,age)=('男',30)
select * from students where (sex,age) =(select sex,age from students where sex='男' order by age desc limit 1
表级子查询
例5:查询数据库和系统测试的课程成绩
select * from scores
inner join
(select * from courses where name in ('数据库',‘系统测试’)) as c on scores.courseNo= c.courseNo
子查询中特定关键字使用
in 范围
格式:主查询where条件in(列子查询)
any | some任意一个
格式:主查询where列=any (列子查询)
在条件查询的结果中匹配任意一个即可,等价于in
all
格式:主查询where列=all(列子查询):等于里面所有
格式:主查询where列<>all(列子查询):不等一其中所有
select * from students where age in (select age from students where age between 18 and 20)
