客户端程序通过TCP通信传送"小文件"到服务器
源码 (不包含通信框架源码,通信框架源码请另行下载)
上一篇文章写了如何通过TCP通信发送图片到客户端,有朋友问如何传送文件,本文将就如何发送文件进行探讨。
对于比较小的文件,可以把文件转化成字节形式,用契约类包装一下,服务器收到后,再把字节转化成文件即可,这也是本文中实现的方式,这种方式的优点是比较简单灵活,缺点是不适合大文件的发送,也不能显示文件发送的进度。
基于TCP的通信机制,对于比较大的文件,这种方式是不可行的,大文件采用分段发送再合成的方式比较好,以后有时间再对如何发送大文件单独探讨。
本程序基于开源的networkComms2.3.1通信框架
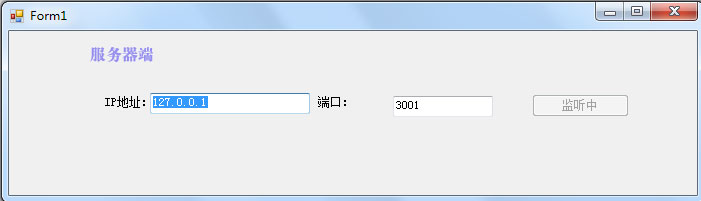
我们先开看一下实现的效果
服务器端:
客户端:


在服务器端,我们把收到的图片保存在D盘根目录下(您可以另外指定路径),打开D盘看到收到的图片如下:

下面看一下具体的过程
第一步,首先进行服务器端的设置
(1)监听端口:
//服务器开始监听客户端的请求
//开始监听某T端口
IPEndPoint thePoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(txtIP.Text), int.Parse(txtPort.Text));
TCPConnection.StartListening(thePoint, false);
button1.Text = "监听中";
button1.Enabled = false;
//此方法中包含服务器具体的处理方法。
StartListening();
(2) 针对文件上传写对应的处理方法:
NetworkComms.AppendGlobalIncomingPacketHandler<FileWrapper>("UploadFile", IncomingUploadFile);
//处理客户端发来的文件
private void IncomingUploadFile(PacketHeader header, Connection connection, FileWrapper wrapper)
{
try
{
writeFile(wrapper._fileData, @"D:" + wrapper.FileName);
ResMsgContract contract = new ResMsgContract();
contract.Message = "上传成功";
//发送回复信息给客户端
connection.SendObject("ResUploadFile", contract);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
<span style="color: #008000;"> //此方法来自博客园</span> private bool writeFile(byte[] pReadByte, string fileName) { FileStream pFileStream = null; try { pFileStream = new FileStream(fileName, FileMode.OpenOrCreate); pFileStream.Write(pReadByte, 0, pReadByte.Length); } catch { return false; } finally { if (pFileStream != null) pFileStream.Close(); } return true; } |
第二步:客户端的设置
(1)连接服务器:
//给连接信息对象赋值
connInfo = new ConnectionInfo(txtIP.Text, int.Parse(txtPort.Text));
//如果不成功,会弹出异常信息
newTcpConnection = TCPConnection.GetConnection(connInfo);
TCPConnection.StartListening(connInfo.LocalEndPoint);
button1.Enabled = false;
button1.Text = "连接成功";
(2)从本地选择文件并上传:
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
openFileDialog2.Filter = "所有文件|*.*";
if (openFileDialog2.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
string shortFileName = System.IO.Path.GetFileName(openFileDialog2.FileName);
FileWrapper fileWrapper = new FileWrapper(shortFileName, ReadFile(openFileDialog2.FileName));
//发送图片包装类到服务器,并获取返回信息
ResMsgContract resMessage = newTcpConnection.SendReceiveObject<ResMsgContract>("UploadFile", "ResUploadFile", 8000, fileWrapper);
if (resMessage.Message == "上传成功")
{
MessageBox.Show("文件已经上传到服务器");
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("文件没有发送成功");
}
}
}
(三)关于FileWrapper类
在客户端与服务器端通信的过程中,我们注意到上面的程序中使用了一个FileWrapper类,用来传递文件对象。
FileWrapper类,存放在MessageContract类库中,此类用来保存文件转化后的二级制数据

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using ProtoBuf;
using System.Drawing;
using System.IO;
using ProtoBuf;
namespace MessageContract
{
[ProtoContract]
public class FileWrapper
{
/// <summary>
/// 把Image对象存储为私有的字节数组
/// </summary>
[ProtoMember(1)]
public byte[] _fileData;
/// <summary>
/// 图片名称
/// </summary>
[ProtoMember(2)]
public string FileName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 私有的无参数构造函数 反序列化时需要使用
/// </summary>
private FileWrapper() { }
/// <summary>
/// 创建一个新的 ImageWrapper类
/// </summary>
/// <param name="imageName"></param>
/// <param name="image"></param>
public FileWrapper(string fileName, byte[] file)
{
this.FileName = fileName;
this._fileData = file;
}
}
}
工作到此完成,很少的代码量,就帮我们实现了传递客户端文件保存在服务器的功能。
注意:此种方式并不适合传递比较大的文件,如果文件比较大,最好以分段传送文件的形式发送.
