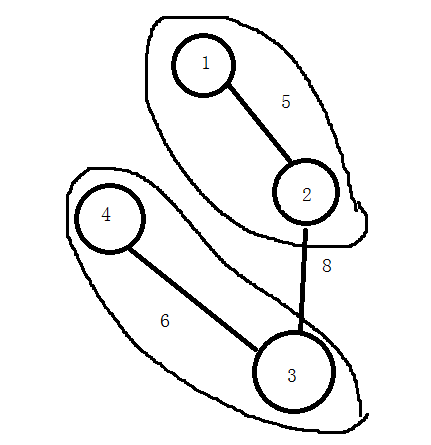
示例1
输入
2
4
1 2 5
2 3 8
3 4 6
6
1 3 5
3 2 3
4 5 4
4 3 9
4 6 10
输出
11
31
说明
In the first example, you can divide them into (1,2), and (3,4), then the minimum sum of length is 5+6=11
In the second example, you can divide them into (1,3),(2,4),(5,6), hen the minimum sum of length is 5+(3+9)+(10+4)=31
1. 推理
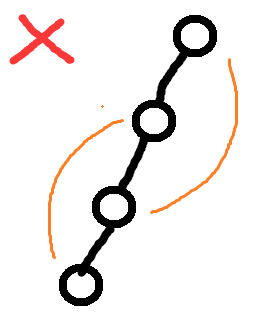
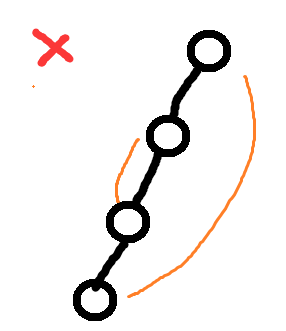
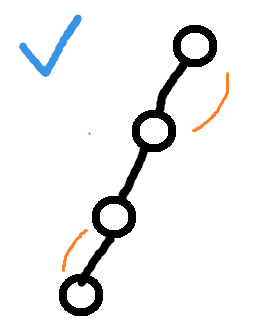
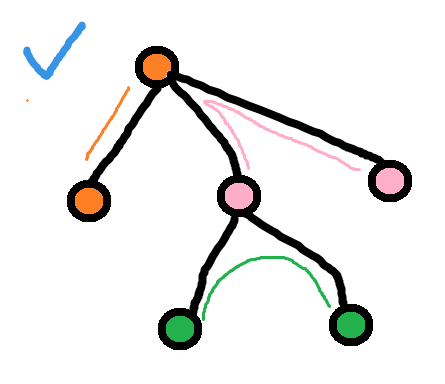
图a
图b
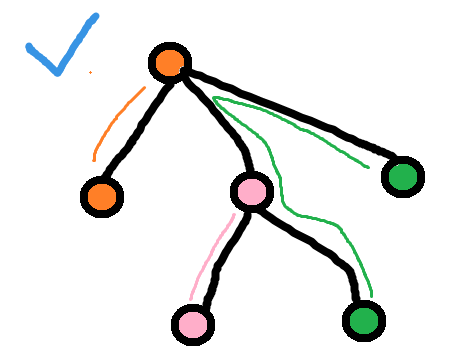
通过观察,每个边在最小距离和中只有选or不选, 不能重复选择(假设方案有重复,则必有更优的方案)
2. DFS
为了尽量避免选重边,尽可能在节点所在子树内部里寻找答案(比如上面的图a,b中, 尽量选择图a这样辈分差得不多, 条理更清晰的)
- 若一棵子树中的节点有偶数个(含当前根节点),那么两两配对即可,不用添加新的边权。
- 若一棵子树有奇数个节点(含当前根节点),那么当前子树除根节点外都可以内部消化掉, 根节点只能回老家找它的兄弟子树or父亲连边。
实现方法为DFS, 不妨以①为根节点, 向邻接点(除父节点)递归, 每次都要记录当前子树的节点个数, 并在递归回来的时候更新
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4+10, M = 2e4+10;
int h[M], w[M], e[M], ne[M], idx;
long long res;
int treesize[N];
void add(int x, int y, int z)//增加单向边, x--(z)-->y
{
e[idx]=y, ne[idx]=h[x], w[idx]=z, h[x]=idx++;
}
void dfs(int u, int fa, int len)
{
treesize[u] = 1;
for(int i = h[u]; ~i; i=ne[i])//遍历临接点
{
int j = e[i];
if(j == fa) continue;
dfs(j, u, w[i]); //向下递归子树
treesize[u] += treesize[j];
}
if(treesize[u]%2) res += len; //以u为根的整棵树的点数(含u)
}
int main()
{
int t, n;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t --)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
res = 0, idx = 0;
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
memset(treesize, 0, sizeof(treesize));
int x, y, z;
for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i ++){
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &z);
add(x, y, z), add(y, x, z);
}
dfs(1, 0, 0);
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
return 0;
}