一、实现一个链表
代码1:
class Node:
def __init__(self,value):
self.value = value
self.next = None
def listPrint(arr):
head = Node(arr[0])
p = head
for i in range(1,len(arr)):
p.next = Node(arr[i])
p = p.next
return head
arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
head = listPrint(arr)
代码2:
class Node:
def __init__(self,value):
self.value = value
self.next = None
#建立一个链表
def listPrint1(arr):
head = Node(arr[0])
p = head
for i in range(1,len(arr)):
p.next = Node(arr[i])
p = p.next
return head
#对head进行逆序:
def listPrint2(head):
arr = []
while head:
arr.append(head)
head = head.next
arr = arr[::-1]
for i in range(1,len(arr)):
arr[i-1].next = arr[i]
return arr[0]
arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
head1 = listPrint1(arr)
head2 = listPrint2(head1)
二、题目:复制含有随机指针节点的链表

简单的思路:
采用一个字典存储,key存储原来链表结构,value存储新建链表结构。返回结果直接为key头结点对应的value值。
代码:
class Node: def __init__(self,value): self.value = value self.next = None self.rand = None def copylist(head): if not head: return head dic = {} cur = head while cur: dic[cur] = Node(cur.value) cur = cur.next cur = head while cur: if cur.next: dic[cur].next = dic[cur.next] else: dic[cur].next = None if cur.rand: dic[cur].rand = dic[cur.rand] else: dic[cur].rand = None cur = cur.next return dic[head] if __name__ == '__main__': head = Node(1) p = head for i in range(2,5): p.next = Node(i) p = p.next p = head while p.next: p.rand = p.next.next p = p.next res = copylist(head)
进阶的思路:
步骤1:将复制的链表插入到原来的链表中,比如:1→2→3→None。变成 1→1'→2→2‘→3→3’→None。
步骤2:将复制的节点next和rand复制进去。
步骤3:将新建的长链表进行拆分。
代码:
class Node: def __init__(self,value): self.value = value self.next = None self.rand = None def copylist(head): if not head: return head #步骤1:复制链表 cur = head while cur: next = cur.next cur.next = Node(cur.value) cur.next.next = next cur = next #重新调整复制链表的rand cur = head while cur: cur.next.rand = cur.rand.next if cur.rand else None cur = cur.next.next #拆分长链表,即重新调整原来链表和复制链表的next cur = head res = head.next while cur: curcopy = cur.next cur.next = curcopy.next curcopy.next = cur.next.next if cur.next else None cur = cur.next return res if __name__ == '__main__': head = Node(1) p = head for i in range(2,5): p.next = Node(i) p = p.next p = head while p.next: p.rand = p.next.next p = p.next res = copylist(head)
三、题目:将搜索二叉树转换成双向链表

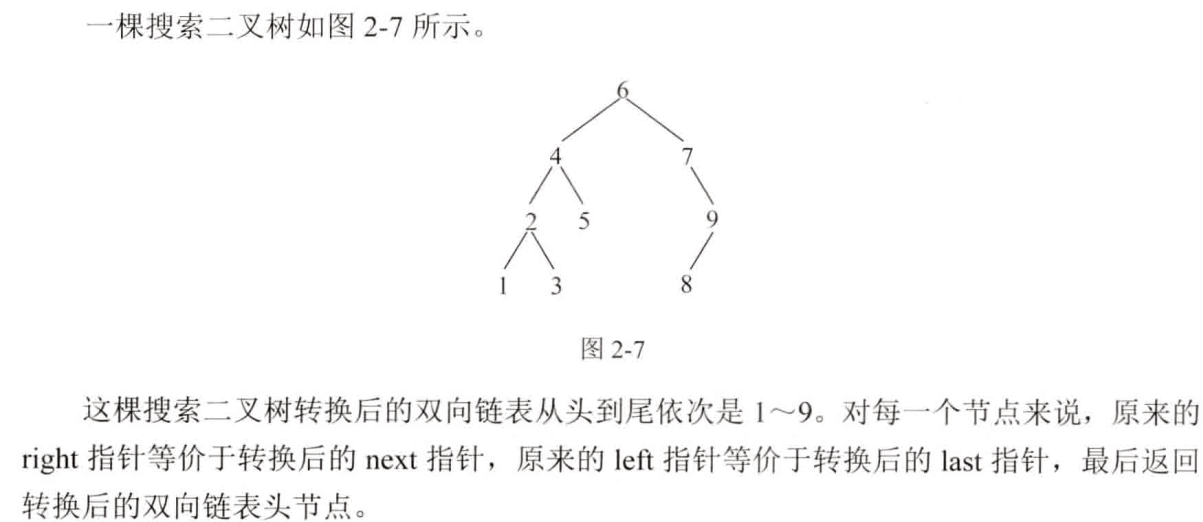
方法一思路:

法一代码:
class Node: def __init__(self,value): self.value = value self.left = None self.right = None class Tree: def __init__(self,root): self.value = root self.left = None self.right = None #前序遍历树 def preTree(root): if not root: return [] List = [] left = preTree(root.left) right = preTree(root.right) List.extend(left) List.append(root.value) List.extend(right) return List #将树转化成链表 def TreetoList(root): List = preTree(root) if not List: return None head = Node(List[0]) pre = head pre.left = None cur = None for i in range(1,len(List)): cur = Node(List[i]) pre.right = cur cur.left = pre pre = cur pre.right = None return head root = Tree(3) root.left = Tree(2) root.right = Tree(4) root.left.left = Tree(1) root.right.right = Tree(5) TreetoList(root)
方法二思路:
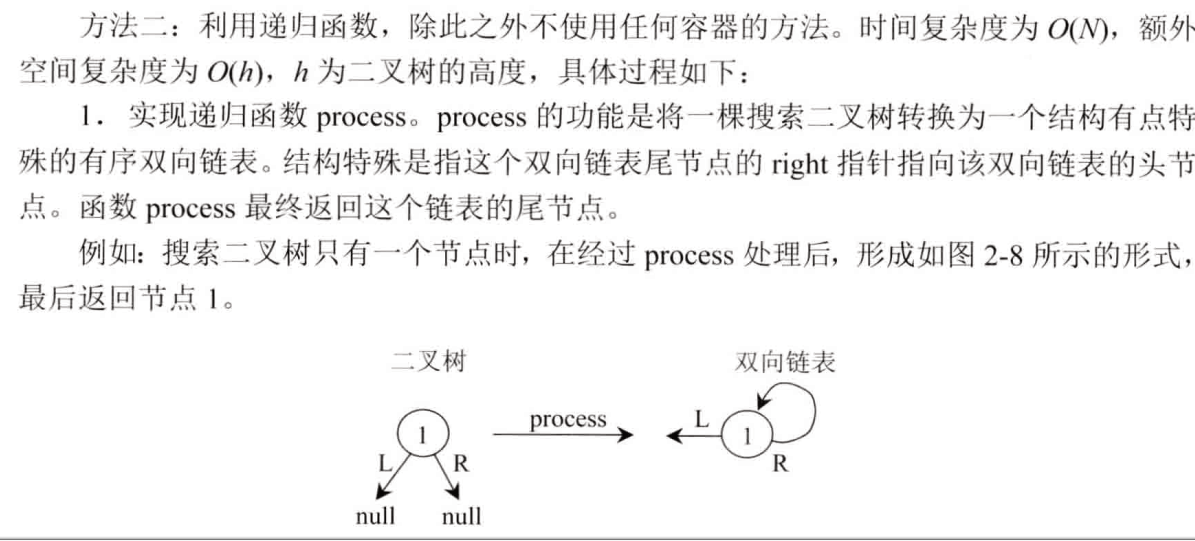
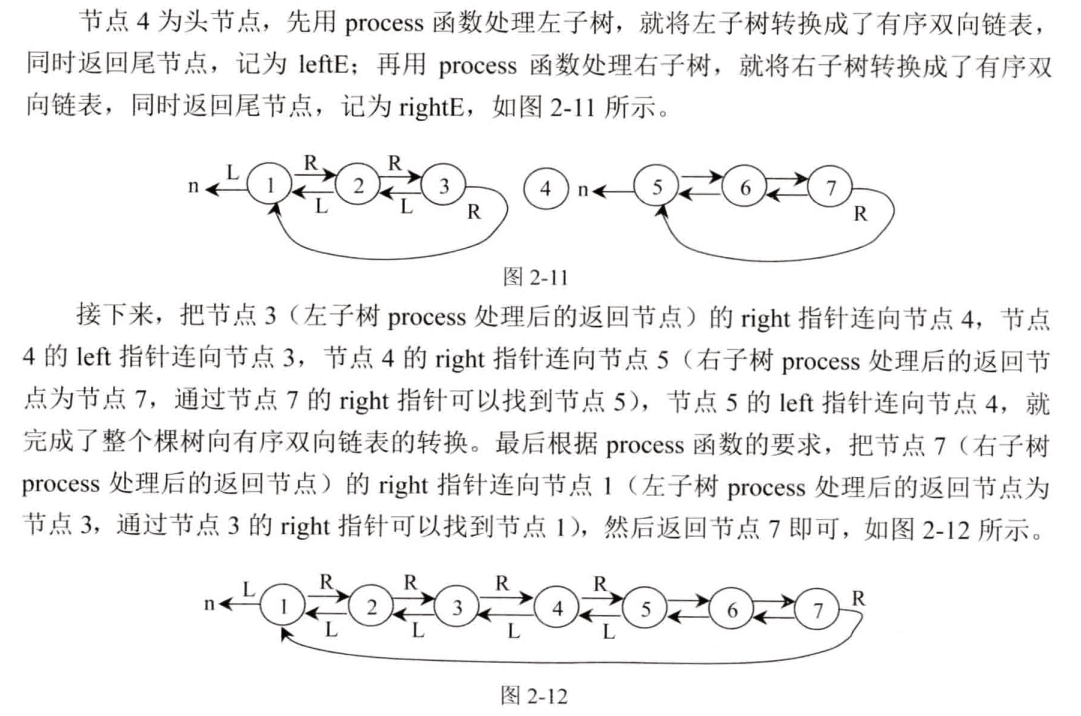

四、题目:打印连个有序链表的公共部分
给定两个有序链表的头指针 head1 和 head2 ,打印两个链表的公共部分。
思路:

代码:
class Node:
def __init__(self,value):
self.value = value
self.next = None
def compareLian(head1,head2):
# res = 0
while head1 and head2:
if head1.value < head2.value:
head1 = head1.next
elif head1.value == head2.value:
print(head1.value)
head1 = head1.next
head2 = head2.next
else:
head2 = head2.next
head1 = Node(1)
head1.next = Node(2)
head1.next.next = Node(5)
head2 = Node(2)
head2.next = Node(5)
head2.next.next = Node(6)
compareLian(head1,head2)
五、判断一个链表是否为回文结构
题目:

思路1:采用栈存储遍历完链表,再看栈的数据是不是回文结构
思路2:将链表折半,将链表右半部分放入栈中,栈取数和左半部分链表值一样,则为回文。
class Node: def __init__(self,value): self.val = value self.next = None def isPal(head): if not head or head.next == None: return True stack = [] n = 0 p = head slow , fast = head , head while fast and fast.next: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next.next right = slow while right: stack.append(right.val) right = right.next left = head while left != slow and stack: if left.val != stack.pop(): return False left = left.next return True if __name__ == '__main__': head= Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(1) print(isPal(head))
六、如何展出单链表中的倒数第k个元素(遍历)
设置一个快慢指针:
快指针比慢指针先走k步。
直到快指针走到终点,慢指针所指的节点为结果。
解释:共n个节点,慢指针走到第n-k步时,快指针走到终点n。
class Node: def __init__(self,value): self.val = value self.next = None def findKth(head,k): if not head: return False slow , fast = head , head for i in range(k): fast = fast.next while fast: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next return slow.val if __name__ == '__main__': head = Node(1) p = head k = 2 for i in range(2,6): p.next = Node(i) p = p.next print(findKth(head,k))