栈的定义
* 栈仅能在线性表的一端进行操作
栈顶(Top) : 允许操作的一端
栈底(Bottom) :不允许操作的一端
栈的性质
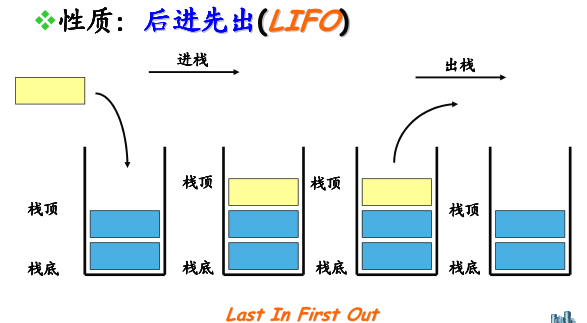
栈的操作
# 栈的一些常用操作
* 创建栈
* 销毁栈
* 清空栈
* 进栈
* 出栈
* 获取栈顶元素
* 获取栈的大小
栈的顺序存储实现
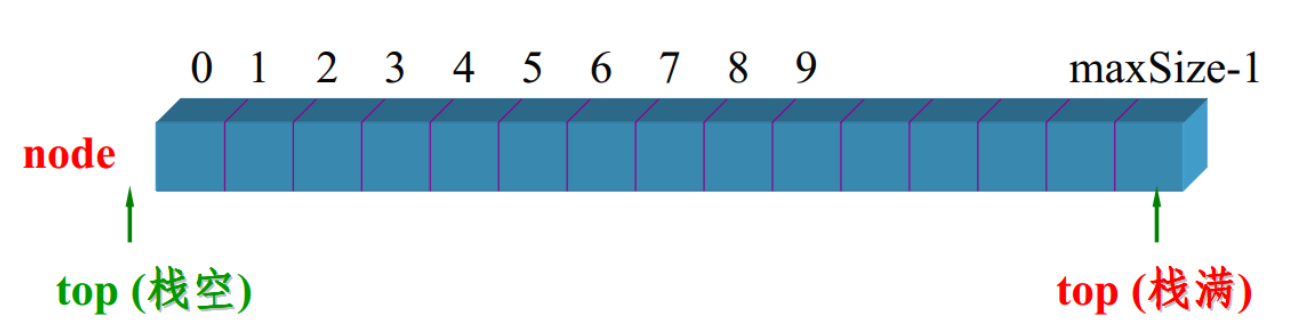
下面的顺序栈是不能支持结构体的!
现在我们先来实现顺序栈,由于之前我们实现了顺序表,现在代码复用,用其来实现顺序栈
SeqStack.h

#ifndef _SEQSTACK_H_ #define _SEQSTACK_H_ typedef void SeqStack; SeqStack* SeqStack_Create(int capacity); void SeqStack_Destroy(SeqStack* stack); void SeqStack_Clear(SeqStack* stack); int SeqStack_Push(SeqStack* stack, void* item); void* SeqStack_Pop(SeqStack* stack); void* SeqStack_Top(SeqStack* stack); int SeqStack_Size(SeqStack* stack); int SeqStack_Capacity(SeqStack* stack); #endif
SeqStack.c

#include "SeqStack.h" #include "SeqList.h" SeqStack* SeqStack_Create(int capacity) { return SeqList_Create(capacity); } void SeqStack_Destroy(SeqStack* stack) { SeqList_Destroy(stack); } void SeqStack_Clear(SeqStack* stack) { SeqList_Clear(stack); } int SeqStack_Push(SeqStack* stack, void* item) { return SeqList_Insert(stack, item, SeqList_Length(stack)); //压栈一般由尾部压栈 } void* SeqStack_Pop(SeqStack* stack) { return SeqList_Delete(stack, SeqList_Length(stack) - 1); //最后一个元素出栈 } void* SeqStack_Top(SeqStack* stack) { return SeqList_Get(stack, SeqList_Length(stack) - 1); //获取栈顶元素 } int SeqStack_Size(SeqStack* stack) { return SeqList_Length(stack); } int SeqStack_Capacity(SeqStack* stack) { return SeqList_Capacity(stack); }
复用之前的代码
SeqList.c

#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> #include "SeqList.h" typedef unsigned int TSeqListNode; typedef struct _tag_SeqList { int capacity; int length; TSeqListNode* node; } TSeqList; SeqList* SeqList_Create(int capacity) // O(1) { TSeqList* ret = NULL; if( capacity >= 0 ) { ret = (TSeqList*)malloc(sizeof(TSeqList) + sizeof(TSeqListNode) * capacity); } if( ret != NULL ) { ret->capacity = capacity; ret->length = 0; ret->node = (TSeqListNode*)(ret + 1); } return ret; } void SeqList_Destroy(SeqList* list) // O(1) { free(list); } void SeqList_Clear(SeqList* list) // O(1) { TSeqList* sList = (TSeqList*)list; if( sList != NULL ) { sList->length = 0; } } int SeqList_Length(SeqList* list) // O(1) { TSeqList* sList = (TSeqList*)list; int ret = -1; if( sList != NULL ) { ret = sList->length; } return ret; } int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList* list) // O(1) { TSeqList* sList = (TSeqList*)list; int ret = -1; if( sList != NULL ) { ret = sList->capacity; } return ret; } int SeqList_Insert(SeqList* list, SeqListNode* node, int pos) // O(n) { TSeqList* sList = (TSeqList*)list; int ret = (sList != NULL); int i = 0; ret = ret && (sList->length + 1 <= sList->capacity); ret = ret && (0 <= pos); if( ret ) { if( pos >= sList->length ) { pos = sList->length; } for(i=sList->length; i>pos; i--) { sList->node[i] = sList->node[i-1]; } sList->node[i] = (TSeqListNode)node; sList->length++; } return ret; } SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList* list, int pos) // O(1) { TSeqList* sList = (TSeqList*)list; SeqListNode* ret = NULL; if( (sList != NULL) && (0 <= pos) && (pos < sList->length) ) { ret = (SeqListNode*)(sList->node[pos]); } return ret; } SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList* list, int pos) // O(n) { TSeqList* sList = (TSeqList*)list; SeqListNode* ret = SeqList_Get(list, pos); int i = 0; if( ret != NULL ) { for(i=pos+1; i<sList->length; i++) { sList->node[i-1] = sList->node[i]; } sList->length--; } return ret; }
SeqList.h

#ifndef _SEQSTACK_H_ #define _SEQSTACK_H_ typedef void SeqStack; SeqStack* SeqStack_Create(int capacity); void SeqStack_Destroy(SeqStack* stack); void SeqStack_Clear(SeqStack* stack); int SeqStack_Push(SeqStack* stack, void* item); void* SeqStack_Pop(SeqStack* stack); void* SeqStack_Top(SeqStack* stack); int SeqStack_Size(SeqStack* stack); int SeqStack_Capacity(SeqStack* stack); #endif
main.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "SeqStack.h" /* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */ int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { SeqStack* stack = SeqStack_Create(20); int a[10]; int i = 0; for (i = 0; i<10; i++) { a[i] = i; SeqStack_Push(stack, a + i); } printf("Top: %d ", *(int*)SeqStack_Top(stack)); printf("Capacity: %d ", SeqStack_Capacity(stack)); printf("Length: %d ", SeqStack_Size(stack)); while (SeqStack_Size(stack) > 0) { printf("Pop: %d ", *(int*)SeqStack_Pop(stack)); } SeqStack_Destroy(stack); return 0; }
输出结果:

没有输出?代码?
由于编译器是64位,此时把编译环境换成32位。
输出结果:
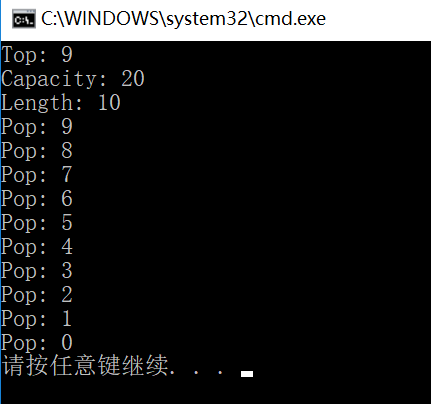
结果如上所示,为什么呢?
看一下表头的定义和顺序表的创建:
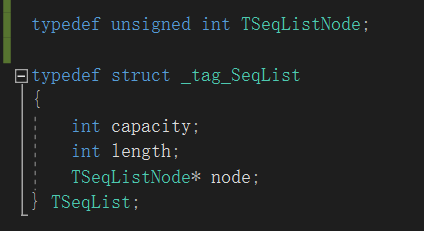
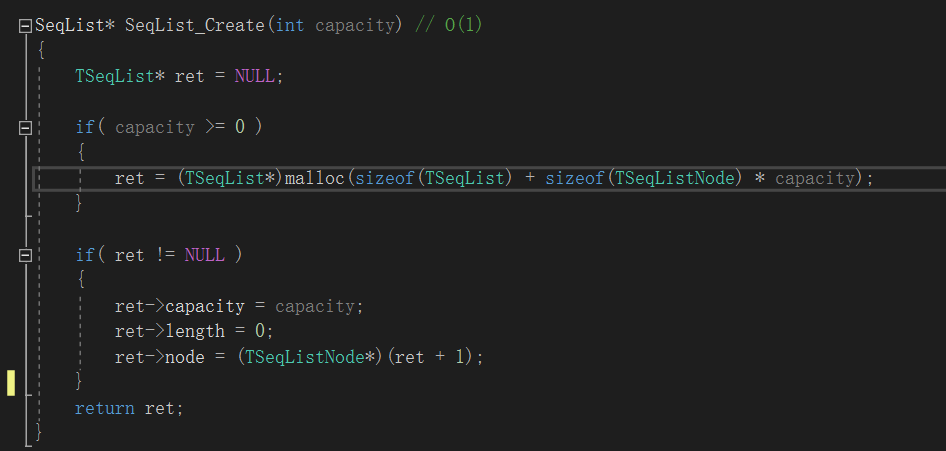
在32位系统上,指针为4字节。在64位系统上指针为8字节。
在顺序表的创建中,malloc的内存是:表头的结构体[4字节+4字节+指针(4字节或8字节)] + 4字节*capacity
再看看顺序表的插入函数和get函数:
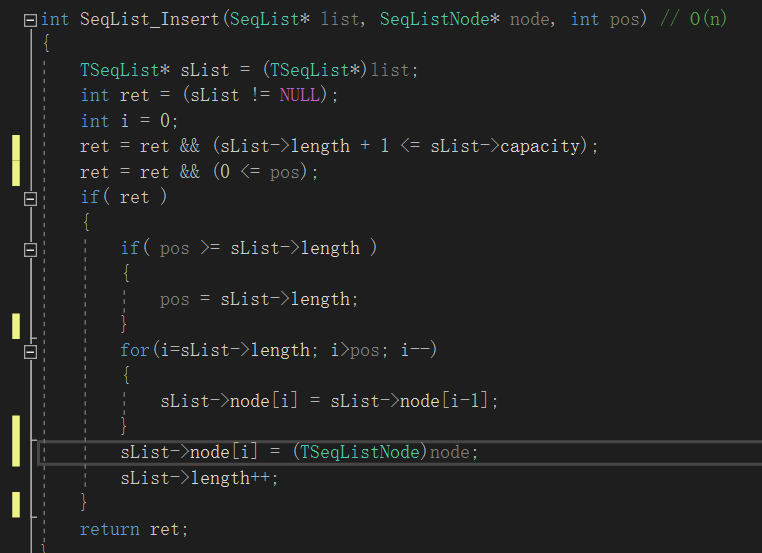
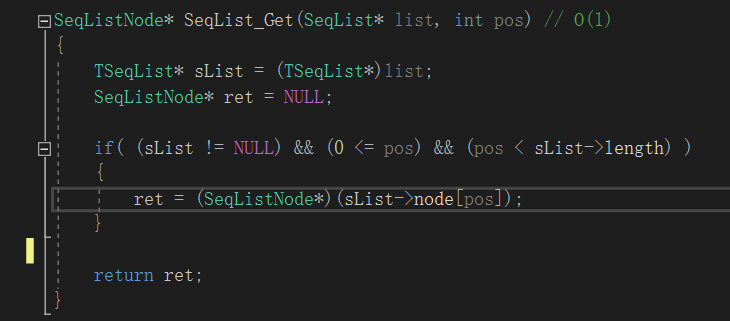
在64位系统中,指针为8字节,在插入函数中,node强转成TseqListNode(unsigned int)赋值给sList->node[i](指针)。指针的偏移是8字节。
顾把一个8字节的指针强转成4字节,发生指针截断,这里就会出错。
改进代码为:
把SeqList.c文件中的typedef unsigned int TSeqListNode;
替换为:
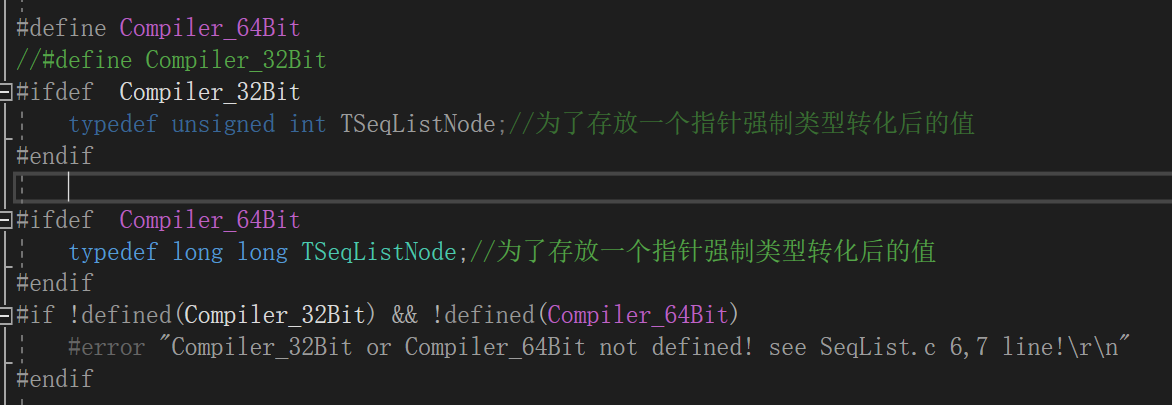
这样如果编译器为64位,则开启64位的宏,如果编译器为32位,则开启32位的宏。
栈的链式实现:
链式栈是可以支持结构体的,但是要求和链式表一样需要包含特定的头,为了后续的历程复用,下面不使用结构体类型入栈操作。
eg:
LinkStack.h
#ifndef _LINKSTACK_H_ #define _LINKSTACK_H_ //抽象数据类型 typedef void LinkStack; //创建顺序栈 LinkStack* LinkStack_Create(); //销毁 void LinkStack_Destroy(LinkStack* stack); //清除 void LinkStack_Clear(LinkStack* stack); //压栈 int LinkStack_Push(LinkStack* stack, void* item); //出栈,弹出 void* LinkStack_Pop(LinkStack* stack); //栈顶 void* LinkStack_Top(LinkStack* stack); //栈大小 int LinkStack_Size(LinkStack* stack); #endif
源文件:LinkStack.c
#include <malloc.h> #include "LinkStack.h" #include "LinkList.h" typedef struct _tag_LinkStackNode { LinkListNode header; void* item; } TLinkStackNode; LinkStack* LinkStack_Create() { return LinkList_Create(); } void LinkStack_Destroy(LinkStack* stack) { LinkStack_Clear(stack); LinkList_Destroy(stack); } void LinkStack_Clear(LinkStack* stack) { while( LinkStack_Size(stack) > 0 ) { LinkStack_Pop(stack); } } int LinkStack_Push(LinkStack* stack, void* item) { TLinkStackNode* node = (TLinkStackNode*)malloc(sizeof(TLinkStackNode)); int ret = (node != NULL) && (item != NULL); if( ret ) { node->item = item; ret = LinkList_Insert(stack, (LinkListNode*)node, 0); } if( !ret ) { free(node); } return ret; } void* LinkStack_Pop(LinkStack* stack) { TLinkStackNode* node = (TLinkStackNode*)LinkList_Delete(stack, 0); void* ret = NULL; if( node != NULL ) { ret = node->item; free(node); } return ret; } void* LinkStack_Top(LinkStack* stack) { TLinkStackNode* node = (TLinkStackNode*)LinkList_Get(stack, 0); void* ret = NULL; if( node != NULL ) { ret = node->item; } return ret; } int LinkStack_Size(LinkStack* stack) { return LinkList_Length(stack); }
注意,上面的push操作时插入到链表首的,这样更快一些,不用循环到链表尾部。
链式栈的清除不能直接调用链式表的清除,否则产生内存泄露,这里主要是为了之后的栈的例子,所以使用基本类型元素入栈,如果实现成可以支持结构体入栈的形式,直接调用链式表的清除函数即可,这个留给大家练手,可参考链式表的实现。
链式栈的销毁是在调用了栈的清除函数之后再次调用链式表的销毁构成的,其他的复用没有什么变化。
main.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "LinkStack.h" /* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */ int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { LinkStack* stack = LinkStack_Create(); int a[10]; int i = 0; for(i=0; i<10; i++) { a[i] = i; LinkStack_Push(stack, a + i); } printf("Top: %d ", *(int*)LinkStack_Top(stack)); printf("Length: %d ", LinkStack_Size(stack)); while( LinkStack_Size(stack) > 0 ) { printf("Pop: %d ", *(int*)LinkStack_Pop(stack)); } LinkStack_Destroy(stack); return 0; }
输出结果和顺序栈是一样的。
