一. 常用的数组的高阶函数
假设, 现在有一个数组, 我们要对数组做如下一些列操作
1. 找出小于100的数字:
2. 将小于100的数字, 全部乘以2:
3. 在2的基础上, 对所有数求和:
通常我们会怎么做呢?
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <p>找出小于100的数字:</p> <p>将小于100的数字, 全部乘以2: </p> <p>对所有数求和:</p> <button @click="getNum()">计算</button> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data: { nums: [10, 20, 100, 30, 320, 55, 80, 210], num1:0, num2:0, num3:0 }, methods: { getNum(){ // 1. 找出<100的数字 let newNum1 = [] for(let num of this.nums) { if (num < 100) { newNum1.push(num) } } this.num1=newNum1 console.log(newNum1) // 2. 对小于100的数字*2 let newNum2 = [] for(let num of newNum1) { newNum2.push(num * 2) } this.num2 = newNum2 console.log(newNum2) // 3. 对小于100的数字*2后求和 let newNum3 = 0; for(let num of newNum2) { newNum3 += num } this.num3 = newNum3 console.log(newNum3) } } }) </script> </body> </html>
在上面的demo中, 我们全部都是使用循环来进行计算, 并且最后达到了我们想要的效果. 点击计算按钮, 查看计算结果:

在js高阶函数里面, 有一些高阶函数是可以直接计算得到上面的效果的. 下面主要介绍三个高阶函数
- filter
- map
- reduce
1. filter函数
filter()方法会创建一个新数组,原数组的每个元素传入回调函数中,回调函数中有return返回值,若返回值为true,这个元素保存到新数组中;若返回值为false,则该元素不保存到新数组中;原数组不发生改变。
- 语法: array.filter(function(currentValue,index,arr), thisValue)
- 参数
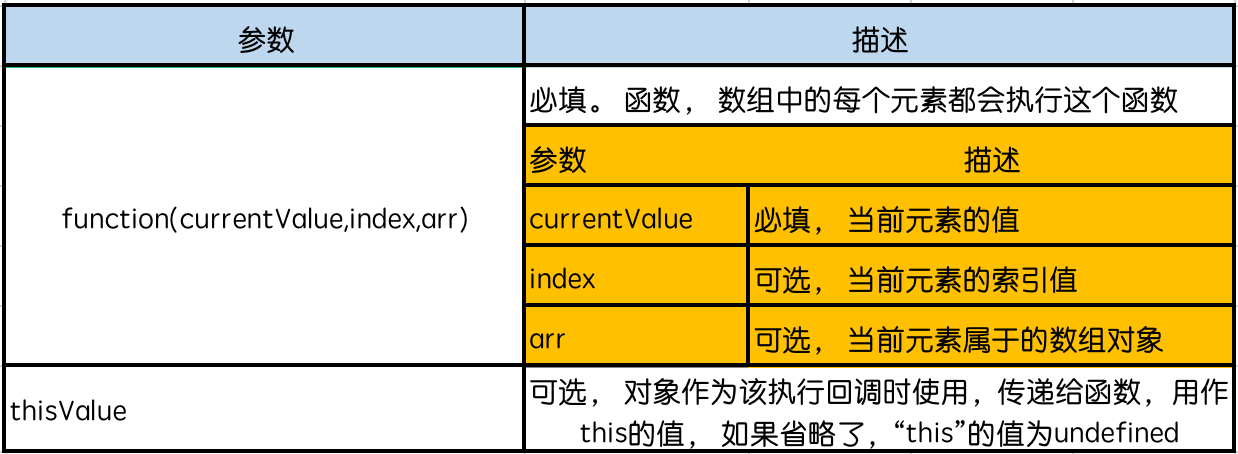
举例1: 返回数组中<100的元素
getNums() { // 来看看filter的用法
let num1 = [10 ,20, 100, 30, 320, 55. 80, 210] let newNum1 = this.nums.filter(function (num) { return num < 100; }) console.log(newNum1) }
- filter()函数的入参是一个function, 出参是一个新的数组
- function函数也有参, 这里只传入了第一个入参, 表示: 循环遍历时的数组元素.
- function的返回值类型是true或false, 如果返回结果是true, 则返回新数组中有这个元素, 返回结果是false, 则返回新数组中没有这个元素
举例2: 利用filter,可以巧妙地去除Array的重复元素:
filter()接收的回调函数,其实可以有多个参数。通常我们仅使用第一个参数,表示Array的某个元素。回调函数还可以接收另外两个参数,表示元素的位置和数组本身:
let nums = [10, 20, 100, 30, 320, 55, 80, 210, 20, 55, 320]
let newNum2 = this.nums.filter(function(element, index, self) {
return self.indexOf(element) == index
})
运行结果
[10, 20, 100, 30, 320, 55, 80, 210]
去除重复元素依靠的是indexOf总是返回第一个元素的位置,后续的重复元素位置与indexOf返回的位置不相等,因此被filter滤掉了。
2. map函数
方法返回一个新数组,新数组中的每一个元素为原始数组对应每一个元素调用函数处理后的值;不会对空数组进行编辑,不改变原来的数组。
- 语法: array.every(function(item,index,array){})
- 参数:
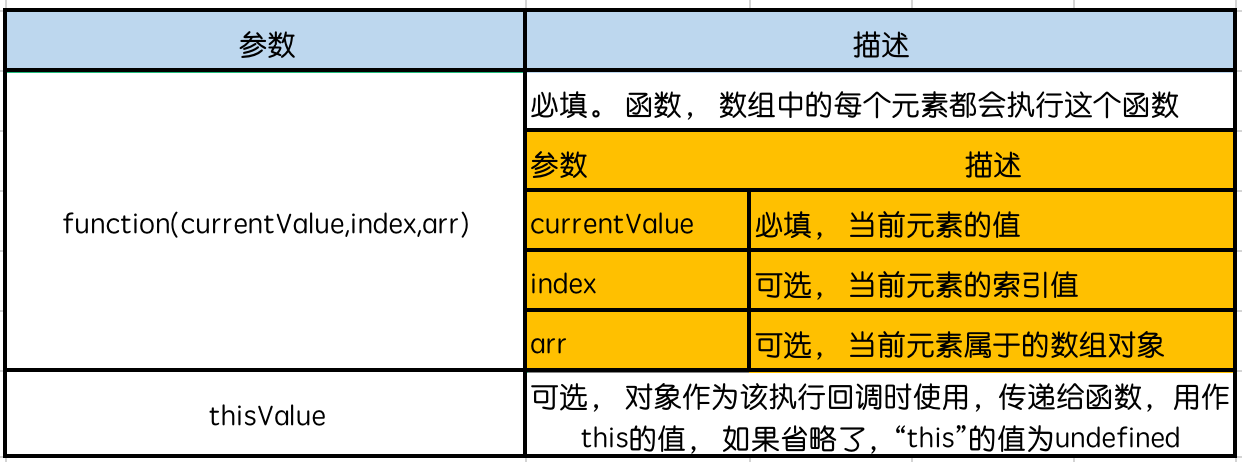
举例1: 求数组中所有元素*2后的数组
let nums = [10, 20, 100, 30, 320, 55, 80, 210, 20, 55, 320]
let newNum1 = this.nums.map(function (num) {
return num * 2;
})
console.log(newNum1)
输出结果:
[20, 40, 200, 60, 640, 110, 160, 420, 40, 110, 640]
3. reduce函数
reduce() 方法接收一个函数作为累加器,reduce 为数组中的每一个元素依次执行回调函数,数组中被删除或从未被赋值的元素不处理.
- 语法: arr.reduce(callback,[initialValue])
- 参数
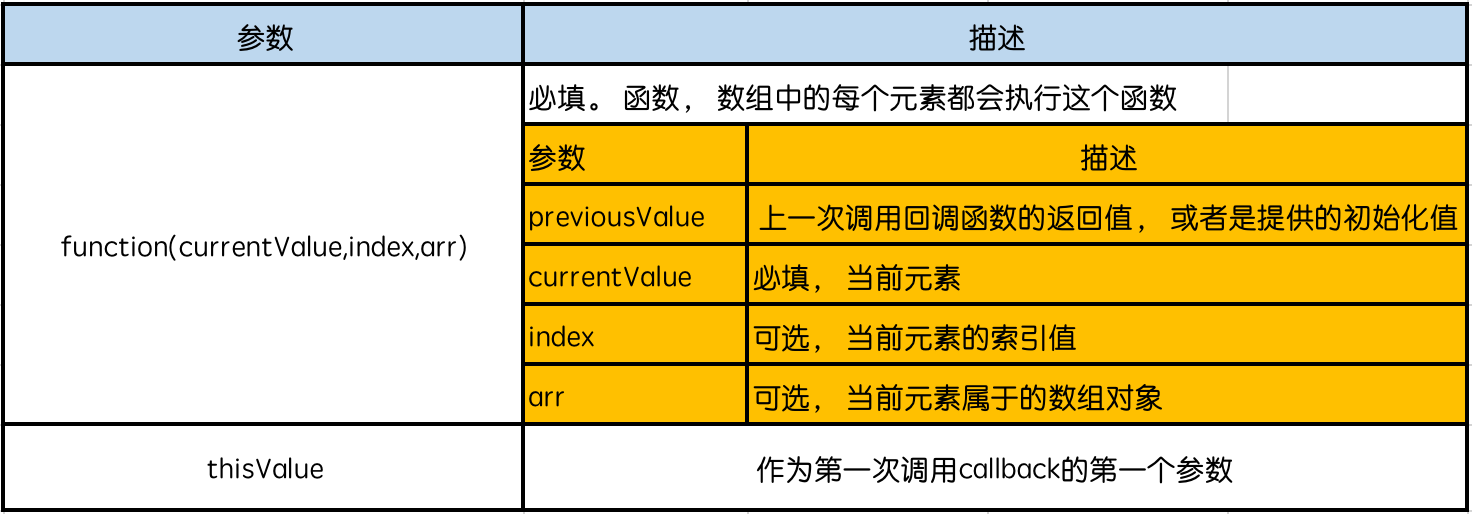
案例1: 求一个数组的和
// reduce的用法
let nums = [10, 20, 100, 30, 320, 55, 80, 210, 20, 55, 320]
let newNum1 = this.nums.reduce(function (total, num) {
return num + total;
}, 0)
console.log(newNum1)
二. 综合案例1
结合filter, map, reduce三个函数, 获取数组中<100的元素, 然后对这些元素同意*5, 最后求*5后的所有元素的和
// reduce的用法 let nums = [10, 20, 100, 30, 320, 55, 80, 210, 20, 55, 320] let newNum1 = this.nums.filter(function (number) { return number < 100 }).map(function (number) { return number * 5 }).reduce(function (total, num) { return num + total; }, 0) console.log(newNum1)
输出结果: 1220
其实还有更简单的算法, lambda表达式
// reduce的用法 let nums = [10, 20, 320] let newNum11 = nums.filter(num => num < 100).map(num => num * 5, this).reduce((total, num) => total + num) console.log(newNum11)
执行结果: 150
三.综合案例2
显示一个列表, 选中那个那个变色, 使用vue实现

可以思考两分钟, 看看, 如何来设计.
在vue中, 这个过程将非常简单
- 第一步: 定义了一个isCurrentIndex用来记录当前选中元素的下标.
- 第二步: 在class属性中设置 :isCurrentIndex == index. 表示选中元素的下标显示红色, 其他不显示红色.
- 第三步: 定义一个click事件, 每次点击事件, 修改选中的下标值
代码如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.action {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in languages" :class="{action:isCurrentIndex == index}" @click="changeCurrentIndex(index)"> {{index}}--{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
languages: ["java", "php", "python", "go", "c语言"],
isCurrentIndex:0
},
methods: {
changeCurrentIndex(index) {
this.isCurrentIndex = index
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
四. 综合案例3
我们要做一个表格, 具体内容如下
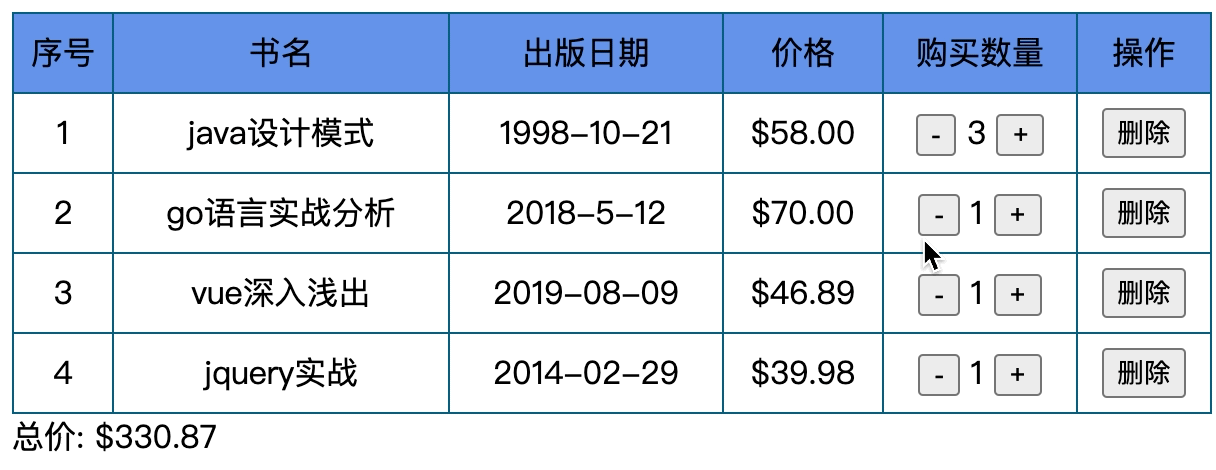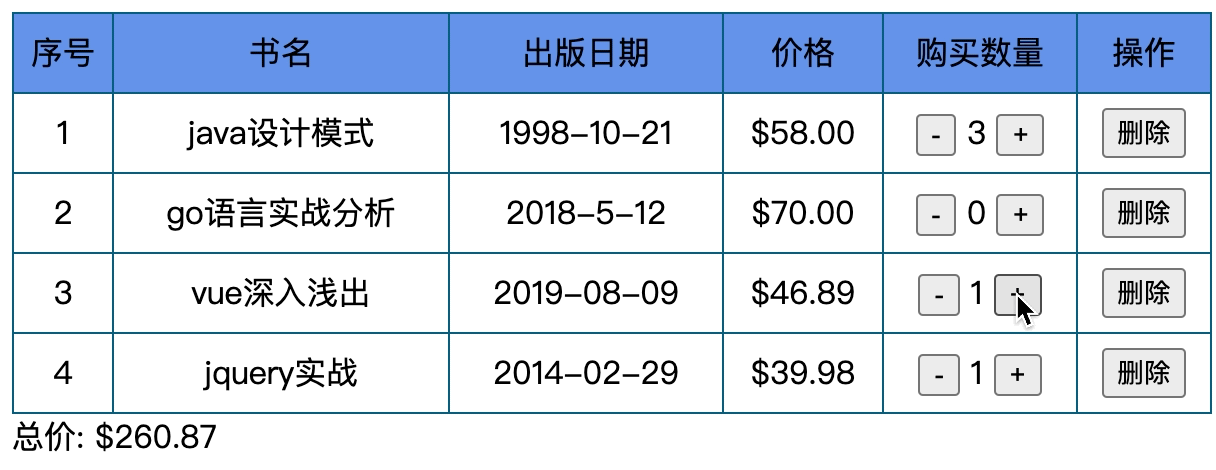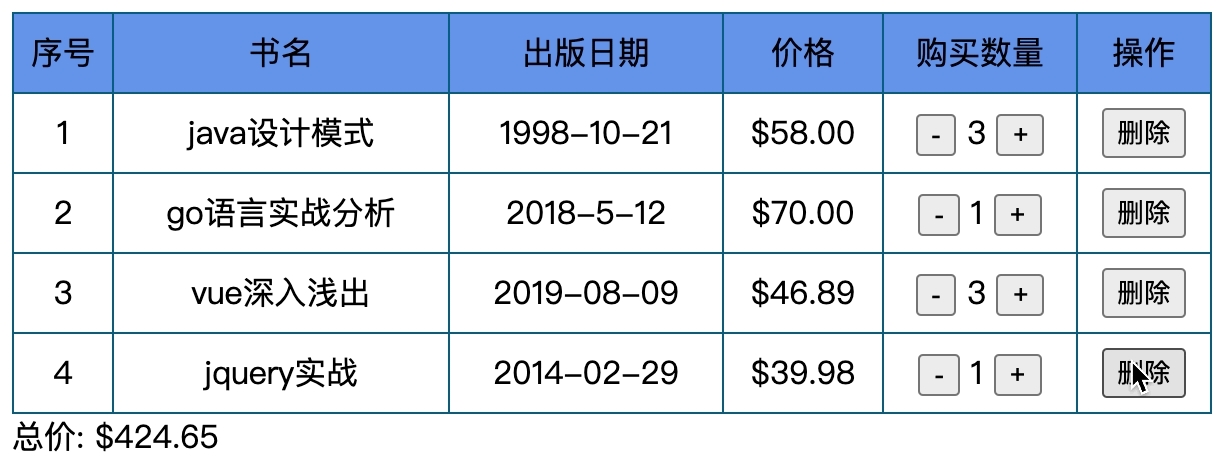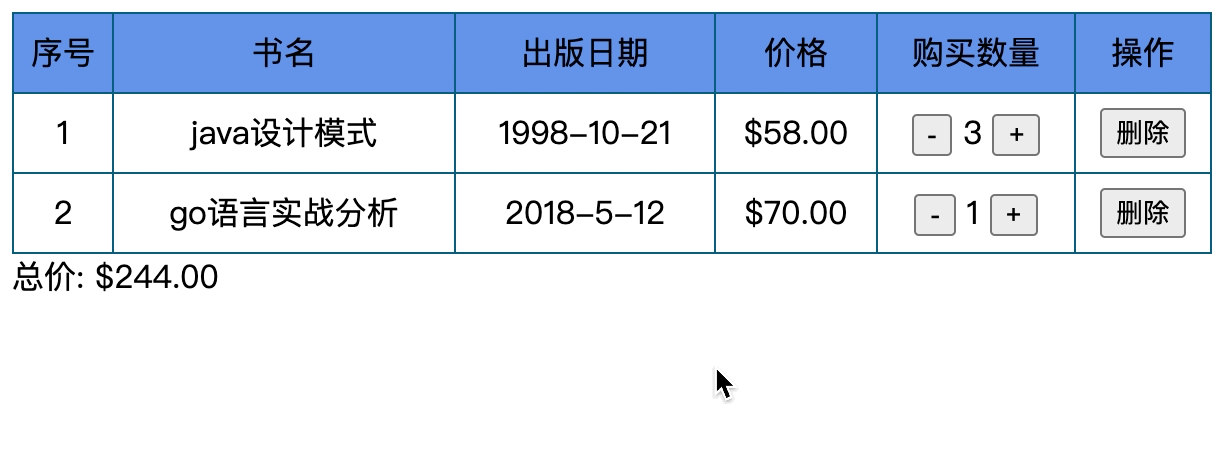
主要有哪些东西呢?
- 有n本书, 书有书名, 出版日期, 价格, 数量, 操作
- 价格保留两位小数, 数量可增减, 最多减到0,
- 操作可以删除表格 ,当表格没有数据时显示无数据
- 随时计算总价格.
下面来看看这个代码如何实现, 结合我们之前学过的js高阶函数
第一步: 定义了n本书, 放在vue的data属性里面
data: { books: [ {name:"java设计模式", publishDate:"1998-10-21", price: 58.00, count: 1}, {name:"go语言实战分析", publishDate:"2018-5-12", price: 70.00, count: 1}, {name:"vue深入浅出", publishDate:"2019-08-09", price: 46.89, count: 1}, {name:"jquery实战", publishDate:"2014-02-29", price: 39.98, count: 1} ], total: 0 },
定义了一个总价格, 用来保存计算后的总价格
第二步: 画table
<div id="app"> <table border="1"> <thead> <tr> <td>序号</td> <td>书名</td> <td>出版日期</td> <td>价格</td> <td>购买数量</td> <td>操作</td> </tr> </thead> <tbody v-if="books.length==0"> <tr> <td colspan="6" >没有数据</td> </tr> </tbody> <tbody v-else> <tr v-for="(item, index) in books" > <td>{{index+1}}</td> <td>{{item.name}}</td> <td>{{item.publishDate}}</td> <td>{{item.price| priceUnit}} </td> <td> <button @click="sub(index)">-</button> {{item.count}} <button @click="add(index)">+</button> </td> <td> <button @click="del(index)">删除</button> </tr> </tbody> </table> <label id="sum">总价: {{getTotal() | priceUnit}} </label> </div>
在这里我们循环遍历了data数据, 然后对价格进行了处理, 增加了单位, 对数量增加了增减的button. 最后定义了一个删除功能
第三步. 使用过滤器格式化价格
在对价格进行格式化的时候, 使用了管道符.这是过滤器的写法. 不加过滤器之前, 价格是58. 加了过滤器之后是: $58.00, 增加了一个美元符号, 价格保留两位小数
因为不止有一个地方会用到加单位, 所以, 我们将其定义为一个方法. 如下写法
filters: { priceUnit(price) { return "$" + price.toFixed(2) } }
这里定义了过滤器的写法. 类似于methods. 里面定义一个方法. 其实这个方法可不可以放在methods中呢? 也可以, 但是放在filters有一个好处. 可以使用管道符写法
<td>{{item.price | priceUnit}} </td>
使用过滤器, 会自动将 | 前面的值作为参数传递给priceUnit
第四步: 定义methods, 对图书数量进行增减, 且做少不能少于0
sub(index) { if (this.books[index].count <= 0) { this.books[index].coun = 0; } else { this.books[index].count --; } }, add(index) { this.books[index].count ++; },
这个就不多说了, 普通函数写法
第五步: 计算总额
计算总额有多种写法, 常规写法
getTotal() { let totalPrice = 0; for(let i = 0; i < this.books.length; i++) { totalPrice += this.books[i].price * this.books[i].count; } return totalPrice; },
循环遍历books, 价格和数量乘积的和
推荐使用js的高阶函数
getTotal() { // 使用数组的高阶函数计算每种书的价格总和 return this.books.map((book)=>book.price * book.count).reduce((total,num) => total + num) },
在回顾一下
- map是对数组的每一个元素执行操作
- reduce是对数组中所有元素求和
第六步: 删除表格行
del(index){ this.books.splice(index,1) }
删除行, 使用splice删除指定的data中的元素, 就可以了
