技术在于交流、沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性
介绍11种STL标准库的算法,从这11种算法中总结一下算法的基本使用
1.accumulate() 累加
2.for_each() for一段区间 做你指定的行为
3.replace(), replace_if(), replace_copy() 替换函数
4.count(), count_if() 计数
5.find() 查找
6.sort() 排序
7.binary_search()查看元素是否在指定区间
下面的仿函数都没有继承自 binary_function<T,T,bool>, unary_function<T,bool>,但是在实际操作中,声明仿函数一定要继承自binary_function<T,T,bool>,unary_function<T,bool>
下一节内容会介绍为什么要继承自这两个类
一 accumulate(),累加,将指定区域内的value累加起来
源码及参数介绍

//默认累加算法,将传进的__first(begin()迭代器)位置,至__last(end()迭代器),与init求和 template<typename _InputIterator, typename _Tp> inline _Tp accumulate(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last, _Tp __init) { // concept requirements __glibcxx_function_requires(_InputIteratorConcept<_InputIterator>) __glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__first, __last); for (; __first != __last; ++__first) __init = __init + *__first; return __init; } //自定义accumulate 按照指定的要求做”累加”操作 template<typename _InputIterator, typename _Tp, typename _BinaryOperation> inline _Tp accumulate(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last, _Tp __init, _BinaryOperation __binary_op) { // concept requirements __glibcxx_function_requires(_InputIteratorConcept<_InputIterator>) __glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__first, __last); for (; __first != __last; ++__first) __init = __binary_op(__init, *__first); return __init; }
基本使用
#include <iostream> #include <functional> #include <numeric> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; namespace wzj000 { int myfunc(int x, int y) {return x+2*y;} struct myclass{ int operator()(int x, int y){return x+3*y;} }; void test_accumulate() { int init = 100; int num[] {10, 20, 30}; cout<<"default accumulate: " << accumulate(num, num+3, init)<< endl; //100 + 10 + 20 + 30 默认累加 cout << "using minus: " << accumulate(num, num+3, init, minus<int>())<< endl; //100 - 10 - 20 - 30 将累加改为递减 cout << "using custom function: " << accumulate(num, num+3, init, myfunc)<< endl; // 100 + 2*10 + 2*20 + 2*30 自定义"累加"规则 func cout << "suing custom object: " << accumulate(num, num+3, init, myclass())<< endl; // 100 + 3*10 + 3*20 + 3*30自定义"累加"规则 仿函数 } }
测试结果

二 for_each() for一段区间 做你指定的行为
源码及参数介绍

template <class Inputerator, class Function> Function for_each(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, Function f) {//参数1 起始点 参数2 终点, 参数3 想要执行的操作 for( ; first != last; ++first) { f(*first); } return f; }
基本使用
namespace wzj001 { void myfunc(int i) { cout << " - " << i; } struct myclass{ void operator()(int i) { cout << " ^ " << i; } }; void test_for_each() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myfunc); cout << endl; } void test_for_each_classFunc() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()); cout << endl; } }
测试结果

三 replace() 替换函数
replace_if()
replace_copy()
源码及参数介绍

template <class ForwardIterator, class T> void replace(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T & old_value, const T& new_value) {//范围内所有等于old_value者都一new_value取代 for( ; first != last; ++first) { if(*first == old_value) *first = new_value; } } template <class Inputerator, class Inputerator, class T> void replace_if(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, Predicate pred, const T& new_value) {//范围内所有满足pred()为true之元素都以new_value取代 for( ; first != last; ++first) { if(pred(*first)) *first = new_value; } } template <class Inputerator, class Outputerator, class T> Outputerator replace_copy(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, Outputerator result, const T & old_value, const T& new_value) {//范围内所有等于old_value者都以new_value放置新区域 //不符合者原值放入新区域 for( ; first != last; ++first, ++result) { *result = *first == old_value ? new_value : *first; } }
基本使用
namespace wzj002 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i) { return i >=10 ? true : false; } }; void test_replace() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; replace(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), 20 ,30); cout << "replace: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } void test_replace_if() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; replace_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass(), 30); cout << "replace_if: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } void test_replace_copy() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; vector<int> myNewVector; myNewVector.resize(3); replace_copy(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myNewVector.begin(), 20, 10); cout << "replace_if_New: "; for(auto i : myNewVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "replace_if_Old: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } }
测试结果

四 count() 计数
count_if()
源码及参数介绍

template <class Inputerator, class Outputerator, class T> typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type; count(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T& value) { typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type; for( ; first != last; ++first) if(*first == value) //满足要求 值 == value 累计+1 ++n; return n; } template <class Inputerator, class Outputerator, class Predicate> typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type; count_if(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, Predicate pred) { typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type; for( ; first != last; ++first) if(pred(*first)) //满足指定要求 累计 +1 ++n; return n; }
count()和count_if()是全局算法,适用于array,vector,list,forward_list, deque
map,set,unordered_set/map由于是关联式容器,所有有自己的count()和count_if()函数
基本使用
namespace wzj003 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i) { return i >= 20; } }; void test_count() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; cout << "count(): "<< count(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), 20) <<endl; } void test_count_if() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 10, 20, 20, 30, 30}; cout << "count_if(): " << count_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()) <<endl; } }
测试结果

五 find() 查找
find_if()
find()和find_if()是全局算法,适用于array,vector,list,forward_list, deque
map,set,unordered_set/map由于是关联式容器,所有有自己的find()和find_if()函数
源码及参数介绍
template <class Inputerator, class T> Inputerator find_if(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T& value) { while(first != last && *first != value) ++first; return first; } template <class Inputerator, class Predicate> Inputerator find_if(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, Predicate pred) { while(first != last && !pred(*first)) ++first; return first; }
基本使用
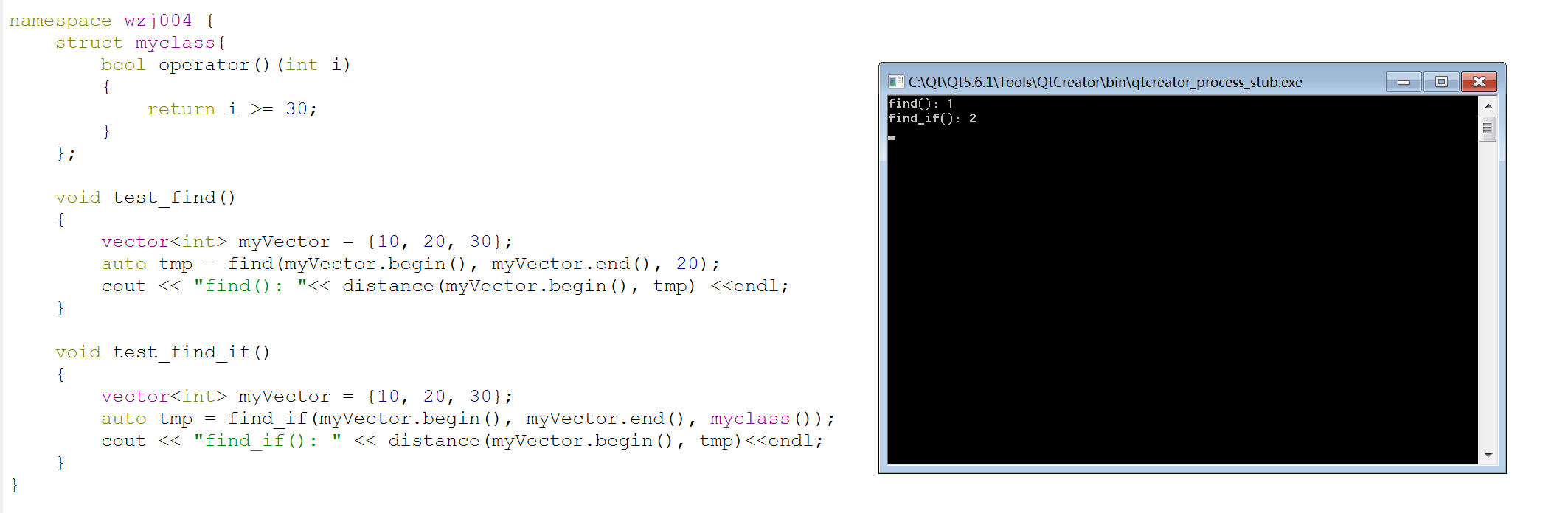
namespace wzj004 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i) { return i >= 30; } }; void test_find() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; auto tmp = find(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), 20); cout << "find(): "<< distance(myVector.begin(), tmp) <<endl; } void test_find_if() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; auto tmp = find_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()); cout << "find_if(): " << distance(myVector.begin(), tmp)<<endl; } }
测试结果
六 sort 排序
list和forward_list有成员sort()函数
set/map自动排序
array,vector,deque用全局sort()
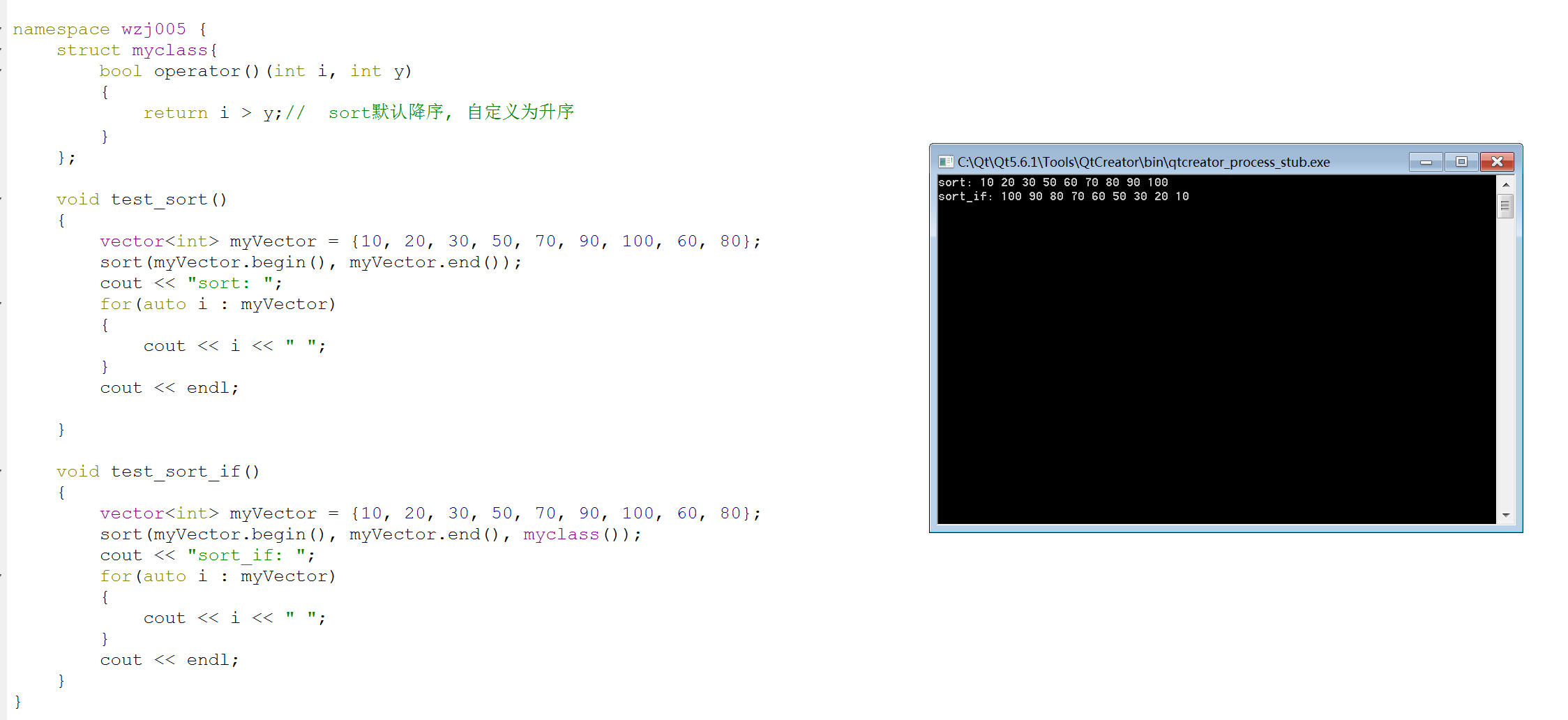
namespace wzj005 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i, int y) { return i > y;// sort默认降序, 自定义为升序 } }; void test_sort() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 90, 100, 60, 80}; sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end()); cout << "sort: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } void test_sort_if() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 90, 100, 60, 80}; sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()); cout << "sort_if: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } }
测试结果
七 binary_search()查看元素是否在指定区间内
源码及参数介绍

template <class Inputerator, class T> bool binary_search(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T& val) {//返回元素是否在指定区间 first = std::lower_bound(first,last,val); return (first != last && !(val < *first)); }
基本使用
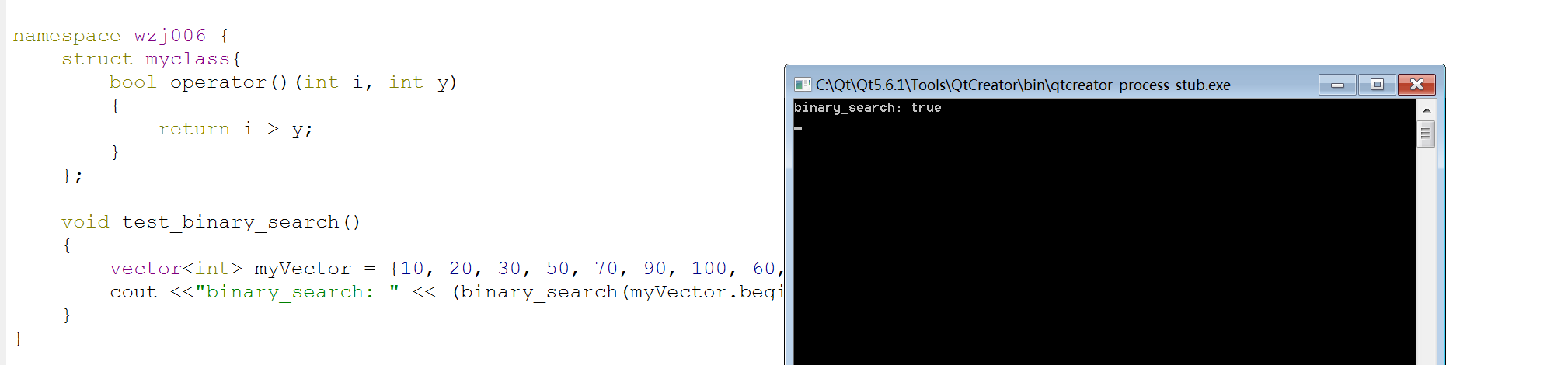
namespace wzj006 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i, int y) { return i > y; } }; void test_binary_search() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 90, 100, 60, 80}; cout <<"binary_search: " << (binary_search(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), 50) ? "true" : "false") << endl; } }
测试结果
全部测试代码

#include <iostream> #include <functional> #include <numeric> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; namespace wzj000 { int myfunc(int x, int y) {return x+2*y;} struct myclass{ int operator()(int x, int y){return x+3*y;} }; void test_accumulate() { int init = 100; int num[] {10, 20, 30}; cout<<"default accumulate: " << accumulate(num, num+3, init)<< endl; //100 + 10 + 20 + 30 默认累加 cout << "using minus: " << accumulate(num, num+3, init, minus<int>())<< endl; //100 - 10 - 20 - 30 将累加改为递减 cout << "using custom function: " << accumulate(num, num+3, init, myfunc)<< endl; // 100 + 2*10 + 2*20 + 2*30 //自定义"累加"规则 func cout << "suing custom object: " << accumulate(num, num+3, init, myclass())<< endl; // 100 + 3*10 + 3*20 + 3*30//自定义"累加"规则 仿函数 } } namespace wzj001 { void myfunc(int i) { cout << " - " << i; } struct myclass{ void operator()(int i) { cout << " ^ " << i; } }; void test_for_each() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myfunc); cout << endl; } void test_for_each_classFunc() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()); cout << endl; } } namespace wzj002 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i) { return i >=10 ? true : false; } }; void test_replace() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; replace(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), 20 ,30); cout << "replace: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } void test_replace_if() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; replace_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass(), 30); cout << "replace_if: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } void test_replace_copy() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; vector<int> myNewVector; myNewVector.resize(3); replace_copy(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myNewVector.begin(), 20, 10); cout << "replace_if_New: "; for(auto i : myNewVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; cout << "replace_if_Old: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } } namespace wzj003 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i) { return i >= 20; } }; void test_count() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; cout << "count(): "<< count(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), 20) <<endl; } void test_count_if() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 10, 20, 20, 30, 30}; cout << "count_if(): " << count_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()) <<endl; } } namespace wzj004 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i) { return i >= 30; } }; void test_find() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; auto tmp = find(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), 20); cout << "find(): "<< distance(myVector.begin(), tmp) <<endl; } void test_find_if() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30}; auto tmp = find_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()); cout << "find_if(): " << distance(myVector.begin(), tmp)<<endl; } } namespace wzj005 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i, int y) { return i > y;// sort默认降序, 自定义为升序 } }; void test_sort() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 90, 100, 60, 80}; sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end()); cout << "sort: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } void test_sort_if() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 90, 100, 60, 80}; sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()); cout << "sort_if: "; for(auto i : myVector) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; } } namespace wzj006 { struct myclass{ bool operator()(int i, int y) { return i > y; } }; void test_binary_search() { vector<int> myVector = {10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 90, 100, 60, 80}; cout <<"binary_search: " << (binary_search(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), 50) ? "true" : "false") << endl; } } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { wzj000::test_accumulate(); wzj001::test_for_each(); wzj001::test_for_each_classFunc(); wzj002::test_replace(); wzj002::test_replace_if(); wzj002::test_replace_copy(); wzj003::test_count(); wzj003::test_count_if(); wzj004::test_find(); wzj004::test_find_if(); wzj005::test_sort(); wzj005::test_sort_if(); wzj006::test_binary_search(); return 0; }
参考侯捷<<STL源码剖析>>
