Codeforces Round #600 (Div. 2)
A. Single Push
思路
你可以进行最多一次操作:选择三个数(l, r, k),且(1le lle rle n)且(k>0)。使得(a)数组可以转化为(b)数组。
Note: (n le 100;000)
数形结合。
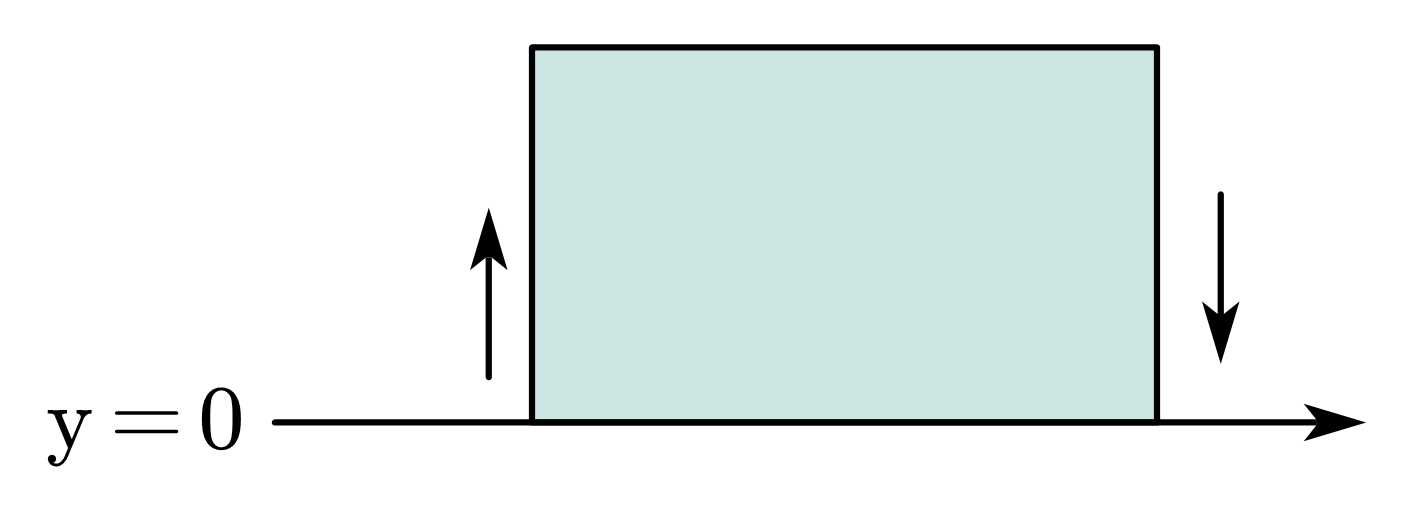
做a与b的差分。由图可知在边界左右均为0的情况下,最多有两次差别。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define DEBUG 0
// #define int long long
#define pb push_back
#define vt std::vector
#define lb lower_bound
#define sz(x) (int(x.size()))
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mst(x, bit) memset(x, bit, sizeof(x))
#define rep(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i < (r); ++ i)
#define forr(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i >= (r); -- i)
#define dmp(x) cerr << __LINE__ << "->" << #x << " " << x << "
"
using ll = long long;
using db = double;
using pii = pair<int, int>;
using pll = pair<ll, ll>;
template<typename... Args>
inline void wpr(Args... args) { std::cout << '
'; }
template<typename T, typename... Args>
void wpr(T val, Args... args) { std::cout << val << " "; wpr(args...); }
const int maxn = 1e5 + 50;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
void solve(){
int n;
std::cin >> n;
vt<int> a(n), b(n), dlt(n + 2, 0);
rep (i, 0, n) std::cin >> a[i];
rep (i, 0, n) std::cin >> b[i];
rep (i, 0, n) dlt[i + 1] = b[i] - a[i];
// 数形结合,绘图可以发现,左右边界都为 0,此时保证只有两个波动。
int cnt = 0;
rep (i, 1, n + 2){
if (dlt[i] < 0) { wpr("no"); return; }
if (dlt[i] != dlt[i - 1]) ++ cnt;
}
if (cnt <= 2) wpr("yes");
else wpr("no");
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
std::cin >> t;
while (t--) solve();
return 0;
}
B. Silly Mistake
思路
设整数(x),当其为正数时认为其进入办公室,当其为负数时认为其出办公室。一个人一天最多进一次,且不能在没进来前出去。每天结束时办公室没人。请你将一个序列(a)划分为多天保证每天都是合法的。
Note: (nle100;000;-1e6le a_i le 1e6)
对于每个people定义三个状态:(利用const int定义,学到了。)
WAIT代表等待有人进入。COME代表已经有人进入。LEFT代表人已经出去了。
同时我们定义ofs代表办公室的人数,利用贪心的想法,每次ofs == 0时便结束一天。基于该思想判断是否合法,请注意新的一天需要你清空状态。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define DEBUG 0
// #define int long long
#define pb push_back
#define vt std::vector
#define lb lower_bound
#define sz(x) (int(x.size()))
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mst(x, bit) memset(x, bit, sizeof(x))
#define rep(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i < (r); ++ i)
#define forr(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i >= (r); -- i)
#define dmp(x) cerr << __LINE__ << "->" << #x << " " << x << "
"
using ll = long long;
using db = double;
using pii = pair<int, int>;
using pll = pair<ll, ll>;
template<typename... Args>
inline void _wpr_(Args... args) { std::cout << '
'; }
template<typename T, typename... Args>
inline void _wpr_(T val, Args... args) { std::cout << " " << val; _wpr_(args...); }
template<typename T, typename... Args>
void wpr(T val, Args... args) { std::cout << val; _wpr_(args...); }
const int maxn = 1e6 + 50;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int WAIT = 0, COME = 1, LEFT = 2;
int m[maxn];
void solve(){
int n; std::cin >> n;
// ofc means the count of office
int ofc = 0;
// cur denote the current array. ans means answer array.
vt<int> cur, ans;
rep (i, 0, n){
int x; std::cin >> x;
int abx = abs(x);
cur.pb(abx);
if (x > 0){
if (m[abx] != WAIT) { wpr(-1); return; }
m[abx] = COME;
++ ofc;
}else {
if (m[abx] != COME) { wpr(-1); return; }
m[abx] = LEFT;
-- ofc;
}
if (0 == ofc){
ans.pb(sz(cur));
for (auto x: cur) m[x] = WAIT;
cur.clear();
}
}
// if not over, return false.
if (!cur.empty()) { wpr(-1); return; }
std::cout << sz(ans) << "
";
rep (i, 0, sz(ans)) std::cout << ans[i] << "
"[i == sz(ans) - 1];
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
// std::cin >> t;
while (t--) solve();
return 0;
}
C. Sweets Eating
思路
一共有 (n) 个糖果,每个糖果浓度为(a_i)。一个人每天最多吃(m)个糖。在第(d)天吃浓度为(a_k)的糖的伤害为(d cdot a_k)。请你给出在吃(k)糖的情况下的最小伤害。
Note: (1le m le n le 200;000; 1le a_i le 200;000)
显然,策略非常清晰:浓度高的糖果,需要尽可能早的吃。排序即可。
但是,这里涉及到一共分层的问题。
例如:
m = 2
day add Δ
1 f1 0
2 f2 0
3 f3 f1
4 f4 f2
5 f5 f1 + f3
实际上,这里有一个分层的感觉。这种涉及到分桶,进位的大多可以与模数之间联系。我们分(m)个桶,当你新添加第(j)天时,由于需要额外增加,会把bucket[j % m]桶中的加到答案中,再进一步更新桶。数很大,注意开long long。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define DEBUG 0
#define int long long
#define pb push_back
#define vt std::vector
#define lb lower_bound
#define sz(x) (int(x.size()))
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mst(x, bit) memset(x, bit, sizeof(x))
#define rep(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i < (r); ++ i)
#define forr(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i >= (r); -- i)
#define dmp(x) cerr << __LINE__ << "->" << #x << " " << x << "
"
using ll = long long;
using db = double;
using pii = pair<int, int>;
using pll = pair<ll, ll>;
template<typename... Args>
inline void wpr(Args... args) { std::cout << '
'; }
template<typename T, typename... Args>
void wpr(T val, Args... args) { std::cout << val << " "; wpr(args...); }
const int maxn = 1e5 + 50;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
void solve(){
int n, m;
std::cin >> n >> m;
vt<int> f(n);
rep (i, 0, n) {
std::cin >> f[i];
}
sort(all(f));
ll ans = 0;
// Layering is related to modulus.
// Saving the sum of number which have same modulus.
vt<ll> buck(m + 1, 0);
rep (k, 0, n){
ans += f[k];
ans += buck[k % m];
buck[k % m] += f[k];
std::cout << ans << "
"[k == n - 1];
}
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
// std::cin >> t;
while (t--) solve();
return 0;
}
D. Harmonious Graph
思路
给定(n)个点,(m)条边的无向图。假设
harmonious的定义是:
- 假如存在(l)到(r)的路径((l < r)),则存在所有((l, m) quad min(l, r))。
请问,假如希望该图满足
harmonious性质,需要增加最少多少个边。Note: (3le nle200;000; 1 le m le 200;000)
Solution1
不难想到将用DSU去处理。假设DSU中的某个连通分量的最小值为lower,最大值为upper。显然,我们需要使得其中所有的点都相互连接,只需要upper - lower + 1 - size(连通分量)。但是,假如我们将其看成区间的形式([lower, upper]),可能存在区间交的情况,我们需要进行区间合并之后再对每个联通分量进行处理。时间复杂度为(O(mlog n)),主要为DSU合并的时间。
但是,通过思考,我们可以发现一个简单的规律。
Solution2
假设DSU中的终极Father永远是连通分量中最大的数。不妨定义(parent(i) 为 i的源点)。那么,假如parent(i) > i则说明区间([i, parent[i]]) 都需要合并。因此,我们每次合并((i, i + 1))即可,这样我们可以通过一次扫描简单的完成任务。
Code
// for Solution2
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define DEBUG 0
#define int long long
#define pb push_back
#define vt std::vector
#define lb lower_bound
#define sz(x) (int(x.size()))
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mst(x, bit) memset(x, bit, sizeof(x))
#define rep(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i < (r); ++ i)
#define forr(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i >= (r); -- i)
#define dmp(x) cerr << __LINE__ << "->" << #x << " " << x << "
"
using ll = long long;
using db = double;
using pii = pair<int, int>;
using pll = pair<ll, ll>;
template<typename... Args>
inline void wpr(Args... args) { std::cout << '
'; }
template<typename T, typename... Args>
void wpr(T val, Args... args) { std::cout << val << " "; wpr(args...); }
const int maxn = 1e5 + 50;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct DSU{
int n, cnt;
// here mx, mn, tot is useless. There are useful for solution 1
vt<int> parent, mx, mn, tot;
void init(int n){
// 1-index
this->n = n; cnt = n;
parent.resize(n + 1), mx.resize(n + 1), mn.resize(n + 1), tot.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++ i){
parent[i] = mx[i] = mn[i] = i;
tot[i] = 1;
}
}
int find(int x){
return x == parent[x] ? x : parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
bool to_union(int x, int y){
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y) return false;
-- cnt;
if (y > x) swap(x, y);
parent[y] = x;
tot[x] += tot[y];
mx[x] = max(mx[x], mx[y]);
mn[x] = min(mn[x], mn[y]);
return true;
}
};
void solve(){
int n, m;
std::cin >> n >> m;
DSU dsu1;
dsu1.init(n);
rep (i, 0, m){
int u, v; std::cin >> u >> v;
dsu1.to_union(u, v);
}
int ans = 0;
rep (i, 1, n){
if (dsu1.find(i) <= i) continue;
ans += dsu1.to_union(i + 1, i);
}
wpr(ans);
}
signed main(){
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
// std::cin >> t;
while (t--) solve();
return 0;
}
E. Antenna Coverage
思路
给定(n)个点,每个点的位置为(x_i)能力值为(s_i),其覆盖范围是([x_i-s_i, x_i+s_i])。
你可以通过消耗一枚硬币增加某个点的一个能力值。
给定最大值(m),计算覆盖([1cdots m])需要的最小硬币数量。
Note:
- (1le n le 80; n le m le 100; 000;)
- (1le x_i le m; 0le s_i le m)
这题刚开始觉得是E肯定比较难,哪知道很套路。因为(n)足够小,我们可以用(mathcal{O(ncdot m)})的算法解决。
假设(dp(i):=完成前i个覆盖的最小值)。
其状态转移如下:
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define DEBUG 0
// #define int long long
#define pb push_back
#define vt std::vector
#define lb lower_bound
#define sz(x) (int(x.size()))
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define mst(x, bit) memset(x, bit, sizeof(x))
#define rep(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i < (r); ++ i)
#define forr(i, l, r) for (ll i = (l); i >= (r); -- i)
#define dmp(x) cerr << __LINE__ << "->" << #x << " " << x << "
"
using ll = long long;
using db = double;
using pii = pair<int, int>;
using pll = pair<ll, ll>;
template<typename... Args>
inline void _wpr_(Args... args) { std::cout << '
'; }
template<typename T, typename... Args>
inline void _wpr_(T val, Args... args) { std::cout << " " << val; _wpr_(args...); }
template<typename T, typename... Args>
void wpr(T val, Args... args) { std::cout << val; _wpr_(args...); }
const int maxn = 1e5 + 50;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int dp[maxn];
int can[maxn];
void solve(){
int n, m; std::cin >> n >> m;
// fi -> position x, se -> scope
vt<pii> f;
// can -> if the position i is include?
rep (i, 0, n){
int x, c; std::cin >> x >> c;
rep (j, max(1, x - c), min(m, x + c) + 1) can[j] = 1;
f.pb(make_pair(x, c));
}
dp[0] = 0;
rep (i, 1, m + 1){
dp[i] = i;
if (can[i]) dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i - 1]);
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i - 1] + 1);
rep (j, 0, n){
// if it is exceeded, not consider.
if (f[j].first > i) continue;
// Len -> cost
int Len = max(0ll, i - f[j].first - f[j].second);
// transfrom from (xi - ci - cost - 1)[the left of the point.]
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[max(0, f[j].first - f[j].second - Len - 1)] + Len);
}
}
wpr(dp[m]);
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
// std::cin >> t;
while (t--) solve();
return 0;
}
后记
- A: 数形结合,增加
dummy node防止边界问题。 - B: 模拟题,贪心考虑。
- C: 和分层有关的考虑模数
- D: 连通分量考虑
DSU,考虑遍历优化策略 - E: 多思考
dp...