【背景】
最近在看django官方文档的class-based-views这一节的时候一直不得要领,感觉自己清楚,但是回想起来又没有脉络;于是没有办法只
能是“暗中观察”django的源码了。 刚打开源码看了没有多久就疑窦丛生,比如说下面这一段,能看的出get_object方法中用到的self.kwargs
属性是在哪里设置过呢?如果没有设置直接用是会有报错的,详细内容看下面源码
class SingleObjectMixin(ContextMixin): """ Provide the ability to retrieve a single object for further manipulation. """ model = None queryset = None slug_field = 'slug' context_object_name = None slug_url_kwarg = 'slug' pk_url_kwarg = 'pk' query_pk_and_slug = False def get_object(self, queryset=None): """ Return the object the view is displaying. Require `self.queryset` and a `pk` or `slug` argument in the URLconf. Subclasses can override this to return any object. """ # Use a custom queryset if provided; this is required for subclasses # like DateDetailView if queryset is None: queryset = self.get_queryset() # Next, try looking up by primary key. pk = self.kwargs.get(self.pk_url_kwarg) slug = self.kwargs.get(self.slug_url_kwarg) if pk is not None: queryset = queryset.filter(pk=pk) # Next, try looking up by slug. if slug is not None and (pk is None or self.query_pk_and_slug): slug_field = self.get_slug_field() queryset = queryset.filter(**{slug_field: slug}) # If none of those are defined, it's an error. if pk is None and slug is None: raise AttributeError( "Generic detail view %s must be called with either an object " "pk or a slug in the URLconf." % self.__class__.__name__ ) try: # Get the single item from the filtered queryset obj = queryset.get() except queryset.model.DoesNotExist: raise Http404(_("No %(verbose_name)s found matching the query") % {'verbose_name': queryset.model._meta.verbose_name}) return obj def get_queryset(self): """ Return the `QuerySet` that will be used to look up the object. This method is called by the default implementation of get_object() and may not be called if get_object() is overridden. """ if self.queryset is None: if self.model: return self.model._default_manager.all() else: raise ImproperlyConfigured( "%(cls)s is missing a QuerySet. Define " "%(cls)s.model, %(cls)s.queryset, or override " "%(cls)s.get_queryset()." % { 'cls': self.__class__.__name__ } ) return self.queryset.all() def get_slug_field(self): """Get the name of a slug field to be used to look up by slug.""" return self.slug_field def get_context_object_name(self, obj): """Get the name to use for the object.""" if self.context_object_name: return self.context_object_name elif isinstance(obj, models.Model): return obj._meta.model_name else: return None def get_context_data(self, **kwargs): """Insert the single object into the context dict.""" context = {} if self.object: context['object'] = self.object context_object_name = self.get_context_object_name(self.object) if context_object_name: context[context_object_name] = self.object context.update(kwargs) return super().get_context_data(**context)
【众里寻它】
一看SingleObjectMixin类的定义发现它里面并没有kwargs这个属性、所以这个kwargs属性应该在是定义在它的父类里、ContextMixin源码如下
class ContextMixin: """ A default context mixin that passes the keyword arguments received by get_context_data() as the template context. """ extra_context = None def get_context_data(self, **kwargs): kwargs.setdefault('view', self) if self.extra_context is not None: kwargs.update(self.extra_context) return kwargs
!我的天kwargs没有在父类里、也不可能在object类里面。粗看起来get_object方法用使用self.kwargs已经违反Python这门语言的基本法了,但是
这个的可能性也不太;django这么有名的一个项目,而且自己在使用这上块的功能时并没有出问题。
【刻苦学习在View.as_view方法中发现新的天地】
class View: http_method_names = ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace'] def __init__(self, **kwargs): for key, value in kwargs.items(): setattr(self, key, value) @classonlymethod def as_view(cls, **initkwargs): """Main entry point for a request-response process.""" #不允许给View的实例传入get/post/head这样的字段、原因是这些名字是留给方法用的! for key in initkwargs: if key in cls.http_method_names: raise TypeError("You tried to pass in the %s method name as a " "keyword argument to %s(). Don't do that." % (key, cls.__name__)) #如下View类中已经定义了这个“名字”,为了防止实例覆盖类的同名属性所以这里也不支持传入同名属性 if not hasattr(cls, key): raise TypeError("%s() received an invalid keyword %r. as_view " "only accepts arguments that are already " "attributes of the class." % (cls.__name__, key)) #如果上面的检查都过了,但是django并没有步入通常的套路。它在这里定义了一个叫view的函数,它在view中创建View类的实例 def view(request, *args, **kwargs): #通过as_veiw中传入的参数来创建一个view实例、由__init__可以知道它是对**kwargs全盘接收的 #initkwargs是通过闭包的形式记录下来的 self = cls(**initkwargs) #在没有指定`head`方法的情况下就直接用`get`来处理`head` if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'): self.head = self.get #下面这三行搞的对于任何一个通过上述方试创建出来的View实例都有了request、args、kwargs这三个属性 self.request = request self.args = args self.kwargs = kwargs #调用 调度方法、以调度方法的返回结果为view这个Function的执行结果、由于调度方法会调用get | post | head ... 而这些方法都返回 #HttpResponse所以view最终返回的就是HttpResponse的实例 return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) view.view_class = cls view.view_initkwargs = initkwargs update_wrapper(view, cls, updated=()) update_wrapper(view, cls.dispatch, assigned=()) return view def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """根据http的不同请求方式、调用不同的方法、并返回HttpResponse""" if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names: handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed) else: handler = self.http_method_not_allowed return handler(request, *args, **kwargs) def http_method_not_allowed(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """用于设定当客户端使用了不被支持的请求方式时应该如何处理 """ logger.warning( 'Method Not Allowed (%s): %s', request.method, request.path, extra={'status_code': 405, 'request': request} ) return HttpResponseNotAllowed(self._allowed_methods())
可以看到as_view里面做了一个操作叫 self.kwargs = kwargs 、看到了希望!我的三观还能保全、还要进一步求证这两个self.kwargs是不是同一个
【找到关键】
1、在使用View时只能用as_view方式
urlpatterns = [ path('publishers/', PublisherList.as_view()), ]
2、我们并不直接使用SingleObjectMixin而是使用DetailView、而DetailView就给实例加上了self.kwargs = kwargs这一层逻辑
class BaseDetailView(SingleObjectMixin, View): """A base view for displaying a single object.""" def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): self.object = self.get_object() context = self.get_context_data(object=self.object) return self.render_to_response(context) class SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin(TemplateResponseMixin): template_name_field = None template_name_suffix = '_detail' class DetailView(SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin, BaseDetailView): """ Render a "detail" view of an object. By default this is a model instance looked up from `self.queryset`, but the view will support display of *any* object by overriding `self.get_object()`. """
可以看到BaseDetailView把SingleObjectMixin和View、也就是说第一个BaseDetailView的实例都会有kwargs属性,这个原因可以追溯到
“刻苦学习在View.as_view方法中发现新的天地”这一节中提到的self.kwargs = kwargs。
由于View的实例都是由as_view创建的、在as_view的逻辑里面就会给实例加上kwargs属性、SingleObjectMixin.get_object中执行self.kwargs
自然就不会有错误了!
【DetailView相关的层次结构】
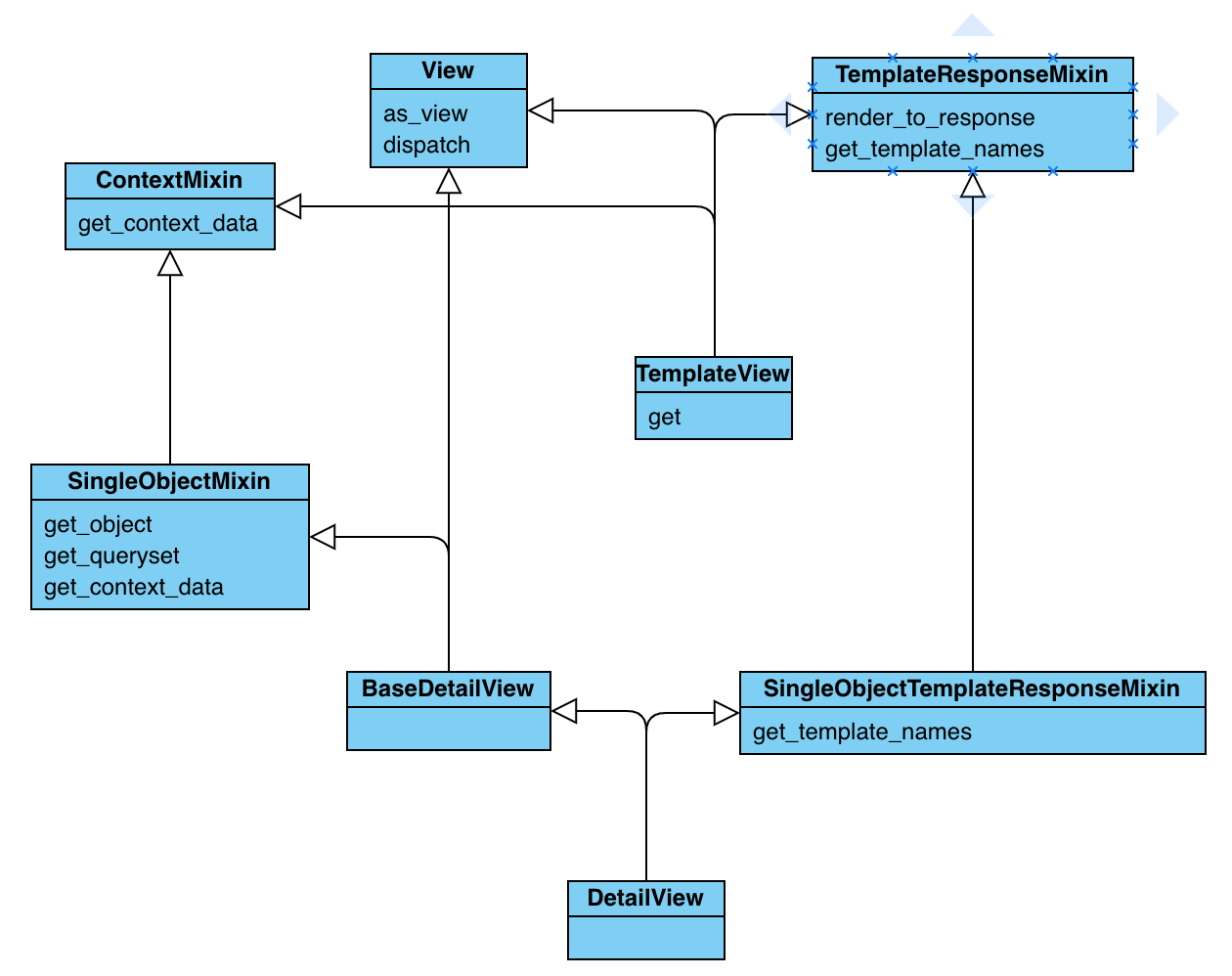
----