ASP.NET MVC采用System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations提供的元数据验证机制对Model实施验证,我们可以在Model类型或者字段/属性上应用相应的ValidationAttribute。但是在默认情况下,对于同一个类型的ValidationAttribute特性只允许一个应用到目标元素上——即使我们将AllowMultiple属性设置为True。这篇文章的目的就是为了解决这个问题。[源代码从这里下载]
一、一个自定义ValidationAttribute:RangeIfAttribute
为了演示在相同的目标元素(类、属性或者字段)应用多个同类的ValidationAttribute,我定义了一个名称为RangeIfAttribute特性用于进行“有条件的区间验证”。如下面的代码片断所示,RangeIfAttribute是RangeAttribute的子类,应用在上面的AttributeUsageAttribute特性的AllowMultiple 属性被设置为True。RangeIfAttribute定义了Property和Value两个属性,分别表示被验证属性/字段所在类型的另一个属性名称和相应的值,只有当指定的属性值与通过Value属性值相等的情况下我们在真正进行验证。具体的验证逻辑定义在重写的IsValid方法中。
1: [AttributeUsage( AttributeTargets.Field| AttributeTargets.Property, AllowMultiple = true)]
2: public class RangeIfAttribute: RangeAttribute
3: {
4: public string Property { get; set; }
5: public string Value { get; set; }
6: public RangeIfAttribute(string property, string value, double minimum, double maximum)
7: : base(minimum, maximum)
8: {
9: this.Property = property;
10: this.Value = value;
11: }
12: protected override ValidationResult IsValid(object value, ValidationContext validationContext)
13: {
14: object propertyValue = validationContext.ObjectType.GetProperty(this.Property).GetValue(validationContext.ObjectInstance,null);
15: propertyValue = propertyValue ?? "";
16: if (propertyValue.ToString()!= this.Value)
17: {
18: return null;
19: }
20: if (base.IsValid(value))
21: {
22: return null;
23: }
24:
25: string[] memberNames = (validationContext.MemberName != null) ? new string[] { validationContext.MemberName } : null;
26: return new ValidationResult(this.FormatErrorMessage(validationContext.DisplayName), memberNames);
27: }
28: }
二、将RangeIfAttribute应用于Employee
我们将RangeIfAttribute特性应在具有如下定义的表示员工的Employee类型的Salary(表示薪水)属性上,另外一个属性Grade表示员工的级别。应用在Salary属性上的RangeIfAttribute特性体现了基于级别的薪水区间验证规则:对于G7、G8和G9的员工,其薪水分别在2000~3000,3000~4000和4000~5000范围内。
1: public class Employee
2: {
3: public string Name { get; set; }
4: public string Grad { get; set; }
5: [RangeIf("Grad", "G7", 2000, 3000)]
6: [RangeIf("Grad", "G8", 3000, 4000)]
7: [RangeIf("Grad", "G9", 4000, 5000)]
8: public decimal Salary { get; set; }
9: }
现在我们创建如下一个EmployeeController,其默认的两个Index操作方法定义如下。在HttpPost的Index操作中,如果验证成功我们将“验证成功”字样作为ModelError添加到ModelState中。
1: public class EmployeeController : Controller
2: {
3: public ActionResult Index()
4: {
5: return View(new Employee());
6: }
7:
8: [HttpPost]
9: public ActionResult Index(Employee employee)
10: {
11: if (ModelState.IsValid)
12: {
13: ModelState.AddModelError("", "验证成功");
14: return View(new Employee());
15: }
16: else
17: {
18: return View(new Employee());
19: }
20: }
21:
22: }
下面是Index操作默认的View的定义:
1: @model MultipleValidator.Models.Employee
2: @{
3: ViewBag.Title = "Employee Management";
4: }
5: @Html.ValidationSummary(true)
6: @using (Html.BeginForm())
7: {
8: @Html.EditorForModel()
9: <input type="submit" value="Save" />
10: }
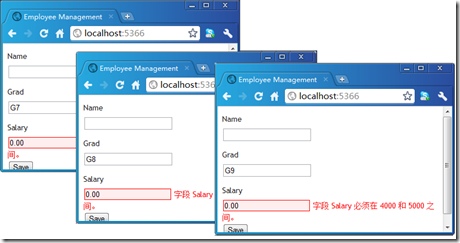
遗憾的是,ASP.NET MVC并不能按照我们希望的方对我们的输入进行验证。如下面的截图所示,我们只有在输入G9的时候,系统才能实施成功地验证,对于G7和G8则被输入的Salary值(0.00)是合法的。
三、重写TypeId属性解决问题
之所以会发生上述的这种现象,原因在于被应用到Salary属性上的RangeIfAttribute特性,最终只有最后一个(Value=“G9”)被使用到。ASP.NET MVC在生成包括验证特性的Model的元数据的时候,针对某个元素的所有ValidationAttribute是被维护在一个字典上的,而这个字典的值就是Attribute的TypeId属性。在默认的情况下,Attribute的TypeId返回的是自身的类型,所以导致应用到相同目标元素的同类ValidationAttribute只能有一个。幸好Attribute的TypeId属性是可以被重写的,县在我们在RangeIfAttribute中按照如下的方式对这个属性进行重写:
1: [AttributeUsage( AttributeTargets.Field| AttributeTargets.Property, AllowMultiple = true)]
2: public class RangeIfAttribute: RangeAttribute
3: {
4: //其他成员
5: private object typeId;
6: public override object TypeId
7: {
8: get
9: {
10: return (null == typeId) ? (typeId = new object()) : typeId;
11: }
12: }
13: }
再次运行我们的程序则一切正常:
值得一提的是:重写TypeId属性的方式只能解决服务端验证的问题,对于客户端认证无效。