动态规划问题还不是很会,需要再加深
解法1:
思路:双指针。
两个方法很重要!
isalnum(char c):判断字符变量c是否为字母或数字,若是则返回非零,否则返回零。 tolower(char c):把字母字符转换成小写,非字母字符不做出处理。

class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
int lefts=0;
int rights=s.size()-1;
while(lefts<rights){
while(!isalnum(s[lefts])){
lefts++;
if(lefts>=rights)
return true;
}
while(!isalnum(s[rights])){
rights--;
if(lefts>rights){
return false;
}
}
if(tolower(s[lefts])!=tolower(s[rights]))
return false;
lefts++;
rights--;
}
return true;
}
};
解法1:
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLastWord(string s) {
int cnt = 0;
int i = s.size()-1;
while(i>=0 && s[i]==' '){
i--;
}
while(i>=0 && s[i]!=' '){
i--;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
};
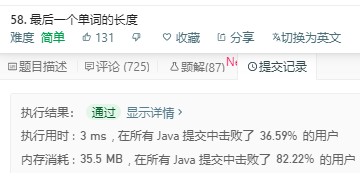
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLastWord(String s) {
String[] words = s.split(" ");
if(words.length==0){
return 0;
}
else{
return words[words.length-1].length();
}
}
}

解法1:
思路:
class Solution {
public:
string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {
string str;
int cur = 0, i = num1.size()-1, j = num2.size()-1;
while(i>=0 || j>=0 || cur !=0){
if(i>=0) cur += num1[i--] - '0';
if(j>=0) cur += num2[j--] - '0';
str += to_string(cur % 10);
cur /= 10;
}
reverse(str.begin(),str.end());
return str;
}
};
这个题和上个题的算法是一样的哦,只不过不是字符串了,而是变为了数组。


class Solution {
public:
vector<int> addToArrayForm(vector<int>& A, int K) {
vector<int> result;
for(int i=A.size()-1; i>=0;--i){
int num = A[i];
K += num;
int remind = K % 10;
result.insert(result.begin(),remind);
K /= 10;
}
if(K){
while(K > 9){//如果K 比较大,那么此时还需要把K循环放进去,比如[0], K = 10000 的情况
int remind = K % 10;
result.insert(result.begin(),remind);
K /= 10;
}
result.insert(result.begin(),K);
}
return result;
}
};

解法1:
思路:代码中的i 变量用来记录每个子串的第一个位置。当每当有重复子串时,i就会移动。当j-i+1 > max时,max 就更新。最后返回max
比如abcdcdefj 时就会返回5. 这里i 变量最为关键。

class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int size,i=0,j,k,max=0;
size = s.size();
for(j=0;j<size;++j){
for(k=i;k<j;++k){
if(s[k]==s[j]){
i = k+1;
break;
}
}
if(j-i+1>max){
max = j-i+1;
}
}
return max;
}
};
解法1:
动态规划
思路:
// 创建动态规划表格matrix
// matrix[left][right]表示下标从left到right的子串(以下简写为s[left, right])是否是回文的
// 若是,则值为其长度;否则,值为0
// matrix所有元素初始化为0
/ 用left表示当前子串起始下标,right表示当前子串结束下标。left <= right。
// 基本情形:
// 1. left == right,此时子串只有一个字符,一定是回文的,且长度为1
// 2. left == right - 1,此时子串有两个字符,当且仅当两个字符相同,子串是回文的,且长度为2// 迭代:从长度为3的子串开始
// 当且仅当s[left] == s[right],且s[left + 1, right - 1]是回文的,s[left, right]是回文的
// 换言之,若s[left] == s[right],且s[left + 1][right - 1] > 0,则s[left, right] = s[left + 1, right - 1] + 2
// 注意要按列而不是按行遍历!
// 原因是,在表格中,s[left + 1][right - 1]是在s[left][right]的右下角
// 只有按列遍历,才能保证在计算s[left][right]前,s[left + 1][right - 1]已经被计算过
精简版代码:
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int sLen = s.length();
if(sLen==0) return "";
string res = "";
vector<vector<bool>> f(sLen,vector<bool>(sLen,false));
int maxLen = 0;
int currLen = 0;
for(int i =0;i<sLen;++i){
for(int j =0;j<=i;++j){
if((s[i]==s[j])&&((i-j<2)||(i>0 && f[i-1][j+1]))){
f[i][j] = true;
currLen = i-j+1;
if(currLen > maxLen){
maxLen = currLen;
res = s.substr(j,currLen);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
解法2:中间扩散法:
解法1:用封装好的reverse方法,注意reverse方法的使用。里面是迭代器的指针

class Solution {
public:
string reverseStr(string s, int k) {
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while(it < s.end() && it+k <=s.end()){
reverse(it,it+k);
it = it+2*k;
}
if(it+k>s.end()){
reverse(it,s.end());
}
return s;
}
};
此题还未到国外LeetCode 去参考别人答案
解法1:
思路:hash
自己写的

class Solution {
public:
int firstUniqChar(string s) {
unordered_map<char,int> result;
for(auto c : s){
result[c]++;
}
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i){
if(result[s[i]]==1){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
解法1:自己写的
思路:挨个写出对应的循环判断,需要判断三种情况,时间复杂度O(3N)

class Solution {
public:
bool detectCapitalUse(string word) {
int i=0;
for(;i<word.size();++i){
if(word[i]-'A'>=32){
continue;
}
else break;
}
if(i==word.size()) return true;//全是小写
int j=0;
for(;j<word.size();++j){
if(word[j]-'A'<32){
continue;
}
else break;
}
if(j==word.size()) return true; //全是大写
int k =0;
if(word[k]-'A'<32){
++k;
for(;k<word.size();++k){
if(word[k]-'A'>=32){
continue;
}
else break;
}
if(k==word.size()) return true;
}
return false;
}
};
解法1:思路:KMP算法。
详情见KMP算法的日记

class Solution {
public:
void calcKMPNextArray(const string & needle,vector<int> & next){
next.resize(needle.size());
//计算next数组的过程其实是needle与needle自己进行匹配
next[0]=-1;
for(int i=1,j=-1;i<needle.size();i++){
while(j>=0 && needle[i]!=needle[j+1]) //第三天再次写这个算法,写成了needle[i]==needle[j].唉,感觉这本质还是没理解透彻
j = next[j];
if(needle[i]==needle[j+1])//第三天再回顾这个算法,写成了needle[i]!=needle[j+1]
j++;
next[i]=j;
}
//优化 next 数组,可以去除多余的跳跃步骤
for(int i=0;i<needle.size();i++){
while(next[i]>=0 && needle[i+1]==needle[next[i]+1])
next[i]=next[next[i]];
}
}
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
if(needle.size()<=0)
return 0;
vector<int> next;
calcKMPNextArray(needle,next);
int i,j;
for(i=0,j=-1;i<haystack.size();i++){
while(j>=0 && haystack[i]!=needle[j+1])
j = next[j];
if(haystack[i]==needle[j+1])
j++;
//注意,结束时,j 应该到达needle最后一个字符处,并没有超出
//从上一句可以看出,最后一次 j++ 绝对不会超出needle索引范围
if(j+1>=needle.size()) //这里必须要注意
return i-needle.size()+1;
}
return -1;
}
};
解法2:
暴力解法

int strStr(char * haystack, char * needle){
int i=0,j=0,t=i;
while(haystack[i]&&needle[j]){
if(haystack[i]==needle[j]){
++i;
++j;
continue;
}
else{
t = t+1;
i = t;
j = 0;
}
}
if(needle[j] == '�'){
return t;
}
return -1;
}
解法1

JAVA 版
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {
int[] charsCount = new int[26];//计算26字母数量
boolean[] visited = new boolean[26]; //标记字母是否已经入栈
int len = s.length();
char[] sChars = s.toCharArray();
for(char c : sChars){
charsCount[c - 'a']++;
}
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
int index = 0;//最终字符的长度
for(int count : charsCount){
if(count > 0) index++;
}
char[] res = new char[index];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
char c = s.charAt(i);
//有小字符的且满足其前面的字符再小字符后还有同样字符的,则出栈
while(!stack.isEmpty() && c < stack.peek() && charsCount[stack.peek()-'a'] > 1
&& !visited[c - 'a']){
Character pop = stack.pop();
visited[pop - 'a'] = false;
charsCount[pop - 'a']--;
}
if(visited[c - 'a']){
charsCount[c - 'a']--; //重复的字符根据游标往后移动,数量减一
continue;
}
stack.push(c);
visited[c - 'a'] = true;
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
res[--index] = stack.pop();
}
return String.valueOf(res);
}
}

C++版
思路:

class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicateLetters(string s) {
unordered_map<char,int> mp;
unordered_map<char,int> in_st;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i){
mp[s[i]] = i;//记录某个字符出现的最后位置
}
vector<char> st;//记录结果的栈
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i){
if(in_st[s[i]]) continue;//栈中有当前遍历字符
while(st.size() && s[i] < st.back() && mp[st.back()] > i){
//栈顶元素会在之后的位置出现
--in_st[st.back()];
st.pop_back();
//出栈并抹除记录
}
st.push_back(s[i]);
++in_st[s[i]];
//压栈,并记录出现过
}
string res;
for(auto& i : st) res += i;
return res;
}
};

解法1:

思路1:此题可以近似看成一个求26进制的题,但是值得注意的是对于26的整数倍,如果我们不加以限制的话就会造成A0的情况出现,而题目给出的条件中是不考虑这种情况的。所以我们只需要排除这种情况对于任何26的整数倍,我们就直接先插入‘Z’,同时还要对原数进行减一的操作。因为如果不进行减一的话对于26所对应的就是AZ(其实就是为了将A0映射为Z要对A0整体减一,由于0-1不够,所以要向A借一位,所以最后就得到了Z。所以我们要插入Z之后再对原数减1。)
class Solution {
public:
string convertToTitle(int n) {
string res;
int temp = 0;
while(n != 0){
temp = n%26;
if(temp == 0){
res = 'Z' + res;
n--;
}
else
res = (char)(temp + 'A'-1) + res;
n = n/26;
}
return res;
}
};
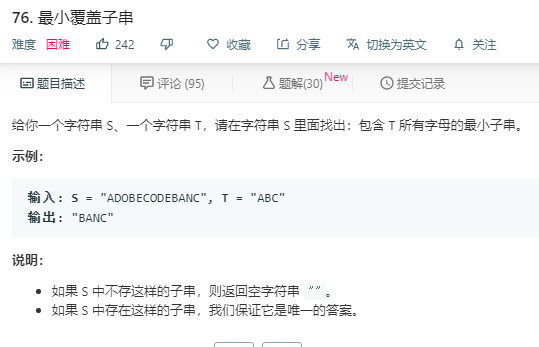
参考题解:
解法:
滑动窗口:
class Solution {
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
//记录最短子串的开始位置和长度
int start = 0, minLen = INT_MAX;
int left = 0, right = 0;
unordered_map<char,int> window;
unordered_map<char,int> needs;
for(char c : t) needs[c]++;
int match = 0;
while(right < s.size()){
char c1 = s[right];
if(needs.count(c1)){
window[c1]++;
if(window[c1] == needs[c1])
match++;
}
right++;
while(match == needs.size()){
if(right - left < minLen){
//更新最小子串的位置和长度
start = left;
minLen = right - left;
}
char c2 = s[left];
if(needs.count(c2)){
window[c2]--;
if(window[c2] < needs[c2]){
match--;
}
}
left++;
}
}
return minLen == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(start,minLen);
}
};
优化版:

class Solution {
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
int count[256] = { 0 };
for (auto c : t) ++count[c];
int len = 0, minLength = s.length();
string res;
for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < s.length(); ++r) {
count[s[r]]--;
if (count[s[r]] >= 0) ++len;
while (len == t.length()) {
if (r - l + 1 <= minLength) {
minLength = r - l + 1;
res = s.substr(l, r - l + 1);
}
count[s[l]]++;
if (count[s[l]] > 0) --len;
++l;
}
}
return res;
}
};
再优化:

class Solution {
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
int count[256] = { 0 };
for(auto c : t) ++count[c];
int len = 0, minLength = s.length();
string res;
for(int l = 0, r= 0;r<s.length();++r){
if(--count[s[r]] >= 0) ++len;
while(len == t.length()){
if(r - l + 1 <= minLength){
minLength = r - l + 1;
res = s.substr(l, r - l + 1);
}
if(++count[s[l++]] > 0) --len;
}
}
return res;
}
};
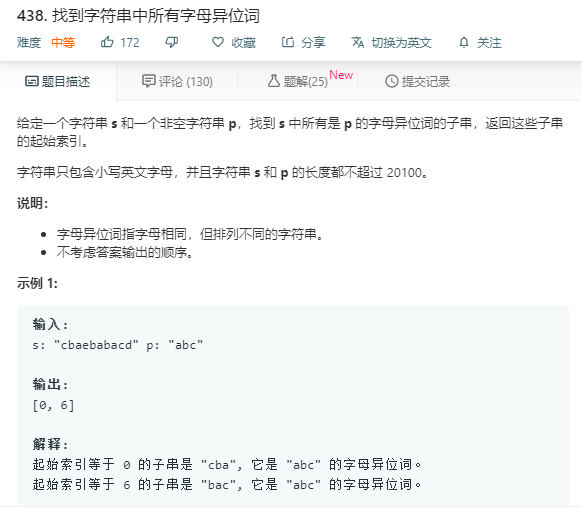

滑动窗口
参考题解:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findAnagrams(string s, string p) {
vector<int> res;
int left = 0, right = 0;
unordered_map<char,int> needs;
unordered_map<char,int> window;
for(char c : p) needs[c]++;
int match = 0;
while(right < s.size()){
char c1 = s[right];
if(needs.count(c1)){
window[c1]++;
if(window[c1] == needs[c1])
match++;
}
right++;
while(match == needs.size()){
//如果window 的大小合适
//就把其实索引left 加入结果
if(right - left == p.size())
res.push_back(left);
char c2 = s[left];
if(needs.count(c2)){
window[c2]--;
if(window[c2] < needs[c2])
match--;
}
left++;
}
}
return res;
}
};

思路:滑动窗口

需要注意的是,因为我们要求的是最长子串,所以需要在每次移动 right 增大窗口时更新 res,而不是像之前的题目在移动 left 缩小窗口时更新 res。
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
unordered_map<char,int> window;
int res = 0;//记录最长长度
while(right < s.size()){
char c1 = s[right];
window[c1]++;
right++;
//如果window中出现重复字符
//开始移动left缩小窗口
while(window[c1] > 1){
char c2 = s[left];
window[c2]--;
left++;
}
res = max(res,right - left);
}
return res;
}
};

其中 window 的数据类型可以视具体情况而定,比如上述题目都使用哈希表充当计数器,当然你也可以用一个数组实现同样效果,因为我们只处理英文字母。
稍微麻烦的地方就是这个 valid 条件,为了实现这个条件的实时更新,我们可能会写很多代码。比如前两道题,看起来解法篇幅那么长,实际上思想还是很简单,只是大多数代码都在处理这个问题而已。
作者:labuladong
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/solution/hua-dong-chuang-kou-suan-fa-tong-yong-si-xiang-by-/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解法1:
JAVA

class Solution {
public int longestSubstring(String s, int k) {
if(k < 2) return s.length();
return process(s.toCharArray(),k,0,s.length()-1);
}
private int process(char[] s,int k,int lo,int hi){
if(hi - lo + 1 < k) return 0;
int[] cnts = new int[26];
for(int i = lo;i <= hi;++i) cnts[s[i]-'a']++;
while(hi - lo + 1 >= k && cnts[s[lo]-'a'] < k) lo++;
while(hi - lo + 1 >= k && cnts[s[hi]-'a'] < k) hi--;
if(hi - lo + 1 < k) return 0;
for(int i = lo;i<=hi;++i){
if(cnts[s[i]-'a'] < k) return Math.max(process(s,k,lo,i-1),process(s,k,i+1,hi));
}
return hi - lo + 1;
}
}
解法2
C++ 递归+分治
class Solution {
public:
int longestSubstring(string s, int k) {
int result = 0;
helper(s,k,result);
return result;
}
void helper(string s,int k,int &result){
unordered_map<char,int> mmap;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
mmap[s[i]]++;
for(auto i:mmap){
if(i.second<k){
int char_index = s.find(i.first);
helper(s.substr(0,char_index),k,result);
helper(s.substr(char_index+1,s.length()),k,result);
return;
}
}
result = result>s.length()?result:s.length();
return;
}
};

分治 + 递归
class Solution {
public:
int longestSubstring(string s, int k) {
if(k <= 1) return s.size();
if(s.empty() || s.size() < k) return 0;
vector<int> hash(128,0);
for(char c : s) ++hash[c];
int i = 0;
while(i < s.size() && hash[s[i]] >= k) ++i;
if(i == s.size()) return s.size();
int l = longestSubstring(s.substr(0,i),k);
while(i < s.size() && hash[s[i]] < k) ++i;
int r = longestSubstring(s.substr(i),k);
return max(l,r);
}
};
解法1:
思路:
四种情况:
- 数组里有空字符串,并且数组里还有自己就是回文的字符串,每出现一个可与空字符串组成两对。
- 如果自己的翻转后的字符串也在数组里,可以组成一对,注意翻转后不能是自己。
- 如果某个字符串能找到一个分割点,分割点前的部分是回文,后半部分翻转后也在数组里,可组成一对。
- 把3反过来,如果后部分是回文,前半部分翻转后在数组里,可组成一对。

class Solution {
public:
bool f(string& s,int left,int right){
while(left < right){
if(s[left++] != s[right--]) return false;
}
return true;
}
vector<vector<int>> palindromePairs(vector<string>& words) {
unordered_map<string,int> m;
set<int> s;
int n = words.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
m[words[i]] = i;//记录哈希
s.insert(words[i].size());//获取每段字符串的长度
}
vector<vector<int>> res;//结果
for(int i = 0;i<n;++i){
string tmp = words[i];
reverse(tmp.begin(),tmp.end());
if(m.count(tmp) && m[tmp] != i){//如果哈希表里有目标字符串且不是自己
res.push_back({m[tmp],i});//记录答案
}
int length = tmp.size();
for(auto it = s.begin();*it !=length;it++){//这段代码是本题的精髓
int d = *it;
if(f(tmp,0,length-d-1) && m.count(tmp.substr(length-d))){
res.push_back({i,m[tmp.substr(length-d)]});
}
if(f(tmp,d,length-1) && m.count(tmp.substr(0,d))){
res.push_back({m[tmp.substr(0,d)],i});
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
思路2:
从每个字符串的第一个字符遍历,依次增加长度。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> palindromePairs(String[] words) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Map<String,Integer> dict = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0;i<words.length;i++){
dict.put(words[i],i);//进哈希表
}
for(int j=0;j<words.length;j++){
String str = words[j];
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
while(left <= right){
String tmpstr = str.substring(left,right);//从每个字符串的第一个字符判断,有没有与之相对应的回文串
Integer k = dict.get(new StringBuilder(tmpstr).reverse().toString());
if(k != null && k != j && isPalindrome(str.substring(left == 0 ? right : 0,left ==0 ? str.length():left))){
ans.add(Arrays.asList(left == 0 ? new Integer[] {j,k}:new Integer[] {k,j}));
}
if(right < str.length()) right++;
else left++;
}
}
return ans;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(String str){
int start = 0,end = str.length()-1;
while(start <= end){
if(str.charAt(start) != str.charAt(end)) return false;
start++;
end--;
}
return true;
}
}
解法1:
递归回溯 ,跟全排列的算法一样
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> result;
vector<string> temp;
bool isPalindrome(string s){
int i=0,j=s.size()-1;
while(i < j){
if(s[i] != s[j]){
return false;
}
i++;
j--;
}
return true;
}
void recursion(string s,int a,int b){
//到字符串末尾了,将本次结果记录下来
if(a > b){
result.push_back(temp);
return;
}
//从index为a开始截取长度为1,2,3...的子串进行验证,成功则用剩下的部分递归
for(int i=1;i<=b-a+1;i++){
if(isPalindrome(s.substr(a,i))){
temp.push_back(s.substr(a,i));
recursion(s,a+i,b);
temp.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
recursion(s,0,s.size()-1);
return result;
}
};
解法2:
DP + 回溯
思路:分两步。第一步对s使用dp方法确定回文子串。第二步使用回溯法进行分割。第一步,dp[i][j]代表s(i,j)是否为回文(包含i和j)字符串,注意当ij之间的字符大于等于3个时,dp[i][j]=dp[i+1][j-1]&&s[i]==s[j],即i递减,j递增,又j>=i,即可确定i,j的递推方向。第二步,dfs(i,j),将s(i,j)放入组合,对dp[j+1][k] (j+1<=k<n)中为true的进行dfs,当j==n-1时,当前组合放入结果。注意dfs的优化,模版类使用传址,复用变量(如字符串s的大小)使用全局变量。
class Solution {
public:
int n;//字符串长度作为全局变量, 这样再dfs里不需声明变量
vector<vector<string>> res;//结果
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
n = s.size();//字符串长度
vector<vector<bool>> dp(n,vector<bool>(n,false));//dp[i][j]表示s(i,j)是否为回文字符串
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){//i递减
for(int j=i;j<n;j++){//j递增,且j>=i
if(i == j)//一个字母是回文
dp[i][j] = true;
else if(i == j-1){//相邻字母,相同是回文
if(s[i] == s[j]){
dp[i][j] = true;
}
}
else{//长度 >= 3, 中间为回文且首尾字母相同为回文
if(s[i] == s[j] && dp[i+1][j-1]){
dp[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
}
vector<string> temp;//组合暂存变量 储存一个有效的回文串分割
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(dp[0][i])
dfs(temp,dp,s,0,i);//从第一个字母开始,向后取回文串进行分割
}
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<string>& temp,vector<vector<bool>>& dp,string s,int i,int j){
temp.push_back(s.substr(i,j-i+1));//s(i,j)放入组合
if(j == n-1){
res.push_back(temp);//到达单词结尾,把当前组合放入结果
}
j++;//从j+1开始继续找回文串
for(int k=j;k<n;k++){
if(dp[j][k])
dfs(temp,dp,s,j,k);
}
temp.pop_back();//尾回溯 退出时删除本轮添加的字符串
}
};
解法1:DP+ 中心扩散法判读回文串
class Solution {
public int minCut(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() <= 1)
return 0;
int len = s.length();
int dp[] = new int[len];
Arrays.fill(dp,len-1);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
//注意偶数长度与奇数长度回文串的特点
mincutHelper(s,i,i,dp);//奇数回文串以1个字符为中心
mincutHelper(s,i,i+1,dp);//偶数回文串以两个字符为中心
}
return dp[len-1];
}
private void mincutHelper(String s,int i,int j,int[] dp){
int len = s.length();
while(i>=0 && j<len && s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)){
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j],(i==0 ? -1 :dp[i-1]) + 1);
i--;
j++;
}
}
}
C++版 中心扩散
class Solution {
public:
int minCut(string s) {
int n = s.size();
vector<int> dp(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) dp[i] = i;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
centerExpand(s,dp,i,i);
centerExpand(s,dp,i,i+1);
}
return dp[n-1];
}
void centerExpand(string& s,vector<int>& dp,int l,int r){
while(l>=0 && r<s.size() && s[l] == s[r]){
if(l==0) dp[r] = 0;
else dp[r] = min(dp[r],dp[l-1]+1);
--l;++r;
}
}
};
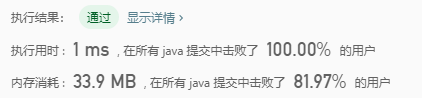
解法1:
思路:
常规思路1:
对于这种括号匹配问题,一般都是使用栈
我们先找到所有可以匹配的索引号,然后找出最长连续数列!
例如:s = )(()()) ,我们用栈可以找到,
位置2和位置3匹配,
位置4和位置5匹配,
位置1和位置6匹配,
这个数组为:2,3,4,5,1,6这是通过栈找到的,我们按递增排序!1,2,3,4,5,6
找出该数组的最长连续数列的长度就是最长有效括号长度!
所以时间复杂度来自排序:O(nlogn)
接下来我们思考,是否可以在省略排序的过程,在弹栈时候进行操作!
直接看代码理解!所以时间复杂度为:O(n)
class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0) return 0;
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
stack.push(-1);
int res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s.charAt(i) == '(') stack.push(i);
else{
stack.pop();
if(stack.isEmpty()) stack.push(i);
else{
res = Math.max(res,i - stack.peek());
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
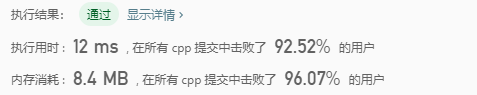
解法2:
思路:
**思路2:**
dp方法:
我们用dp[i]表示以i结尾的最长有效括号;
-
当
s[i]为(,dp[i]必然等于0,因为不可能组成有效的括号; -
那么
s[i]为)2.1 当
s[i-1]为(,那么dp[i] = dp[i-2] + 2;2.2 当
s[i-1]为)并且s[i-dp[i-1] - 1]为(,那么dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 2 + dp[i-dp[i-1]-2];
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0) return 0;
int[] dp = new int[s.length()];
int res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(i > 0 && s.charAt(i)== ')'){
if(s.charAt(i-1) == '('){
dp[i] = (i - 2 >=0 ? dp[i-2] + 2 : 2);
}else if(s.charAt(i - 1) == ')' && i - dp[i-1] - 1 >=0 &&
s.charAt(i - dp[i-1] -1) == '('){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 2 + (i - dp[i-1] -2 >=0 ? dp[i - dp[i-1]-2] : 0);
}
}
res = Math.max(res,dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
}


解法1:
DP 动态规划
class Solution {
public int numDistinct(String s, String t) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0){
return 0;
}
int m = s.length();
int n = t.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m+1][n+1];
//初始化dp[i][0] = 1;
for(int i = 0;i<=m;i++){
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
//按t[0:0] => t[0:n] 的顺序依次匹配
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++){
//因为i < j时 s[0: j-1]的长度比t[0:j-1]小,所以可忽略
for(int i=j;i<=m;i++){
if(s.charAt(i-1) == t.charAt(j-1)){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i-1][j];
}else{
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}
