1.ES6简介
ECMAScript 6.0,是 JavaScript 语言下一代标准,发布于 2015 年 6 月。它的目标是使得 JavaScript 语言可以用来编写复杂的大型应用程序,成为企业级开发语言。
1.1.let,var,const命令
ES6中新增了let命令,和var类似,也是用来声明变量的,
区别:
let声明的变量只在let命令所在的代码块内有效,而var声明的变量会污染全局
let不能重复定义,但是可以修改,但是var可以重复声明,但是会覆盖之前已经声明的
var声明变量存在变量提升,也就是在声明变量之前就可以使用该变量。而let必须先声明再使用
const是用来声明常量的,声明过后值不能在改变,即不能再做声明,作用域与let相同,只在声明所在的块级作用域内有效
1.2.变量的解构赋值
数组解构赋值,就是把数组元素的值按照顺序依次赋值
var [x, y, z] = [10, 20, 30]
x // 10
y // 20
z // 30
对象解构赋值
var {x, y} = {x: 10, y: 20}
x // 10
y // 20
1.3 字符串操作
ES6之前,JavaScript中只有indexOf方法可用来确定一个字符串是否包含在另一个字符串中
现在,还有include(),startwith(),endwith()三种方法:
var s = "Hello world!";
s.includes("o") // true
s.startsWith("Hello") // true
s.endsWith("!") // true
# 这三个方法都支持第2个参数,表示开始匹配的位置
14.模板字符串
模板字符串(template string)是增强版的字符串,用反引号(`)标识。它可以当做普通字符串使用,也可以用来定义多行字符串,或者在字符串中嵌入变量。在模板字符串中嵌入变量
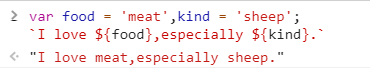
# 这里注意大括号前还有$,别忘记了
1.5函数
关于箭头函数:顾名思义,就是 有一个 => 的函数
常规语法定义的函数:
function funcName(params) {
return params + 2;
}
funcName(2);
// 4
箭头函数:
var funcName = (params) => params + 2
funcName(2);
// 4
箭头函数特点:
如果参数只有一个,可以省略小括号
如果不写return,可以不写大括号
没有arguments变量
不改变this指向
和一般的函数不同,箭头函数不会绑定this,或则说箭头函数不会改变this本来的绑定。导致内部的this就是外层代码块的this。
一般函数,输出得到一个person对象:

箭头函数:

1.6 对象
Object.assign方法用来将源对象(source)的所有可枚举属性复制到目标对象(target)。它至少需要两个对象作为参数,第一个参数是目标对象,第二个参数是源对象。
参数必须都是对象,否则抛出TypeError错误。
Object.assjgn只复制自身属性,不可枚举属性(enumerable为false)和继承的属性不会被复制。
var x = {name: "learning", age: 18};
var y = x;
var z = Object.assign({}, x);
x.age = 20;
x.age // 20
y.age // 20
z.age // 18
1.7面向对象
ES5构造对象的方式是使用构造函数来创造,和构造函数唯一不同是函数名首字母需要大写
function Point(x, y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// 给父级绑定方法
Point.prototype.toSting = function(){
return '(' + this.x + ',' + this.y + ')';
}
var p = new Point(10, 20);
console.log(p.x)
p.toSting();
// 继承
function ColorPoint(x, y, color){
Point.call(this, x, y);
this.color = color;
}
// 继承父类的方法
ColorPoint.prototype = Object.create(Point.prototype);
// 修复 constructor
ColorPoint.prototype.constructor = Point;
// 扩展方法
ColorPoint.prototype.showColor = function(){
console.log('My color is ' + this.color);
}
var cp = new ColorPoint(10, 20, "red");
console.log(cp.x);
console.log(cp.toSting());
cp.showColor()
ES6使用class构造对象
class Point{
constructor(x, y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
} // 不要加逗号
toSting(){
return `(${this.x}, ${this.y})`;
}
}
// 实例化,得到一个对象
var p = new Point(10, 20);
console.log(p.x)
p.toSting();
class ColorPoint extends Point{
constructor(x, y, color){
super(x, y); // 调用父类的constructor(x, y)
this.color = color;
} // 不要加逗号
showColor(){
console.log('My color is ' + this.color);
}
}
var cp = new ColorPoint(10, 20, "red");
console.log(cp.x);
cp.toSting();
cp.showColor()
1.9 Promise
Promise 是异步编程的一种解决方案,比传统的解决方案(回调函数和事件)更合理、更强大。
有了Promise对象,就可以将异步操作以同步操作的流程表达出来,避免了层层嵌套的回调函数。此外Promise 对象提供统一的接口,使得控制异步操作更加容易
详细介绍,查看阮一峰的ECMAScript 6 入门