3166: [Heoi2013]Alo
Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB
Description
Welcome to ALO ( Arithmetic and Logistic Online)。这是一个VR MMORPG ,
如名字所见,到处充满了数学的谜题。
现在你拥有n颗宝石,每颗宝石有一个能量密度,记为ai,这些宝石的能量
密度两两不同。现在你可以选取连续的一些宝石(必须多于一个)进行融合,设为 ai, ai+1, …, a j,则融合而成的宝石的能量密度为这些宝石中能量密度的次大值
与其他任意一颗宝石的能量密度按位异或的值,即,设该段宝石能量密度次大值
为k,则生成的宝石的能量密度为max{k xor ap | ap ≠ k , i ≤ p ≤ j}。
现在你需要知道你怎么选取需要融合的宝石,才能使生成的宝石能量密度最大。
Input
第一行,一个整数 n,表示宝石个数。
第二行, n个整数,分别表示a1至an,表示每颗宝石的能量密度,保证对于i ≠ j有 ai ≠ aj。
Output
输出一行一个整数,表示最大能生成的宝石能量密度。
Sample Input
5
9 2 1 4 7
Sample Output
14
HINT
【样例解释】
选择区间[1,5],最大值为 7 xor 9。
对于 100%的数据有 1 ≤ n ≤ 50000, 0 ≤ ai ≤ 10^9
题解:
我们不难想到在单调队列题目中用过的一种思路:枚举每个点作为次小值,去找比他大的值,那么能满足题目要求的区间大概长这样:
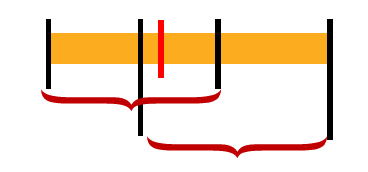
上图中两端被扩起来的区间即为所求。那么现在我们的问题转化为去找每个点从左从右数第二个比他大的值的位置。
这个显然不能用单调队列搞……
由于题目保证每一个数据都不相等,所以我们考虑搞一个set,把数据按权值大小排序,然后插入元素的下标。
由于在插入某个值的时候,比他大的都已经插入了
所以这个时候查询比他大2名的和小2名的即可。
具体实现有一些边界处理的小细节,读者可以结合下面代码思考一下。代码见下:
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <set> 5 using namespace std; 6 typedef long long LL; 7 const int N=50100; 8 struct Trie 9 { 10 Trie *ch[2];int size; 11 Trie(){ch[0]=ch[1]=0,size=0;} 12 }*null=new Trie(),*root[N]; 13 inline Trie* newTrie(){Trie *o=new Trie();o->ch[0]=o->ch[1]=null;return o;} 14 int cnt,stack[N],top;LL bin[40]; 15 set<int>st; 16 struct node{int pos,val;}a[N]; 17 inline bool mt(const node &a,const node &b){return a.val>b.val;} 18 void Insert(Trie *&o,Trie *old,int val,int i) 19 { 20 if(i<0)return; 21 int d=((val&bin[i])==bin[i]); 22 o->ch[d]=newTrie(),o->ch[d^1]=old->ch[d^1]; 23 o->ch[d]->size=old->ch[d]->size+1; 24 Insert(o->ch[d],old->ch[d],val,i-1); 25 } 26 inline int query(int a,int b,int val) 27 { 28 int ret=0; 29 Trie *x=root[a],*y=root[b]; 30 for(int i=30;~i;i--) 31 { 32 int d=(val&bin[i])>>i; 33 if(y->ch[d^1]->size-x->ch[d^1]->size) 34 ret|=bin[i],y=y->ch[d^1],x=x->ch[d^1]; 35 else y=y->ch[d],x=x->ch[d]; 36 } 37 return ret; 38 } 39 int main() 40 { 41 int n;scanf("%d",&n); 42 bin[0]=1;for(int i=1;i<=35;i++)bin[i]=bin[i-1]<<1; 43 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)root[i]=newTrie(); 44 null->ch[0]=null->ch[1]=null; 45 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 46 scanf("%d",&a[i].val),a[i].pos=i,Insert(root[i],root[i-1],a[i].val,30); 47 sort(a+1,a+n+1,mt); 48 st.insert(-1);st.insert(-2);st.insert(-3); 49 st.insert(n+1);st.insert(n+2);st.insert(n+3); 50 st.insert(a[1].pos); 51 int ans=0; 52 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) 53 { 54 set<int>::iterator a1,a2; 55 a2=st.lower_bound(a[i].pos); 56 a1=a2;a2++;a1--;a1--; 57 int l=*a1+1,r=*a2-1; 58 l=max(l,1),r=min(n,r); 59 ans=max(ans,query(l-1,r,a[i].val)); 60 st.insert(a[i].pos); 61 } 62 printf("%d ",ans); 63 }