在开始介绍k8s持久化存储前,我们有必要了解一下k8s的emptydir和hostpath、configmap以及secret的机制和用途。
0x00 Emptydir
EmptyDir是一个空目录,他的生命周期和所属的 Pod 是完全一致的,EmptyDir主要作用可以在同一 Pod 内的不同容器之间共享工作过程中产生的文件。如果Pod配置了emptyDir类型Volume, Pod 被分配到Node上时候,会创建emptyDir,只要Pod运行在Node上,emptyDir都会存在(容器挂掉不会导致emptyDir丢失数据),但是如果Pod从Node上被删除(Pod被删除,或者Pod发生迁移),emptyDir也会被删除,并且永久丢失。
# cat emptydir.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: busybox spec: containers: - name : busybox image: registry.fjhb.cn/busybox imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent command: - sleep - "3600" volumeMounts: - mountPath: /busybox-data name: data volumes: - name: data emptyDir: {}
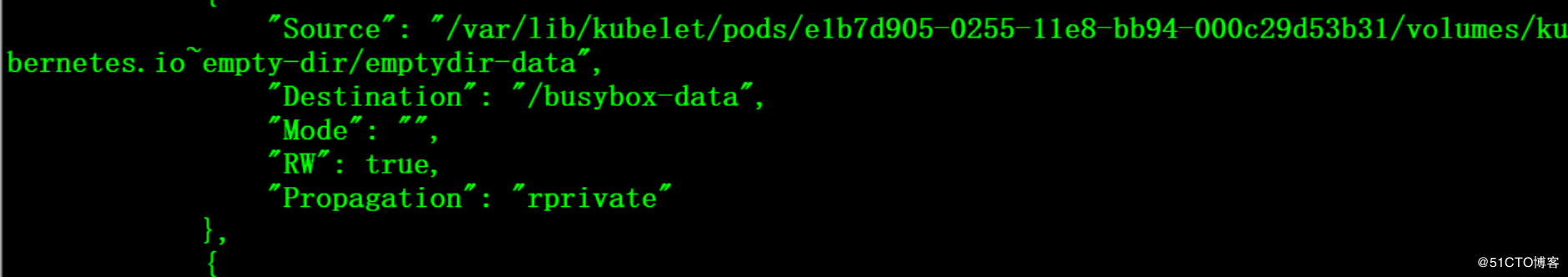
0x01 Hostpath
Hostpath会把宿主机上的指定卷加载到容器之中,如果 Pod 发生跨主机的重建,其内容就难保证了。这种卷一般和DaemonSet搭配使用。hostPath允许挂载Node上的文件系统到Pod里面去。如果Pod有需要使用Node上的东西,可以使用hostPath,不过不过建议使用,因为理论上Pod不应该感知Node的。
# cat hostpath.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: busybox spec: containers: - name : busybox image: registry.fjhb.cn/busybox imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent command: - sleep - "3600" volumeMounts: - mountPath: /busybox-data name: data volumes: - hostPath: path: /tmp name: data
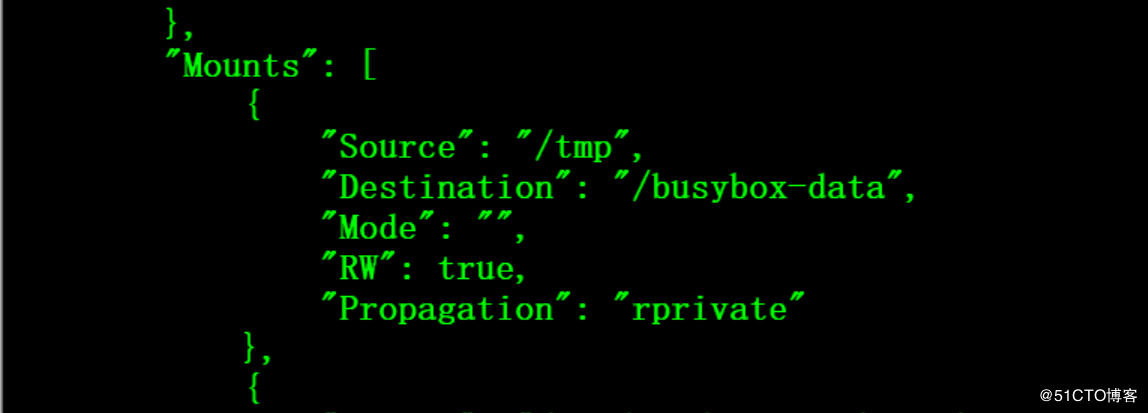
emptyDir和hostPat很多场景是无法满足持久化需求,因为在Pod发生迁移的时候,数据都无法进行转移的,这就需要分布式文件系统的支持。
0x02 Configmap
镜像使用的过程中,经常需要利用配置文件、启动脚本等方式来影响容器的运行方式,如果仅有少量配置,我们可以使用环境变量的方式来进行配置。然而对于一些较为复杂的配置,k8s提供了configmap解决方案。
ConfigMap API资源存储键/值对配置数据,这些数据可以在pods里使用。
ConfigMap跟Secrets类似,但是ConfigMap可以更方便的处理不包含敏感信息的字符串。
当ConfigMap以数据卷的形式挂载进Pod的时,这时更新ConfigMap(或删掉重建ConfigMap),Pod内挂载的配置信息会热更新。这时可以增加一些监测配置文件变更的脚本,然后reload对应服务
ConfigMap的API概念上来说是很简单的。从数据角度来看,ConfigMap的类型只是键值组。应用可以从不同角度来配置。在一个pod里面使用ConfigMap大致有三种方式:
1、命令行参数
2、环境变量
3、数据卷文件
将变量做成configmap

将nginx配置文件做成configmap
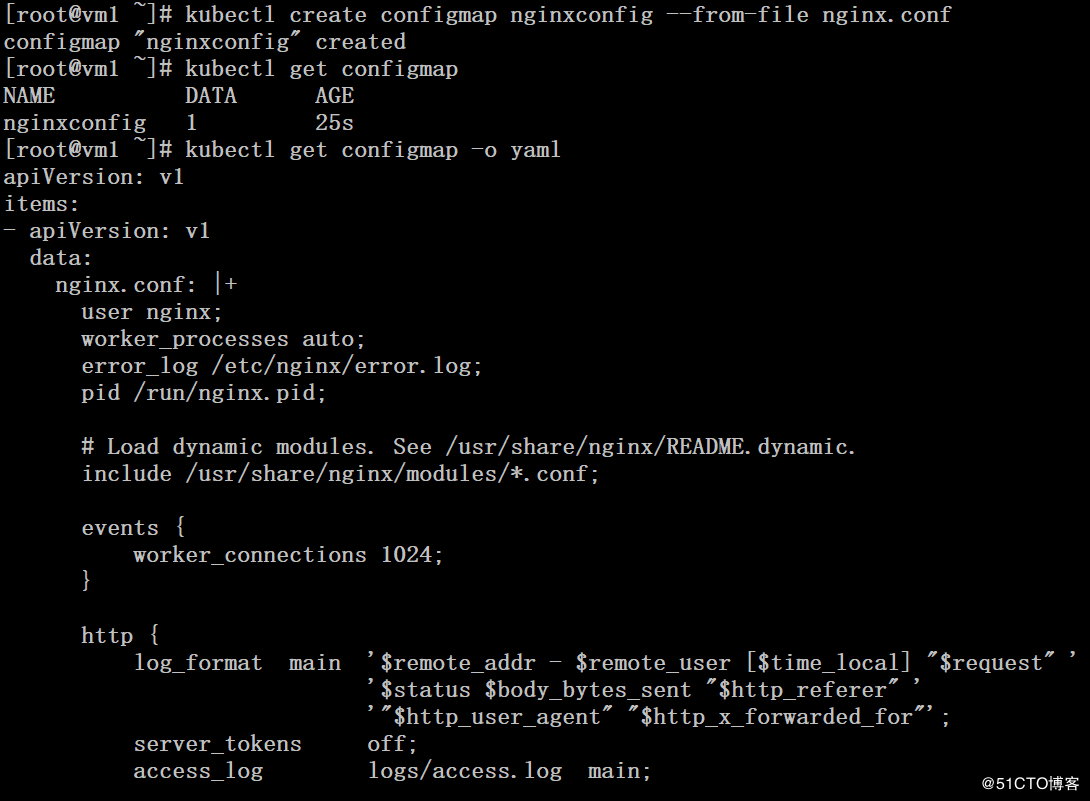
[root@vm1 ~]# cat nginx.conf user nginx; worker_processes auto; error_log /etc/nginx/error.log; pid /run/nginx.pid; # Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic. include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; server_tokens off; access_log /usr/share/nginx/html/access.log main; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; keepalive_timeout 65; types_hash_max_size 2048; include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; server { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server; server_name _; root /usr/share/nginx/html; include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; location / { } error_page 404 /404.html; location = /40x.html { } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { } } }
# kubectl create configmap nginxconfig --from-file nginx.conf # kubectl get configmap # kubectl get configmap -o yaml
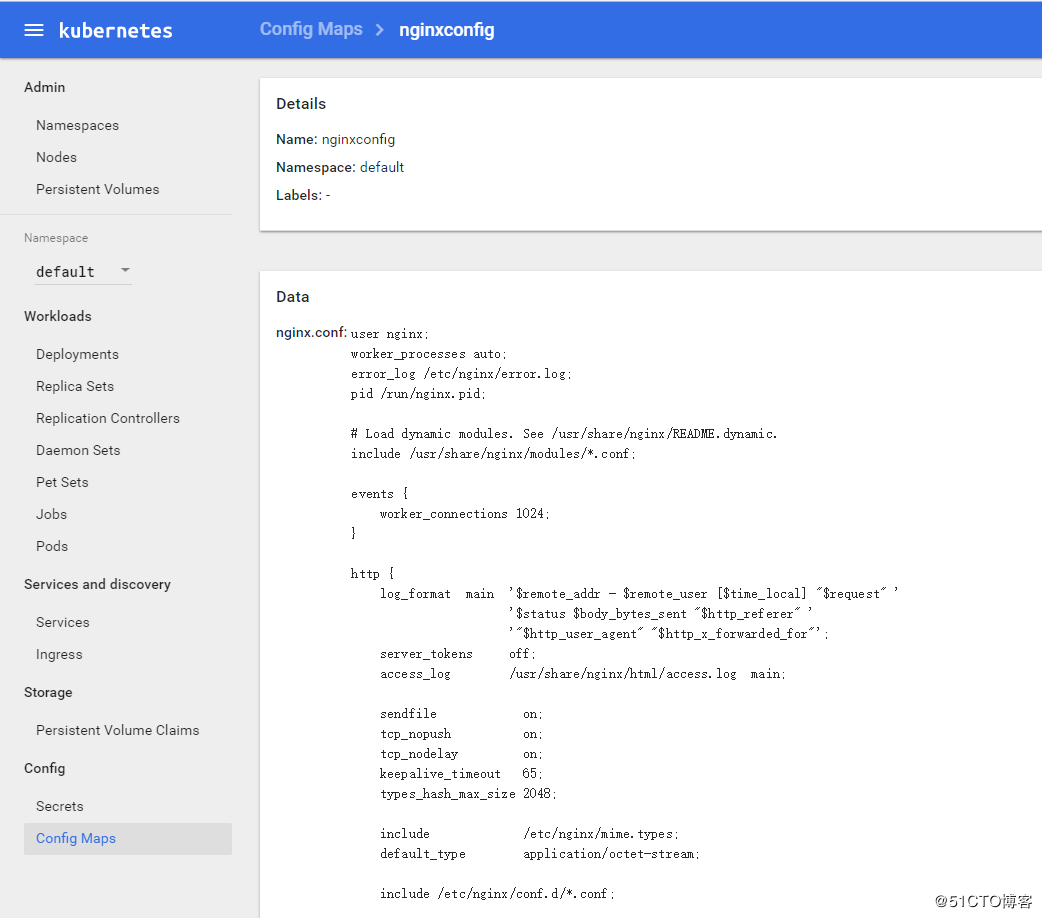
在rc配置文件中使用configmap
# cat nginx-rc-configmap.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ReplicationController metadata: name: nginx labels: name: nginx spec: replicas: 2 selector: name: nginx template: metadata: labels: name: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: docker.io/nginx volumeMounts: - name: nginx-etc mountPath: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf subPath: nginx.conf ports: - containerPort: 80 volumes: - name: nginx-etc configMap: name: nginxconfig items: - key: nginx.conf path: nginx.conf
# kubectl create -f nginx-rc-configmap.yaml
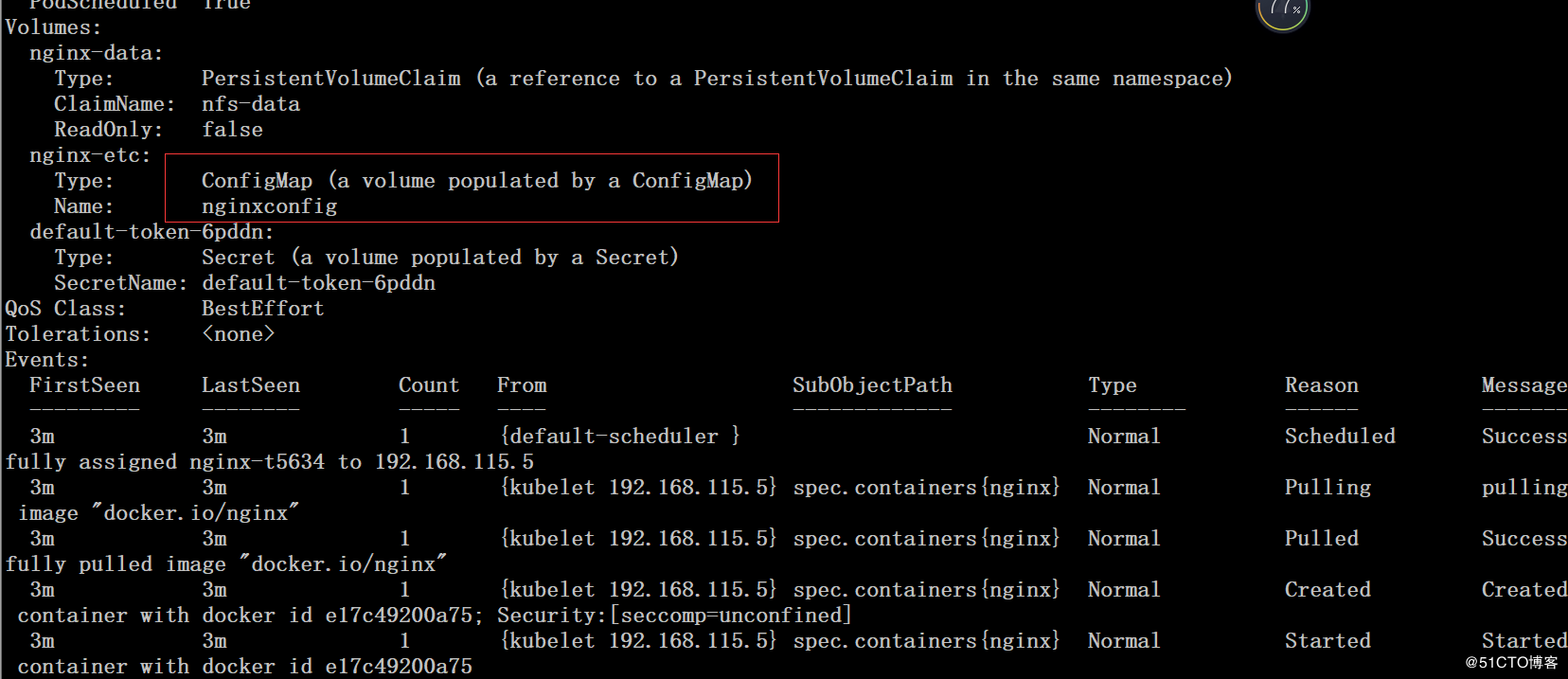
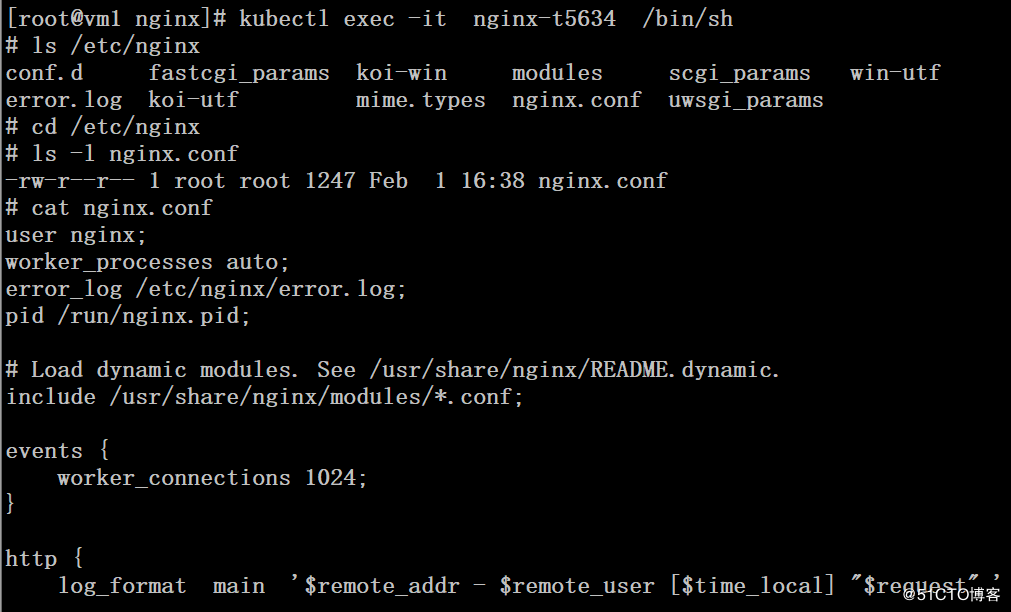
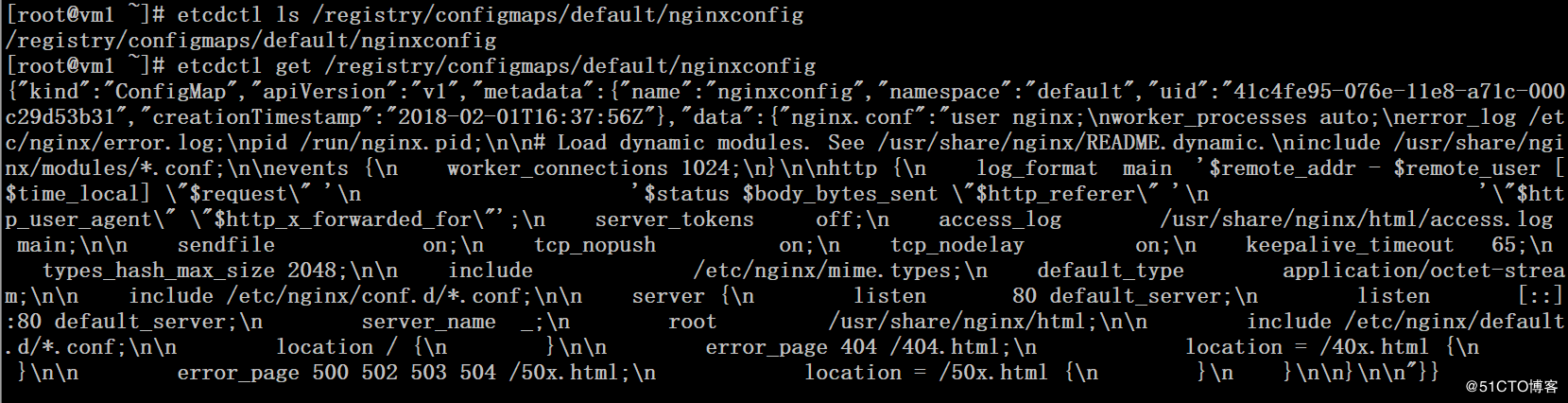
configmap的信息实际是存储在etcd中的,可以使用kubectl edit configmap xxx 来对configmap进行修改
# etcdctl ls /registry/configmaps/default # etcdctl get /registry/configmaps/default/nginxconfig
0x03 Secret
Kubemetes提供了Secret来处理敏感数据,比如密码、Token和密钥,相比于直接将敏感数据配置在Pod的定义或者镜像中,Secret提供了更加安全的机制(Base64加密),防止数据泄露。Secret的创建是独立于Pod的,以数据卷的形式挂载到Pod中,Secret的数据将以文件的形式保存,容器通过读取文件可以获取需要的数据。
目前Secret的类型有3种:
Opaque(default): 任意字符串
kubernetes.io/service-account-token: 作用于ServiceAccount
kubernetes.io/dockercfg: 作用于Docker registry,用户下载docker镜像认证使用
secert的具体配置在前文serviceaccount中已经介绍过了,本文不再赘述。
下面我们来介绍一下k8s的持久化存储方案,目前k8s支持的存储方案主要如下:
分布式文件系统:NFS/GlusterFS/CephFS
公有云存储方案:AWS/GCE/Auzre
0x04 Nfs存储方案
NFS 是Network File System的缩写,即网络文件系统。Kubernetes中通过简单地配置就可以挂载NFS到Pod中,而NFS中的数据是可以永久保存的,同时NFS支持同时写操作。
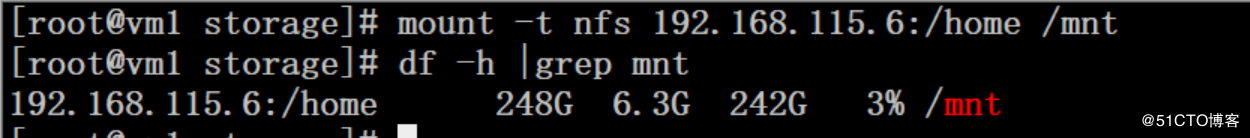
4.1 首先安装nfs
# yum -y install nfs-util* # cat /etc/exports /home 192.168.115.0/24(rw,sync,no_root_squash) # systemctl start rpcbind # systemctl start nfs # showmount -e 127.0.0.1 Export list for 127.0.0.1: /home 192.168.115.0/24
4.2 使用pod直接挂载nfs
要保证集群内所有的node节点都可以挂载nfs
# cat nfs.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: busybox spec: containers: - name : busybox image: registry.fjhb.cn/busybox imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent command: - sleep - "3600" volumeMounts: - mountPath: /busybox-nfsdata name: nfsdata volumes: - name: nfsdata nfs: server: 192.168.115.6 path: /home
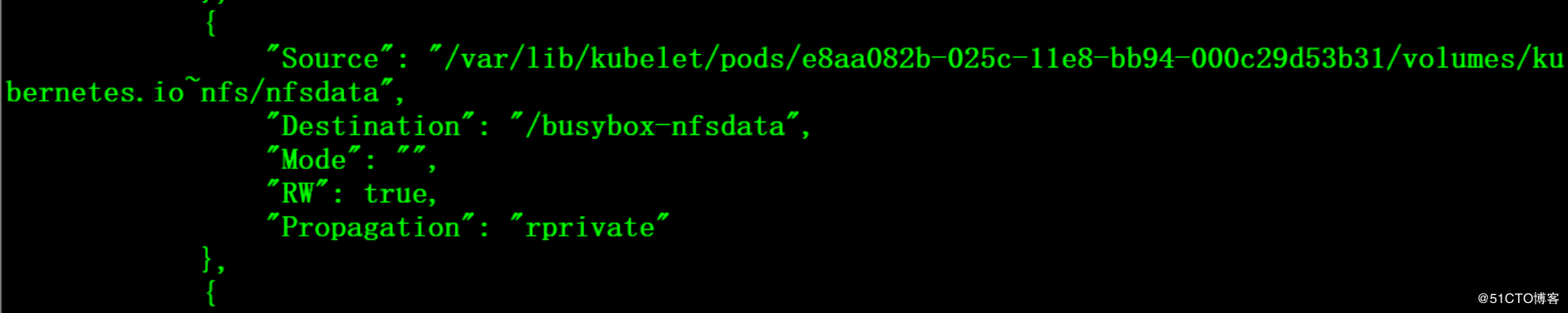

4.3 使用PV和PVC
在实际的使用中,我们通常会将各存储划分成PV,然后和PVC绑定给pod使用。
PV:PersistentVolume
PVC:PersistentVolumeClaim
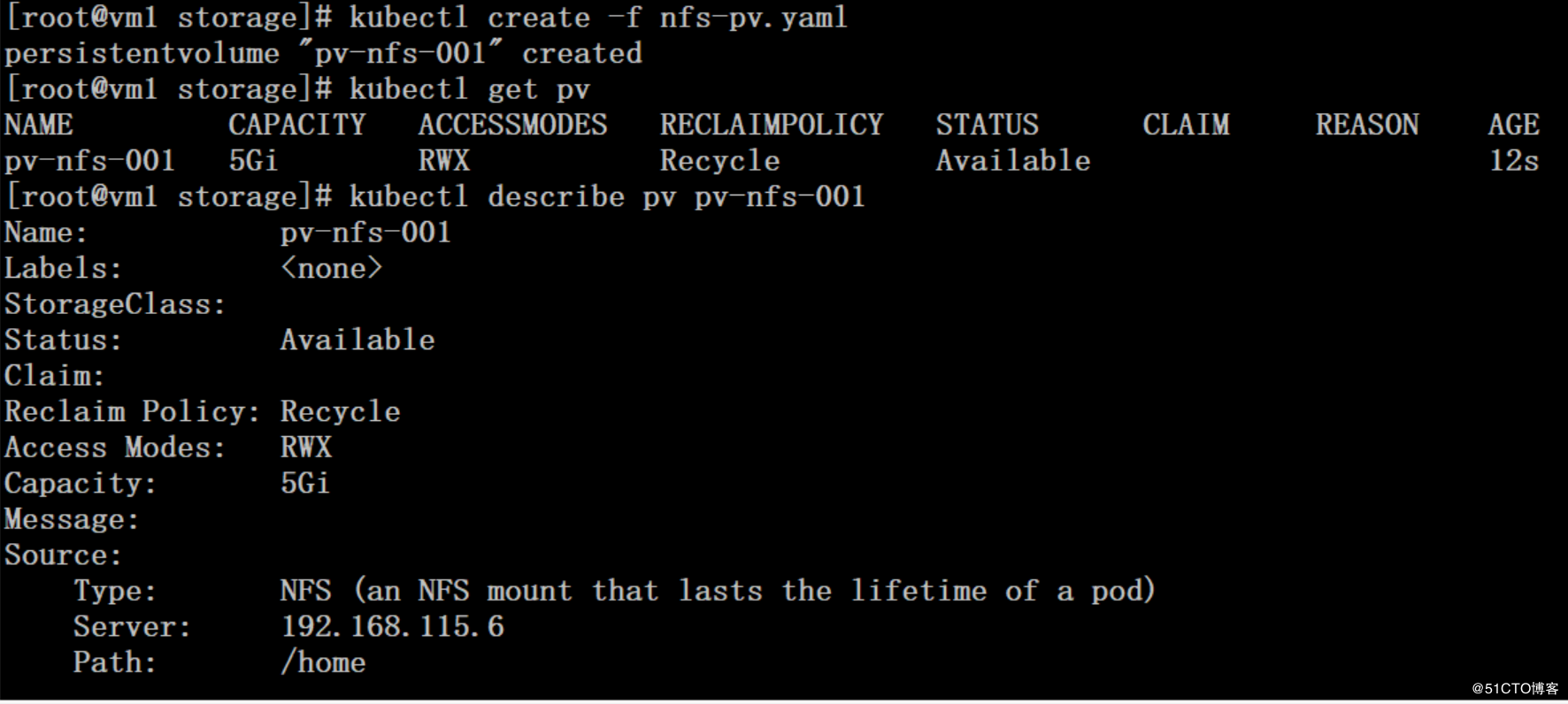
# PV和PVC的生命周期: 供应准备:通过集群外的存储系统或者公有云存储方案来提供存储持久化支持。 静态提供:管理员手动创建多个PV,供PVC使用。 动态提供:动态创建PVC特定的PV,并绑定。 绑定:用户创建pvc并指定需要的资源和访问模式。在找到可用pv之前,pvc会保持未绑定状态。 使用:用户可在pod中像使用volume一样使用pvc。 释放:用户删除pvc来回收存储资源,pv将变成“released”状态。由于还保留着之前的数据,这些数据需要根据不同的策略来处理,否则这些存储资源无法被其他pvc使用。 回收(Reclaiming):pv可以设置三种回收策略:保留(Retain),回收(Recycle)和删除(Delete) 保留策略:允许人工处理保留的数据。 删除策略:将删除pv和外部关联的存储资源,需要插件支持。 回收策略:将执行清除操作,之后可以被新的pvc使用,需要插件支持。 # PV卷阶段状态: Available – 资源尚未被PVC使用 Bound – 卷已经被绑定到PVC了 Released – PVC被删除,PV卷处于释放状态,但未被集群回收。 Failed – PV卷自动回收失败 # PV卷的访问模式 ReadWriteOnce – 单node的读写 ReadOnlyMany – 多node的只读 ReadWriteMany – 多node的读写
创建pv与pvc
# cat nfs-pv.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: pv-nfs-001 spec: capacity: storage: 5Gi accessModes: - ReadWriteMany nfs: path: /home server: 192.168.115.6 persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
# cat nfs-pvc.yaml kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: nfs-data spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany resources: requests: storage: 5Gi
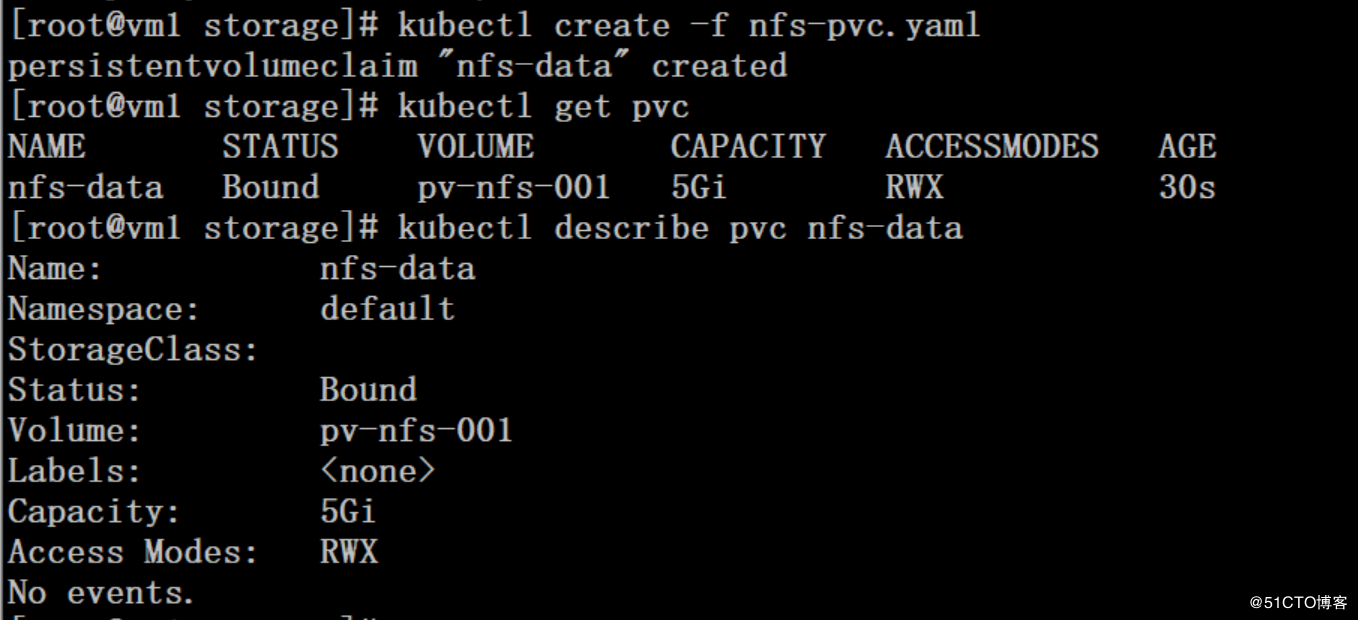
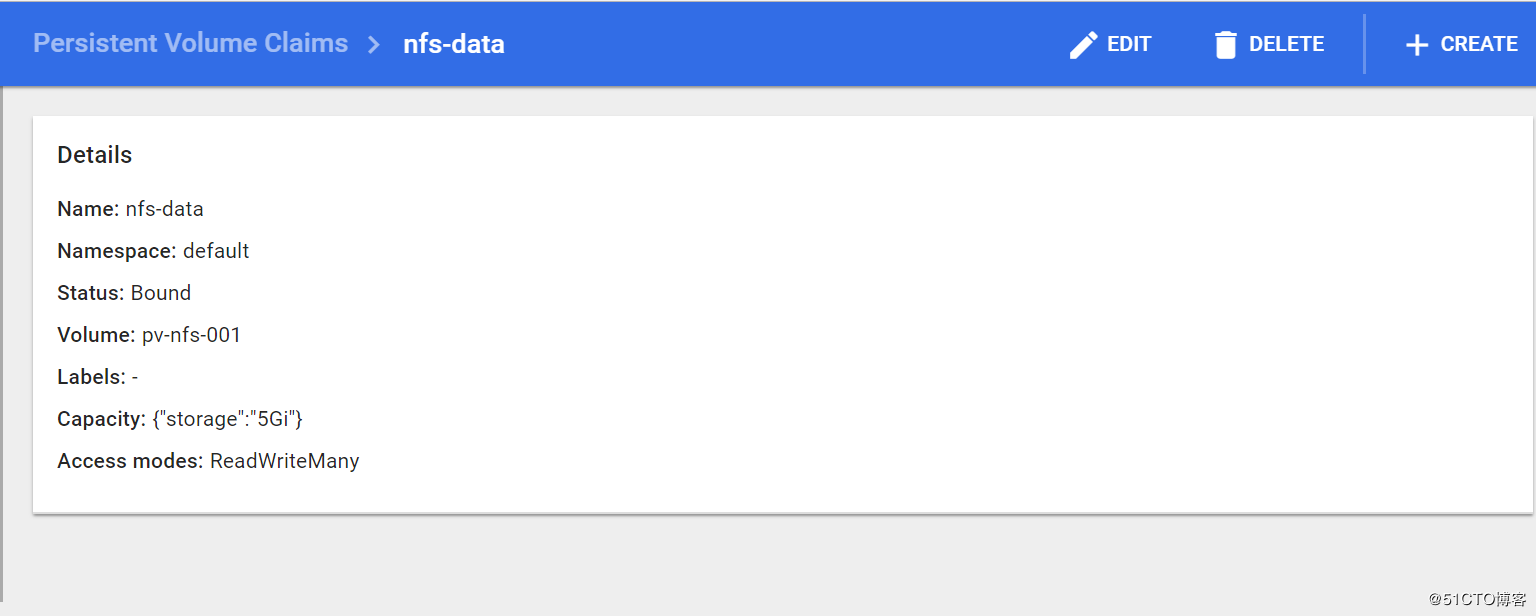
在PVC绑定PV时通常根据两个条件来绑定,一个是存储的大小,另一个就是访问模式。
在rc文件中使用PVC
# cat nginx-rc-configmap.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ReplicationController metadata: name: nginx labels: name: nginx spec: replicas: 2 selector: name: nginx template: metadata: labels: name: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: docker.io/nginx volumeMounts: - name: nginx-data mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html - name: nginx-etc mountPath: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf subPath: nginx.conf ports: - containerPort: 80 volumes: - name: nginx-data persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: nfs-data - name: nginx-etc configMap: name: nginxconfig items: - key: nginx.conf path: nginx.conf