Pytorch 基本数据类型
1、 皆为Tensor
2、 如何表示string
3、 基本数据类型DataType
4、 类型检查
5、 如何创建不同维度张量
(一) 在pytorch中所有数据皆为张量,下面列出在python和pytorch中数据类型之间的对应关系:
|
Python |
Pytorch |
|
Int |
IntTensor of size() |
|
float |
FloatTensor of size() |
|
Int array |
IntTensor of size[d1,d2,…] |
|
Float array |
FloatTensor of size[d1,d2,…] |
|
string |
-- |
(二) 如何表示字符串
在深度学习中字符串表示方法一般采用两种方式:
1、One-hot编码
one-hot是比较常用的文本特征特征提取的方法。
one-hot编码,又称“独热编码”。其实就是用N位状态寄存器编码N个状态,每个状态都有独立的寄存器位,且这些寄存器位中只有一位有效,说白了就是只能有一个状态。
接下来看看怎么应用one-hot:
one-hot在特征提取上属于词袋模型(bag of words),假设语料库中有三句话:
我爱中国
爸爸妈妈爱我
爸爸妈妈爱中国
首先,将语料库中的每句话分成单词,并编号:
1:我 2:爱 3:爸爸 4:妈妈 5:中国
然后,用one-hot对每句话提取特征向量:(图来源于网络)
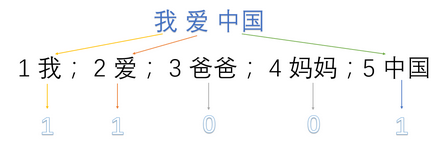


所以最终得到的每句话的特征向量就是:
我爱中国 -> 1,1,0,0,1
爸爸妈妈爱我 -> 1,1,1,1,0
爸爸妈妈爱中国 -> 0,1,1,1,1
那么这样做的优点和缺点都有什么?
优点:
1、解决了分类器处理离散数据困难的问题
2、一定程度上起到了扩展特征的作用(上例中从3扩展到了9)
缺点:
1、one-hot是一个词袋模型,不考虑词与词之间的顺序问题,而在文本中,次的顺序是一个很重要的问题
2、one-hot是基于词与词之间相互独立的情况下的,然而在多数情况中,词与词之间应该是相互影响的
3、one-hot得到的特征是离散的,稀疏的
2、Embedding
代表:word2vec:是一个计算词嵌入/词向量(word embedding)的工具,包含两种训练模型:CBOW模型根据中心词w(t)周围的词如w(t-2)&w(t-1)&w(t+1)&w(t+2)来预测中心词w(t);Skip-gram模型则根据中心词W(t)来预测周围词。
由于one-hot编码得到的矩阵太稀疏而且维度太高了,所以可以将one-hot向量作为word2vec的输入,通过word2vec训练低维词向量(word embedding)。或者直接将得到的编码序列通过word2vec转化成固定维度的向量,及得到自己的word embedding。
(三)、 数据类型
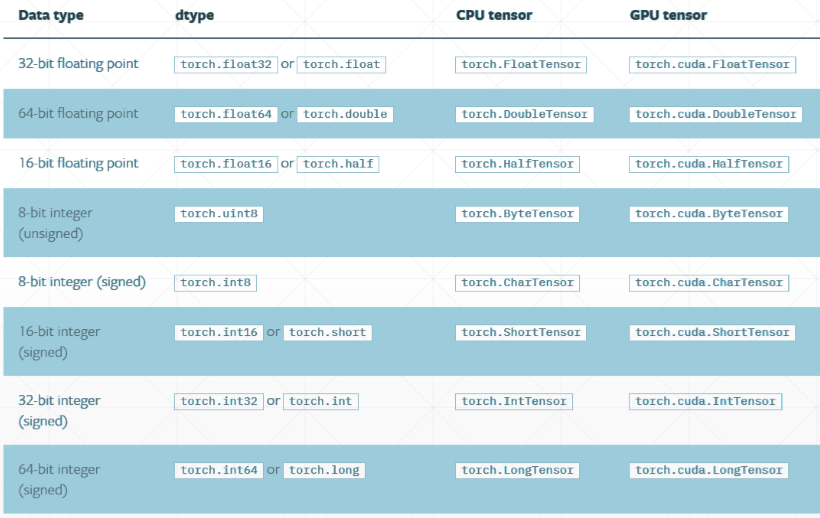
(四)、类型检查
方法: tensor.type()
Type(tensor)
isinstance(tensor,torch.XXXTensor)

1 a = torch.randn(2,3) 2 print(a) 3 print(a.type) 4 print(type(a)) 5 print(isinstance(a,torch.FloatTensor)) 6 print(isinstance(a,torch.cuda.FloatTensor)) 7 # 将 a 搬到 cuda 上 8 a = a.cuda() 9 print(isinstance(a,torch.cuda.FloatTensor)) 10 11 output: 12 tensor([[-0.0357, 1.0596, -0.6204], 13 [ 1.4711, 0.2571, 0.0810]]) 14 <built-in method type of Tensor object at 0x000001CAAEA25990> 15 <class 'torch.Tensor'> 16 True 17 False 18 True
(五)创建不同维度的张量
1、0维
方法:torch.tensor(标量数据)

1 # 0 维数据 2 loss = torch.tensor(1.) 3 print(loss) 4 print(type(loss)) 5 print(len(loss.shape)) 6 print(loss.size()) 7 8 output: 9 tensor(1.) 10 <class 'torch.Tensor'> 11 0 12 torch.Size([])
2、1维
方法:torch.tensor([x])
torch.tensor([a,b])
torch.FloatTensor(x)
torch.from_numpy(x)
torch.ones(x)
# 1 维数据

1 bias = torch.tensor([1.1]) 2 print(bias) 3 print(type(bias)) 4 print(bias.size()) 5 print(len(bias.shape)) 6 7 tensor([1.1000]) 8 <class 'torch.Tensor'> 9 torch.Size([1]) 10 1 11 12 bias2 = torch.tensor([1.1,2.2]) 13 print(bias2) 14 15 tensor([1.1000, 2.2000]) 16 17 18 base3 = torch.FloatTensor(1) 19 print(base3) 20 base4 = torch.FloatTensor(2) 21 print(base4) 22 23 tensor([0.]) 24 tensor([0., 0.]) 25 26 data = np.ones(2) 27 print(data) 28 29 [1. 1.] 30 31 32 torch_data = torch.from_numpy(data) 33 print(torch_data) 34 tensor([1., 1.], dtype=torch.float64) 35 36 37 data1 = torch.ones(2) 38 print(data1) 39 40 tensor([1., 1.])
3、2维
# 二维数据

1 a = torch.randn(2,3) #[2,3] 2 print(a) 3 print(a.shape) 4 print("第一个维度:%d 第二个维度:%d"%(a.size(0),a.size(1))) 5 print("a.shape[1] = %d"%a.shape[1]) 6 7 tensor([[-1.5524, 1.1390, -2.2068], 8 [ 0.2328, -0.2268, 0.5129]]) 9 torch.Size([2, 3]) 10 第一个维度:2 第二个维度:3 11 a.shape[1] = 3
4、3维

1 a = torch.rand(1,2,3) 2 print(a) 3 print(a.shape) 4 print(a[0]) 5 print(list(a.shape)) 6 7 tensor([[[0.8469, 0.1642, 0.5887], 8 [0.4105, 0.7815, 0.3047]]]) 9 torch.Size([1, 2, 3]) 10 tensor([[0.8469, 0.1642, 0.5887], 11 [0.4105, 0.7815, 0.3047]]) 12 [1, 2, 3]
5、4维

1 a = torch.rand(2,3,5,5) 2 print(a) 3 print(a.shape) 4 print(a.numel()) # 占用内存大小 2*3*5*5 5 print(a.dim()) 6 7 tensor([[[[0.9835, 0.7030, 0.4250, 0.8933, 0.7630], 8 [0.2675, 0.6665, 0.6763, 0.0020, 0.4530], 9 [0.1152, 0.3721, 0.4835, 0.0397, 0.8006], 10 [0.8404, 0.8846, 0.5573, 0.8277, 0.1989], 11 [0.4781, 0.1765, 0.6427, 0.6642, 0.1730]], 12 13 [[0.5206, 0.0983, 0.4531, 0.7570, 0.6972], 14 [0.5846, 0.5394, 0.1749, 0.4781, 0.3818], 15 [0.7925, 0.0544, 0.5471, 0.4569, 0.7156], 16 [0.0946, 0.6312, 0.3766, 0.9109, 0.9321], 17 [0.1460, 0.3911, 0.7015, 0.2559, 0.0900]], 18 19 [[0.3793, 0.1128, 0.6240, 0.1820, 0.5367], 20 [0.9884, 0.2246, 0.8867, 0.0365, 0.7996], 21 [0.0432, 0.3133, 0.9813, 0.3101, 0.1730], 22 [0.4255, 0.1069, 0.7456, 0.3309, 0.6482], 23 [0.8402, 0.8412, 0.5927, 0.9402, 0.1271]]], 24 25 [[[0.7033, 0.2369, 0.2151, 0.3082, 0.6550], 26 [0.7924, 0.6553, 0.5363, 0.7973, 0.9910], 27 [0.3186, 0.7235, 0.5424, 0.0890, 0.1040], 28 [0.4235, 0.3804, 0.1197, 0.1409, 0.7581], 29 [0.1459, 0.2897, 0.0287, 0.3721, 0.1573]], 30 31 [[0.0340, 0.7484, 0.9376, 0.2847, 0.8295], 32 [0.8523, 0.5974, 0.3696, 0.9365, 0.4192], 33 [0.4339, 0.1885, 0.6586, 0.7210, 0.8124], 34 [0.7633, 0.7692, 0.6171, 0.5773, 0.0222], 35 [0.5018, 0.6629, 0.6445, 0.1732, 0.7952]], 36 37 [[0.1797, 0.9118, 0.3146, 0.0521, 0.0877], 38 [0.5808, 0.2563, 0.3341, 0.7629, 0.4584], 39 [0.4380, 0.9800, 0.5872, 0.9888, 0.8613], 40 [0.1832, 0.2814, 0.8925, 0.7548, 0.3668], 41 [0.2438, 0.1767, 0.5987, 0.7235, 0.5110]]]]) 42 torch.Size([2, 3, 5, 5])
CNN [b,c,h,w]
b:bitch 图片个数
c:channel 图片通道数
h:hight 图片高度
w:width 图片宽度
