版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
shared_ptr智能指针的一种,它的使用类似于auto_ptr.
shared_ptr它有两个指针,一个指向引用计数,一个指向data.由于拥有引用计数,所有shared_ptr支持容器.
shared_ptr的源码非常复杂这里也不做太多讲解,本文主要介绍一下shared_ptr的基本使用
间接使用
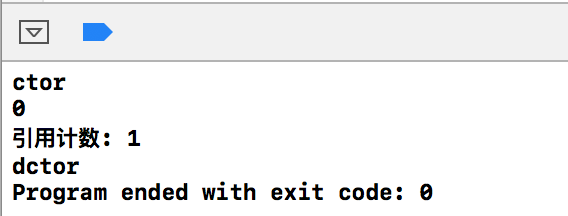
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Person { public: Person() { cout<< "ctor" << endl; } ~Person() { cout<< "dctor" << endl; } int m_age = 0; }; int main() { shared_ptr<Person> person(new Person()); cout << (*person).m_age<< endl; cout << "引用计数: " << person.use_count() << endl; // use_count()返回几个该对象被几个人拥有 return 0; }
输出结果
直接使用
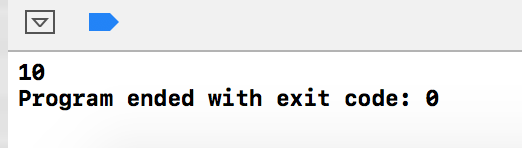
int main() { //赋值操作 int *p = new int (5); int *q = new int (10); shared_ptr<int> tmp_5(p); shared_ptr<int> tmp_10(q); tmp_5 = tmp_10; cout<< * tmp_5 << endl; return 0; }
输出结果
检测拥有者
int main() { //unique() 是否为最初拥有者 Person * p = new Person; shared_ptr<Person> tmp_1(p); cout <<"被拥有个数"<< tmp_1.use_count() <<"是否为最初拥有者"<<tmp_1.unique()<< endl; shared_ptr<Person> tmp_2(tmp_1); cout <<"被拥有个数"<< tmp_2.use_count() <<"是否为最初拥有者"<<tmp_2.unique()<< endl; return 0; }
输出结果

以上是shared_ptr<>的简单使用
下面我来介绍一种类的设计方式Hand/Body(pImpl)
这边设计方式其实就是桥接设计模式,但是个人感觉这种设计类的方式是未来的趋向
他的观点如图
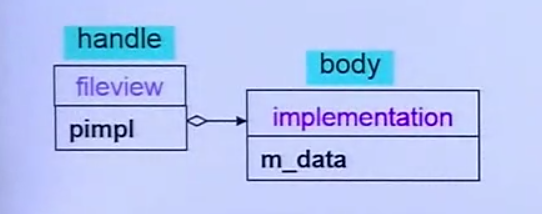
(handle) fileview类只含有一个指针(4字节),指向真正的数据
(body) implementation, 数据 , 方法实现
这样做 handle 内存占用大小会减小很多,并且他有助于move()的实现
此时调用fileview的function时就会调用 implementation内的实现
写一个简单的实现
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include "/Users/oujiken/Qt5.6.1/5.6/Src/qt3d/src/3rdparty/assimp/code/BoostWorkaround/boost/shared_ptr.hpp" using namespace std; class fileview { public: fileview(); ~fileview(); void fileview_close();
... private: struct implementation; boost::shared_ptr<implementation> pimpl; }; struct fileview::implementation { std::vector<char> m_data; }; //ctor fileview::fileview() { pimpl.reset(new implementation()); cout<< "fileview()" <<endl; } void fileview::fileview_close() { pimpl->m_data.clear(); cout<< "close()"<<endl; } ... int main() { fileview * f = new fileview(); f->fileview_close();
cout << sizeof(fileview) <<endl;
return 0; }
输出结果
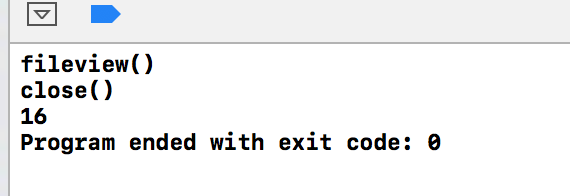
shared_ptr<> 占16字节
如有不正确的地方请指正
参照<<侯捷 C++新标准 C++11>>