题目
Given (n) non-negative integers (a_1,a_2,cdots,a_n), where each represents a point at coordinate((i,a_i)),(n) vetical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line (i) is at ((i,a_i)) and ((i,0)). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and (n) is at least 2.
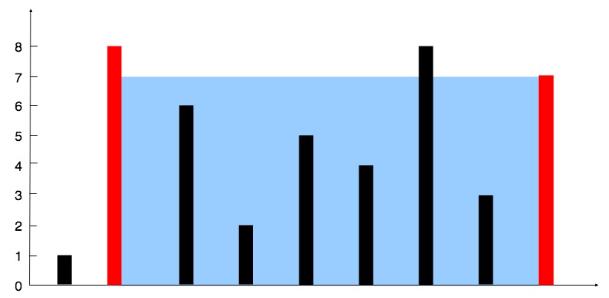
思路1:暴力匹配法
考虑到每一种出现的线段组合,并求出这些组合下的最大面积。
思路2:双指针法
两线段的距离越远,面积越大;同时,线段之间形成的容器区域受到长度较短的那条的线段限制。
在数组中使用双指针,一个指向数组的开头,一个指向末尾。计算线段形成的区域面积,并用(max)存储目前为止获得的最大区域的面积。此外,指针的移动方向是,较短线段的指针向较长线段的指针移动。
由于矩形容器的面积受限于较短长度的线段,当较长线段的指针向较短线段移动时,矩形面积不会增加。但是,当移动较短线段的指针虽然会影响矩形的宽度的减小,但是由于移动的方向是将较短线段的指针向较长线段的指针移动,矩形会获得更大的高度,这可能会导致面积的增加
Tips
双指针法
利用两个指针来遍历数组,一般来说,遍历数组采用的是单指针。两个指针一般用于有序数组,利用两个相同方向或者相反方向的指针完成遍历。(这里的指针并非C中的指针,而是指数组索引)
C++
- 思路1
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>$ height){
int max = 0;
for(int i = 0; i< height.size(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j< height.size(); j++){
int wide = height[i] > height[j] ? height[j] : height[i];
int len = j - i;
int temMax = len * wide;
if(tempMax > max)
max = tempMax;
}
}
return max;
}
};
- 思路2
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height){
int pBegin = 0; //开始指针
int pEnd = height.size() - 1; //末尾指针
int max = 0;
while(pBegin < pEnd){
int minHeight = height[pBegin] < height[pEnd] ? height[pBegin] : height[pEnd];
int tempMax = minHeight * (pEnd - pBegin);
if (tempMax > max)
max = tempMax;
if (height[pBegin] < height[pEnd]){
pBegin ++;
}
else{
pEnd --;
}
}
return max;
}
};
Python
- 思路2
def maxArea(self, height):
"""
:type height: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
pBegin = 0
pEnd = len(height) - 1
resInt = 0
while pBegin < pEnd:
curArea = (pEnd - pBegin) *min(height[pBegin], height[pEnd])
if curArea > resInt:
resInt = curArea
if height[pBegin] < height[pEnd]:
pBegin += 1
else:
pEnd -= 1
return resInt