本节内容:
-
面向对象高级语法部分异常处理
-
经典类vs新式类
-
静态方法、类方法、属性方法
-
类的特殊方法
-
反射
-
-
Socket开发基础
经典类vs新式类
classical vs new style:
- 经典类:深度优先
- 新式类:广度优先
- super()用法
抽象接口
import abcclass Alert(object): '''报警基类''' __metaclass__ = abc.ABCMeta @abc.abstractmethod def send(self): '''报警消息发送接口''' passclass MailAlert(Alert): passm = MailAlert()m.send()class Alert(object):
'''报警基础类'''
def send(self):
'''报警消息发送接口'''
raise NotImplementedError
class Mail_alert(Alert):
def send(self,msg):
print('>>sending...',msg)
if __name__ == '__main__':
A = Mail_alert()
A.send('web server is down.')
静态方法
通过@staticmethod装饰器即可把其装饰的方法变为一个静态方法,什么是静态方法呢?其实不难理解,普通的方法,可以在实例化后直接调用,并且在方法里可以通过self.调用实例变量或类变量;
但静态方法是不可以访问实例变量或类变量的,一个不能访问实例变量和类变量的方法,其实相当于跟类本身已经没什么关系了,它与类唯一的关联就是需要通过类名来调用这个方法
lass Dog(object):
def __init__(self,name): self.name = name @staticmethod #把eat方法变为静态方法 def eat(self): print("%s is eating" % self.name)d = Dog("ChenRonghua")d.eat()Traceback (most recent call last): File "/Users/PycharmProjects/python基础/自动化面向对象高级/静态方法.py", line 17, in <module> d.eat()TypeError: eat() missing 1 required positional argument: 'self'</module>想让上面的代码可以正常工作有两种办法
1. 调用时主动传递实例本身给eat方法,即d.eat(d)
2. 在eat方法中去掉self参数,但这也意味着,在eat中不能通过self.调用实例中的其它变量了
类方法
类方法通过@classmethod装饰器实现,类方法和普通方法的区别是, 类方法只能访问类变量,不能访问实例变量
class Dog(object): def __init__(self,name): self.name = name @classmethod def eat(self): print("%s is eating" % self.name)d = Dog("ChenRonghua")d.eat()Traceback (most recent call last): File "/Users/PycharmProjects/python基础/自动化面向对象高级/类方法.py", line 16, in <module> d.eat() File "/Users/PycharmProjects/python基础/自动化面向对象高级/类方法.py", line 11, in eat print("%s is eating" % self.name)AttributeError: type object 'Dog' has no attribute 'name'属性方法
属性方法的作用就是通过@property把一个方法变成一个静态属性
class Dog(object): def __init__(self,name): self.name = name @property def eat(self): print(" %s is eating" %self.name)d = Dog("ChenRonghua")d.eat()d = Dog("ChenRonghua")d.eat输出 ChenRonghua is eating1. 连接航空公司API查询
2. 对查询结果进行解析
3. 返回结果给你的用户
class Flight(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.flight_name = name
def checking_status(self):
print("checking flight %s status " % self.flight_name)
return 1
@property
def flight_status(self):
status = self.checking_status()
if status == 0 :
print("flight got canceled...")
elif status == 1 :
print("flight is arrived...")
elif status == 2:
print("flight has departured already...")
else:
print("cannot confirm the flight status...,please check later")
@flight_status.setter #修改
def flight_status(self,status):
status_dic = {
0 : "canceled",
1 :"arrived",
2 : "departured"
}
print("�33[31;1mHas changed the flight status to �33[0m",status_dic.get(status) )
@flight_status.deleter #删除
def flight_status(self):
print("status got removed...")
f = Flight("CA980")
f.flight_status
f.flight_status = 2 #触发@flight_status.setter
del f.flight_status #触发@flight_status.deleter
类的特殊成员方法
1. __doc__ 表示类的描述信息
2. __module__ 和 __class__
__module__ 表示当前操作的对象在那个模块
__class__ 表示当前操作的对象的类是什么
3. __init__ 构造方法,通过类创建对象时,自动触发执行。
4.__del__
析构方法,当对象在内存中被释放时,自动触发执行。
注:此方法一般无须定义,因为Python是一门高级语言,程序员在使用时无需关心内存的分配和释放,因为此工作都是交给Python解释器来执行,所以,析构函数的调用是由解释器在进行垃圾回收时自动触发执行的
5. __call__ 对象后面加括号,触发执行。
注:构造方法的执行是由创建对象触发的,即:对象 = 类名() ;而对于 __call__ 方法的执行是由对象后加括号触发的,即:对象() 或者 类()()
6. __dict__ 查看类或对象中的所有成员
7.__str__ 如果一个类中定义了__str__方法,那么在打印 对象 时,默认输出该方法的返回值。
8.__getitem__、__setitem__、__delitem__
用于索引操作,如字典。以上分别表示获取、设置、删除数据
9. __new__ __metaclass__
那么,创建类就可以有两种方式:
a). 普通方式
class Foo(object): def func(self): print 'hello alex'def func(self): print 'hello wupeiqi' Foo = type('Foo',(object,), {'func': func})#type第一个参数:类名#type第二个参数:当前类的基类#type第三个参数:类的成员def func(self): print("hello %s"%self.name) def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name self.age = age Foo = type('Foo',(object,),{'func':func,'__init__':__init__}) f = Foo("jack",22) f.func()
类 是由 type 类实例化产生,类中有一个属性 __metaclass__,其用来表示该类由 谁 来实例化创建,所以,我们可以为 __metaclass__ 设置一个type类的派生类,从而查看 类 创建的过程。
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_ class MyType(type): def __init__(self, child_cls, bases=None, dict=None): print("--MyType init---", child_cls,bases,dict) #super(MyType, self).__init__(child_cls, bases, dict) # def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): # print("in mytype new:",cls,args,kwargs) # type.__new__(cls) def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print("in mytype call:", self,args,kwargs) obj = self.__new__(self,args,kwargs) self.__init__(obj,*args,**kwargs) class Foo(object,metaclass=MyType): #in python3 #__metaclass__ = MyType #in python2 def __init__(self, name): self.name = name print("Foo ---init__") def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): print("Foo --new--") return object.__new__(cls) def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print("Foo --call--",args,kwargs) # 第一阶段:解释器从上到下执行代码创建Foo类 # 第二阶段:通过Foo类创建obj对象 obj = Foo("Alex") #print(obj.name)
类的生成 调用 顺序依次是 __new__ --> __call__ --> __init__
反射
通过字符串映射或修改程序运行时的状态、属性、方法, 有以下4个方法
def getattr(object, name, default=None): # known special case of getattr
"""
getattr(object, name[, default]) -> value
Get a named attribute from an object; getattr(x, 'y') is equivalent to x.y.
When a default argument is given, it is returned when the attribute doesn't
exist; without it, an exception is raised in that case.
"""
pass
判断object中有没有一个name字符串对应的方法或属性
def setattr(x, y, v): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ Sets the named attribute on the given object to the specified value. setattr(x, 'y', v) is equivalent to ``x.y = v''
def delattr(x, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ Deletes the named attribute from the given object. delattr(x, 'y') is equivalent to ``del x.y'' """
class Foo(object): def __init__(self): self.name = 'wupeiqi' def func(self): return 'func' obj = Foo() # #### 检查是否含有成员 #### hasattr(obj, 'name') hasattr(obj, 'func') # #### 获取成员 #### getattr(obj, 'name') getattr(obj, 'func') # #### 设置成员 #### setattr(obj, 'age', 18) setattr(obj, 'show', lambda num: num + 1) # #### 删除成员 #### delattr(obj, 'name') delattr(obj, 'func')
异常处理
1、异常基础
在编程过程中为了增加友好性,在程序出现bug时一般不会将错误信息显示给用户,而是现实一个提示的页面,通俗来说就是不让用户看见大黄页!!!
try: passexcept Exception,ex: pass2、异常种类
python中的异常种类非常多,每个异常专门用于处理某一项异常!!!
对于上述实例,异常类只能用来处理指定的异常情况,如果非指定异常则无法处理。
写程序时需要考虑到try代码块中可能出现的任意异常,可以这样写:
s1 = 'hello'try: int(s1)except IndexError,e: print eexcept KeyError,e: print eexcept ValueError,e: print es1 = 'hello'try: int(s1)except Exception,e: print etry: # 主代码块 passexcept KeyError,e: # 异常时,执行该块 passelse: # 主代码块执行完,执行该块 passfinally: # 无论异常与否,最终执行该块 passtry: raise Exception('我错了。')except Exception,e: print eclass WupeiqiException(Exception): def __init__(self, msg): self.message = msg def __str__(self): return self.messagetry: raise WupeiqiException('我的异常')except WupeiqiException,e: print e# assert 条件assert 1 == 1assert 1 == 2Socket
socket通常也称作"套接字",用于描述IP地址和端口,是一个通信链的句柄,应用程序通常通过"套接字"向网络发出请求或者应答网络请求。
socket起源于Unix,而Unix/Linux基本哲学之一就是“一切皆文件”,对于文件用【打开】【读写】【关闭】模式来操作。socket就是该模式的一个实现,socket即是一种特殊的文件,一些socket函数就是对其进行的操作(读/写IO、打开、关闭)
socket和file的区别:
- file模块是针对某个指定文件进行【打开】【读写】【关闭】
- socket模块是针对 服务器端 和 客户端Socket 进行【打开】【读写】【关闭】
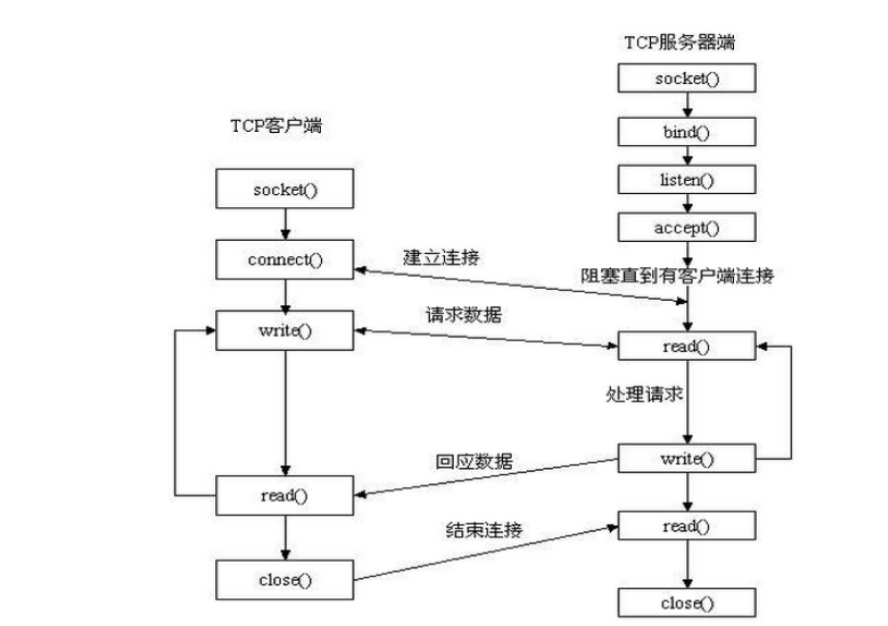
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import socket ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',9999) sk = socket.socket() sk.bind(ip_port) sk.listen(5) while True: print 'server waiting...' conn,addr = sk.accept() client_data = conn.recv(1024) print client_data conn.sendall('不要回答,不要回答,不要回答') conn.close()
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import socket ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',9999) sk = socket.socket() sk.connect(ip_port) sk.sendall('请求占领地球') server_reply = sk.recv(1024) print server_reply sk.close()
更多功能
sk = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM,0)
参数一:地址簇
socket.AF_INET IPv4(默认)
socket.AF_INET6 IPv6
socket.AF_UNIX 只能够用于单一的Unix系统进程间通信
参数二:类型
socket.SOCK_STREAM 流式socket , for TCP (默认)
socket.SOCK_DGRAM 数据报式socket , for UDP
socket.SOCK_RAW 原始套接字,普通的套接字无法处理ICMP、IGMP等网络报文,而SOCK_RAW可以;其次,SOCK_RAW也可以处理特殊的IPv4报文;此外,利用原始套接字,可以通过IP_HDRINCL套接字选项由用户构造IP头。
socket.SOCK_RDM 是一种可靠的UDP形式,即保证交付数据报但不保证顺序。SOCK_RAM用来提供对原始协议的低级访问,在需要执行某些特殊操作时使用,如发送ICMP报文。SOCK_RAM通常仅限于高级用户或管理员运行的程序使用。
socket.SOCK_SEQPACKET 可靠的连续数据包服务
参数三:协议
0 (默认)与特定的地址家族相关的协议,如果是 0 ,则系统就会根据地址格式和套接类别,自动选择一个合适的协议
sk.bind(address)
s.bind(address) 将套接字绑定到地址。address地址的格式取决于地址族。在AF_INET下,以元组(host,port)的形式表示地址。
sk.listen(backlog)
开始监听传入连接。backlog指定在拒绝连接之前,可以挂起的最大连接数量。
backlog等于5,表示内核已经接到了连接请求,但服务器还没有调用accept进行处理的连接个数最大为5
这个值不能无限大,因为要在内核中维护连接队列
sk.setblocking(bool)
是否阻塞(默认True),如果设置False,那么accept和recv时一旦无数据,则报错。
sk.accept()
接受连接并返回(conn,address),其中conn是新的套接字对象,可以用来接收和发送数据。address是连接客户端的地址。
接收TCP 客户的连接(阻塞式)等待连接的到来
sk.connect(address)
连接到address处的套接字。一般,address的格式为元组(hostname,port),如果连接出错,返回socket.error错误。
sk.connect_ex(address)
同上,只不过会有返回值,连接成功时返回 0 ,连接失败时候返回编码,例如:10061
sk.close()
关闭套接字
sk.recv(bufsize[,flag])
接受套接字的数据。数据以字符串形式返回,bufsize指定最多可以接收的数量。flag提供有关消息的其他信息,通常可以忽略。
sk.recvfrom(bufsize[.flag])
与recv()类似,但返回值是(data,address)。其中data是包含接收数据的字符串,address是发送数据的套接字地址。
sk.send(string[,flag])
将string中的数据发送到连接的套接字。返回值是要发送的字节数量,该数量可能小于string的字节大小。即:可能未将指定内容全部发送。
sk.sendall(string[,flag])
将string中的数据发送到连接的套接字,但在返回之前会尝试发送所有数据。成功返回None,失败则抛出异常。
内部通过递归调用send,将所有内容发送出去。
sk.sendto(string[,flag],address)
将数据发送到套接字,address是形式为(ipaddr,port)的元组,指定远程地址。返回值是发送的字节数。该函数主要用于UDP协议。
sk.settimeout(timeout)
设置套接字操作的超时期,timeout是一个浮点数,单位是秒。值为None表示没有超时期。一般,超时期应该在刚创建套接字时设置,因为它们可能用于连接的操作(如 client 连接最多等待5s )
sk.getpeername()
返回连接套接字的远程地址。返回值通常是元组(ipaddr,port)。
sk.getsockname()
返回套接字自己的地址。通常是一个元组(ipaddr,port)
sk.fileno()
套接字的文件描述符