IO流
概念:
IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输
Java对数据的操作是通过流的方式
Java用于操作流的类都在IO包中
流按流向分为两种:输入流,输出流
流按流操作类型分为两种:
字节流:字节流可以操作任何数据,因在计算机任何数据都是以字节的形式存储的
字符流:字符流只能操作纯字符数据,比较方便
IO流常用父类:
字节流的抽象父类
InputStream
OutputStream
字符类的抽象方法:
Reader
Writer
IO程序书写
使用前,导入IO包中的类
使用时,进行IO异常处理
使用后,释放资源
InputStream

import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; public class demo1_FileInputStraem { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //demo1(); FileInputStream fis =new FileInputStream("xxx.txt"); int a; while ((a=fis.read()) !=-1) { System.out.println(a); } fis.close(); } public static void demo1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { FileInputStream fis =new FileInputStream("xxx.txt");//创建流对象 int x=fis.read(); //从硬盘上读取一个字节 System.out.println(x); int y=fis.read(); System.out.println(y); int z=fis.read(); System.out.println(z); int c=fis.read(); System.out.println(c); fis.close(); //关流释放资源 } }
read()方法读取的是一个字节,为什么返回是int,而不是byte
因为字节输入流可以操作任意类型的文件,比如图片音频等,这些文件底层都是以而至今形式的存储的,如果每次读取都返回byte,有可能在读到中间的时候遇到11111111
那么这11111111是byte类型的-1 ,我们的程序是遇到 -1 就会停止不读了,后面的数据就读不到了,所以在读取的时候用int类型接受,如果11111111会在其前面补上
24个0凑足4个字节,那么byte类型的 -1 就变成int类型的255了这样可以保证整个数据读完,而接受标记的 -1 就是int类型
OutputStream
在创建对象的时候是如果没有这个文件夹会帮我创建出来
如果有这个文件就会先将文件清空
参数追加 加true

import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class demo2_OutputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos =new FileOutputStream("yyy.txt"); //创建字节输出流对象,如果没有就自动创建一个 fos.write(97); //俗人写出的是一个int数,但是到文件上的是一个字节,会自动去除前三 个8位 fos.write(98); fos.write(99); System.out.println(fos); fos.close(); } }
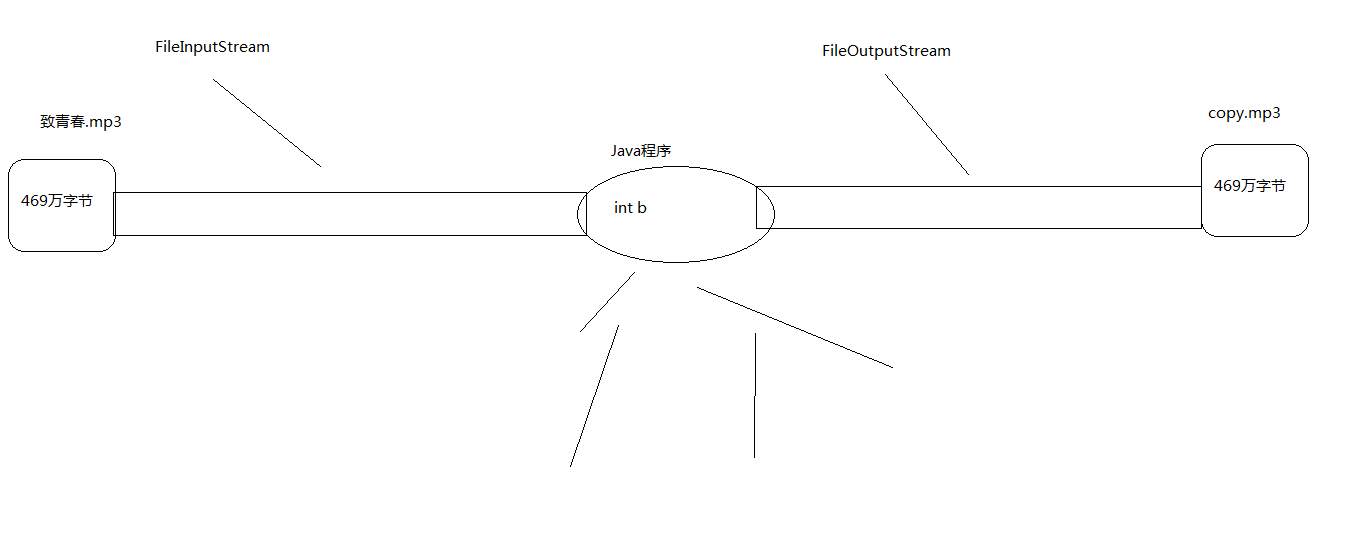
拷贝图片

import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class demo3_Copy { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //demo1(); FileInputStream fil1=new FileInputStream("忽然之间.mp3"); //创建输入流对象,关联双元.jpg FileOutputStream fil2=new FileOutputStream("copy.mp3");//创建输出流对象,关联copy.jpg int b; while ((b =fil1.read()) !=-1) { //在不断的读取每一个字节 fil2.write(b); //将每个字节写出 } fil1.close();//关流释放资源 fil2.close(); } public static void demo1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { FileInputStream fil1=new FileInputStream("1.JPG"); //创建输入流对象,关联双元.jpg FileOutputStream fil2=new FileOutputStream("copy.jpg");//创建输出流对象,关联copy.jpg int b; while ((b =fil1.read()) !=-1) { //在不断的读取每一个字节 fil2.write(b); //将每个字节写出 } fil1.close();//关流释放资源 fil2.close(); } }
拷贝视频图解
字节数组拷贝-available()方法
int read(byte [ ] b):一次读取一个字节数组
write(byte [ ] b):一次写出一个字节数组
available()获取读的文件所有的字节个数
第二种拷贝
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //demo1(); //demo2(); //有可能会导致内存溢出 FileInputStream fil1=new FileInputStream("忽然之间.mp3"); FileOutputStream fil2=new FileOutputStream("copy.mp3"); //int len=fil1.available(); //System.out.println(len); byte [] arr=new byte[fil1.available()];//创建与文件一样大小的字节数组 fil1.read(arr); //将文件上的字节读取到内存中 fil2.write(arr);//将字节数组中的字节数据写到文件上 fil1.close(); fil2.close(); } }
定义小数组
*write(byte [ ] b)
*write(byte [ ] b, int off, int len )写出有效的字节个数
1024 * 8

public class demo_arrayCopy { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //demo1(); FileInputStream fis =new FileInputStream("xxx.txt"); FileOutputStream fos =new FileOutputStream("aaa.txt"); byte[] arr= new byte[2]; int len; while ((len=fis.read(arr)) !=-1) { fos.write(arr,0,len); } fis.close(); fos.close(); } }
BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutputSteram 拷贝
缓冲思想
字节流一次读写一个数字的速度明显比一次读写一个字节的速度快很多
这是加入了数字这样的缓冲区效果,java本身在设计的时候
也考虑到了这样的设计思想(装饰设计模式后面讲解),所以提供了字节缓冲区流
BufferedInputStream
BufferedInputStream内置了一个缓冲区(数字)
从BufferedInputStream中读取一个字节
BufferedInputStream会一次性从文件中读取8192个,存在缓冲区中,返回给程序一个
程序再次读取时,就不用找文件了,直接从缓冲区中获取
知道缓冲区中所有的都被使用过,才重新从文件中读取8192个
BufferedOutputSteram
BufferedOutputSteram 也内置了一个缓冲区(数组)
程序向流中写出字节时,不会直接写道文件,先写到缓冲区中
知道缓冲区写满,BufferedOutputSteram 才会把缓冲区中的数据一次性写到文件里
拷贝代码
FileInputStream fis =new FileInputStream("忽然之间.pm3"); //创建输入流对象,关联mp3 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("copy1.pm3"); //创建输出流对象,关联copy.pm3 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); //创建缓冲区对象,对输入流进行包装让其变得更加强大 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); int b; while ((b=bis.read()) != -1) { bos.write(b); } bis.close(); bos.close();
flus和close
Flus()方法
*用来刷新缓冲区的,刷新后可以再次写出
colse()方法
*用来关闭流释放资源的,如果是带缓冲区的流对象的colse()方法,不但会关闭流,换回再关闭之前刷新缓冲区,关闭后不能再写出
colse 具备刷新的功能,再关闭流之前,就会先刷新一次缓冲区,将缓冲区的字节全都刷新到文件上,再关闭
IO流(字节流读写中文)
字节流读取中文的问题
*字节流再度中文的时候有可能会读到半个中文,造成乱码
字节流写出中文的问题
*字节流直接操作的字节,所以写出中文必须将字符串转换成字节数组
*写出回车换行 write(“ ”.getBytes( ));

public class demo6_Chinese { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //demo1(); FileOutputStream f1= new FileOutputStream("yyy.txt"); f1.write("我爱学习".getBytes()); f1.close(); } public static void demo1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { FileInputStream f1= new FileInputStream("xxx.txt"); byte [] arr =new byte [4]; int len; while((len =f1.read(arr)) != -1){ System.out.println(new String(arr,0,len)); } f1.close(); } }
IO流的标准异常处理
 1.6版本
1.6版本图片加密
public class test1 { //将写出的字节异或上一个出,这个数就是秘钥,解密的时候在此异或就行了 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedInputStream b1 =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("copy.jpg")); BufferedOutputStream b2 =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("copy2.jpg")); int b; while((b =b1.read()) != -1){ b2.write(b ^ 123); } b1.close(); b2.close(); } }
拷贝文件

public class test2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file =getFile(); //获取文件 BufferedInputStream b1=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); BufferedOutputStream b2 =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file.getName())); int b; while((b =b1.read()) != -1){ b2.write(b); } b1.close(); b2.close(); } public static File getFile(){ Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入一个文件的路径"); while(true){ String line =sc.nextLine(); File file =new File(line); //封装成File对象,并进行进行判断 if(!file.exists()){ System.out.println("你录入的文件路径不存在,请重新录入"); }else if(file.isDirectory()){ System.out.println("你录入的文件夹路径,请重新录入"); }else { return file; } } } }
录入数据拷贝文件

public class text3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in); //创建输出流对象,关联text.txt文件 FileOutputStream f1 =new FileOutputStream("text.txt"); System.out.println("请输入数据"); //定义无限循环 while(true){ String line =sc.nextLine(); if("quit".equals(line)){ break; } f1.write(line.getBytes()); f1.write(" ".getBytes()); } f1.close(); } }
