Coursera课程《Using Databases with Python》 密歇根大学
Week4 Many-to-Many Relationships in SQL
15.8 Many-to-Many Relationships
我们之前学的都是One-to-Many的关系,比如说Album与Track的关系。而我们现在要说的是Many-to-Many关系,比如说Books与Authors的关系。
所以我们需要在Books表和Authors的表中间建立一个新表来将它转变成One-to-Many的关系。
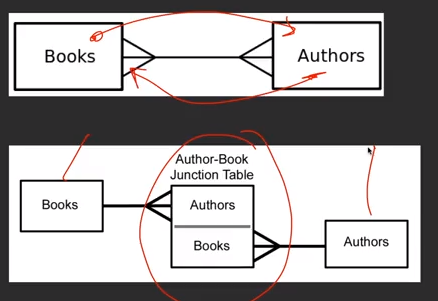
下面是一个数据库的结构。
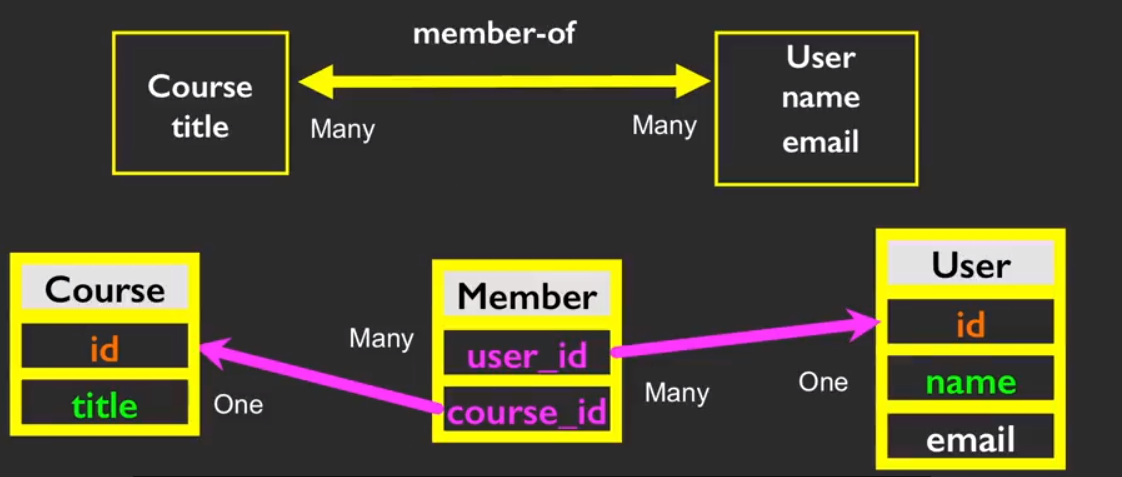
我们来构建它。
CREATE TABLE User (
id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT UNIQUE,
name TEXT,
email TEXT
)
CREATE TABLE Course (
id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT UNIQUE,
title TEXT
)
CREATE TABLE Member (
user_id INTEGER,
course_id INTEGER,
role INTEGER,
PRIMARY KEY (user_id, cpurse_id)
)
然后再插入一些用户和课程。
INSERT INTO User (name, email) VALUES ('Jane','jane@tsugi.org');
INSERT INTO User (name, email) VALUES ('Ed', 'ed@tsugi.org');
INSERT INTO User (name, email) VALUES ('Sue', 'sue@tsugi.org');
INSERT INTO Course (title) VALUES ('Python');
INSERT INTO Course (title) VALUES ('SQL');
INSERT INTO Course (title) VALUES ('PHP');
然后现在向Membership表里插入数据。
INSERT INTO Member (user_id, course_id, role) VALUES (1, 1, 1);
INSERT INTO Member (user_id, course_id, role) VALUES (2, 1, 0);
INSERT INTO Member (user_id, course_id, role) VALUES (3, 1, 0);
INSERT INTO Member (user_id, course_id, role) VALUES (1, 2, 0);
INSERT INTO Member (user_id, course_id, role) VALUES (2, 1, 1);
INSERT INTO Member (user_id, course_id, role) VALUES (2, 3, 1);
INSERT INTO Member (user_id, course_id, role) VALUES (3, 3, 0);

这样就是我们一个Many-to-Many的关系数据库了。
Worked Example:roster.py
import json
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('rosterdb.sqlite')
cur = conn.cursor()
# Do some setup
cur.executescript('''
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS User;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Member;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Course;
CREATE TABLE User (
id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT UNIQUE,
name TEXT UNIQUE
);
CREATE TABLE Course (
id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT UNIQUE,
title TEXT UNIQUE
);
CREATE TABLE Member (
user_id INTEGER,
course_id INTEGER,
role INTEGER,
PRIMARY KEY (user_id, course_id)
)
''')
fname = input('Enter file name: ')
if len(fname) < 1:
fname = 'roster_data_sample.json'
# [
# [ "Charley", "si110", 1 ],
# [ "Mea", "si110", 0 ],
str_data = open(fname).read()
json_data = json.loads(str_data)
for entry in json_data:
name = entry[0];
title = entry[1];
print((name, title))
cur.execute('''INSERT OR IGNORE INTO User (name)
VALUES ( ? )''', ( name, ) )
cur.execute('SELECT id FROM User WHERE name = ? ', (name, ))
user_id = cur.fetchone()[0]
cur.execute('''INSERT OR IGNORE INTO Course (title)
VALUES ( ? )''', ( title, ) )
cur.execute('SELECT id FROM Course WHERE title = ? ', (title, ))
course_id = cur.fetchone()[0]
cur.execute('''INSERT OR REPLACE INTO Member
(user_id, course_id) VALUES ( ?, ? )''',
( user_id, course_id ) )
conn.commit()
作业代码
import json
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('rosterdb.sqlite')
cur = conn.cursor()
# Do some setup
cur.executescript('''
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS User;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Member;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Course;
CREATE TABLE User (
id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT UNIQUE,
name TEXT UNIQUE
);
CREATE TABLE Course (
id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT UNIQUE,
title TEXT UNIQUE
);
CREATE TABLE Member (
user_id INTEGER,
course_id INTEGER,
role INTEGER,
PRIMARY KEY (user_id, course_id)
)
''')
fname = input('Enter file name: ')
if len(fname) < 1:
fname = 'roster_data.json'
# [
# [ "Charley", "si110", 1 ],
# [ "Mea", "si110", 0 ],
str_data = open(fname).read()
json_data = json.loads(str_data)
for entry in json_data:
name = entry[0];
title = entry[1];
role = entry[2]
print((name, title))
cur.execute('''INSERT OR IGNORE INTO User (name)
VALUES ( ? )''', ( name, ) )
cur.execute('SELECT id FROM User WHERE name = ? ', (name, ))
user_id = cur.fetchone()[0]
cur.execute('''INSERT OR IGNORE INTO Course (title)
VALUES ( ? )''', ( title, ) )
cur.execute('SELECT id FROM Course WHERE title = ? ', (title, ))
course_id = cur.fetchone()[0]
cur.execute('''INSERT OR REPLACE INTO Member
(user_id, course_id, role) VALUES ( ?, ?, ? )''',
( user_id, course_id, role ) )
conn.commit()
其实就是上面那个代码,修改了一点点,把role写入member表而已。