Map
Map不同于Collection集合,Map存放的是键值对,且键不能重复
1 .HashMap (底层是哈希表,Java中用链表的数组实现,存取顺序不一致)
这篇博客主要讲集合的,哈希表这样的数据结构就不说明了,后期会补充哈希表,红黑树这样的博文
- 开头变量(太长不截图了,直接复制源码过来解释,如果能看懂英文解释就更好拉)
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // 初始化桶容量16
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; //最大容量2^31
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; //默认装载因子,后面解释
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; //当链表节点小于8个时,转成红黑树
/**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; //树形元素小于6个时,转成链表
/**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts
* between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; //桶的最小可能转化树形结构的大小
//链表的节点
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
//还重写了equals方法,可以看出键值相等才相等
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
- put (相当于Collection的add)
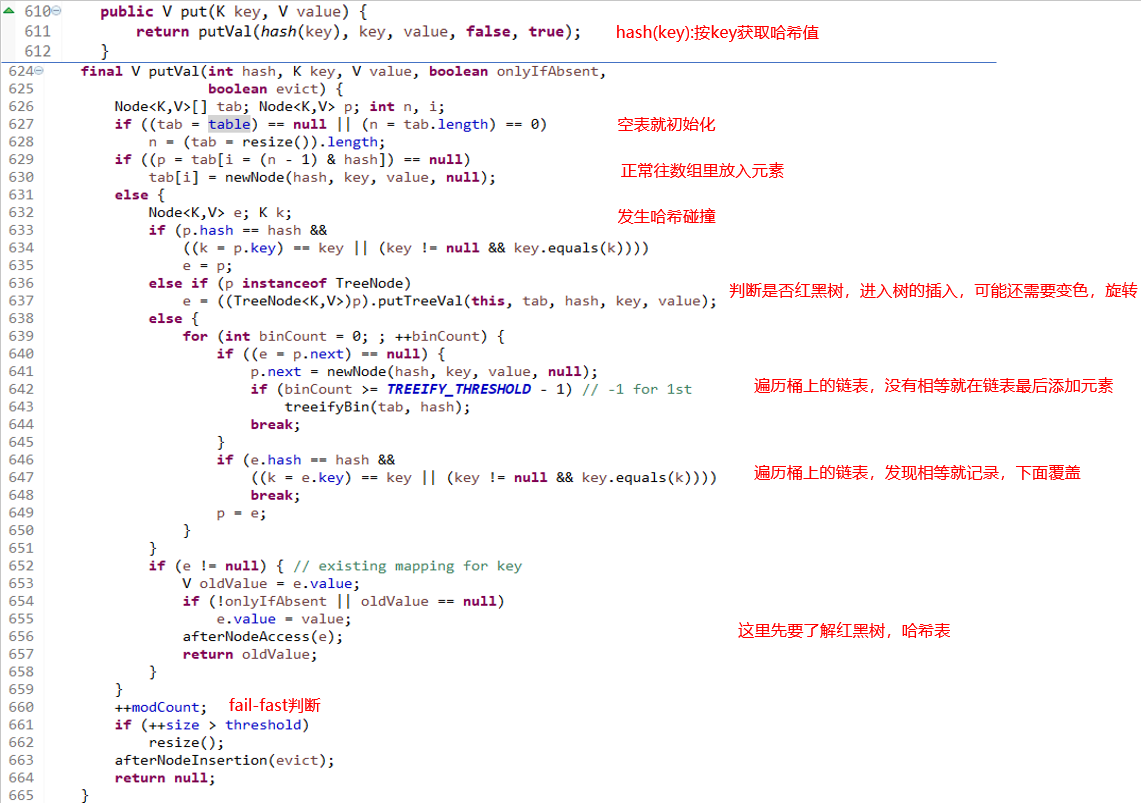
634行 是解决null情况才加了判断
624行 大于8转成红黑树
652行 新值覆盖旧值,返回旧值
- get
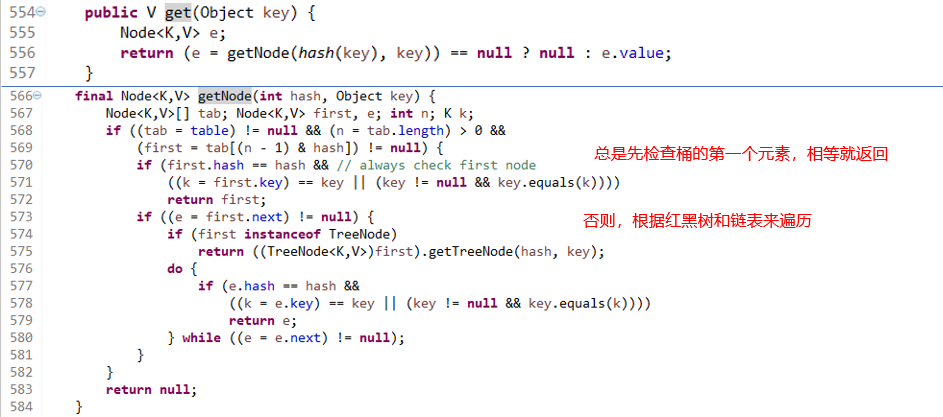
556行 为空返回null,否则返回节点的值
568行 计算的Hash值在桶上才行,而且桶不为空
573行 开始,遍历链表或者红黑树找相同的节点返回,没找到就返回Null
- remove
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
//删除节点的逻辑
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
和get方法差不多,先判断在不在桶上且或不为空
先去桶上找,找不到就遍历,遍历到了就记住这个节点
判断红黑树还是链表,执行各自删除节点操作
总结
- 允许Key,value为null
- 哪条链长于8 那条链就转成红黑树
- 线程不安全,有快速失败机制,后几篇博文会说明
- 当size > 桶数 * factor时候会再散列,即桶数*2倍,如果开始就设置桶大小就省去了再散列耗损
- 因为再散列,所以不同时期遍历顺序可能不一样
- 桶大小二次幂:Hash值太大,不适合映射数组位置,桶大小%Hash值当作位置,2次幂方便位运算,功能等于取模但却快很多
2. Hashtable(已经过时)
-
线程安全,用synchronized修饰,不推荐使用,牺牲锁来换取同步
-
用ConcurrentHashMap代替,1.7/1.8用不同机制解决同步问题
-
不能为null
3. LinkedHashMap(哈希表+双向链表+有序)
- 继承了HashMap,二者大致相同,但因多了双向链表,所以访问有序了
- 访问顺序分为:插入顺序,访问顺序
- 可以为null,不同步
3.1 链表的结点
- Map集合定义了Entry<K,V>接口,他是结点的原型,下面列举了接口重要的方法:equals,hashCode,比较器Comparator
/**
* A map entry (key-value pair). The <tt>Map.entrySet</tt> method returns
* a collection-view of the map, whose elements are of this class. The
* <i>only</i> way to obtain a reference to a map entry is from the
* iterator of this collection-view. These <tt>Map.Entry</tt> objects are
* valid <i>only</i> for the duration of the iteration; more formally,
* the behavior of a map entry is undefined if the backing map has been
* modified after the entry was returned by the iterator, except through
* the <tt>setValue</tt> operation on the map entry.
*
* @see Map#entrySet()
* @since 1.2
*/
interface Entry<K,V> {
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
public static <K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByKey() {
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey());
}
}
- HashMap中继承了该接口
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {内容就不写了,参考上面}
- 而LinkedHashMap又继承了HashMap的Node接口,并命名为Entry,多了头尾指向,
有点混,捋捋就好
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
3.2 结构图
- 默认用插入顺序的
- 黑色部分为HashMap结构图,而红色部分则属于新增的LinkedHashMap内容,其实就是维护了一个双向链表
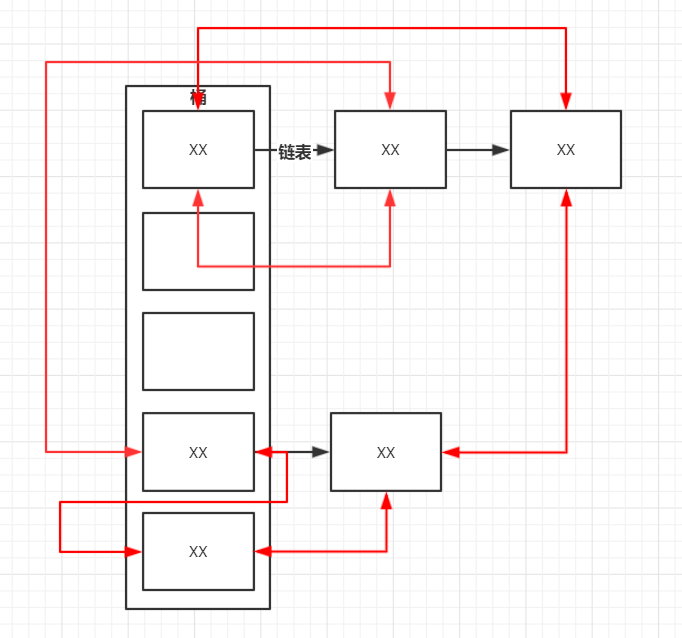
3.3 构造方法
- 参数顺序为初始化容量,影响因子以及
是否访问顺序,默认构造函数为false
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor,boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
//默认构造
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
3.4 存储有序
- 这里的有序分为插入顺序和访问顺序,下面会用代码测试说明,之前还要来认识一下几个方法:
| 返回值 | 方法名 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| Set< K> | keySet() | 返回包含所有key的Set集合 |
| Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> | entrySet() | 返回包含所有entry的Set集合 |
- Map遍历方式
//1.根据key集合访问
for (Object k : map.keySet()){
System.out.println(map.get(k));
}
//2.根据迭代器
Iterator iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
//3.推荐,foreach,如果创建map集合指定了泛型就不用下面那么麻烦强转了
for(Map.Entry<Object,Object> entry : (Set<Map.Entry<Object, Object>>) map.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" +entry.getValue());
}
- 为什么有序
//新建结点
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p); //因为创建结点的时候加入到维护的双向链表尾去了
return p;
}
//加入到链尾,开头变量维护了 head,和tail结点
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}
//维护的变量
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
- 测试
按插入顺序来访问,因为获取的entrySet()被重写了,获取的时是维护的链表set集合
LinkedHashMap<Integer,Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap();
linkedHashMap.put(1, 1);
linkedHashMap.put(2, 2);
linkedHashMap.put(3, 3);
linkedHashMap.put(4, 4);
linkedHashMap.put(5, 5);
for(Map.Entry entry : linkedHashMap.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry);
}
1=1
2=2
3=3
4=4
5=5
按访问顺序来访问,这里的get()就算是访问了
LinkedHashMap<Integer,Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap(10,0.75f,true);
linkedHashMap.put(1, 1);
linkedHashMap.put(2, 2);
linkedHashMap.put(3, 3);
linkedHashMap.put(4, 4);
linkedHashMap.put(5, 5);
//访问了3,所以结构被改变了
linkedHashMap.get(3);
for(Map.Entry entry : linkedHashMap.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry);
}
1=1
2=2
4=4
5=5
3=3
总结
当需要键值对,且还需插入顺序访问的时候采用LinkedHashMap,因为内部还要维护双向链表,损耗性能,不然对比二者推荐使用HashMap
4. TreeMap (Key不能为空,要排序)
- 底层红黑树,是个平衡树,节省查找时间(类似于二分查找?? 以后复习算法写博文时回来填坑)
- 用Comparable,Comparator排序,默认自然排序
- key不能为空,下面563行可以看出,会抛出NullPointerException异常
- put

- get
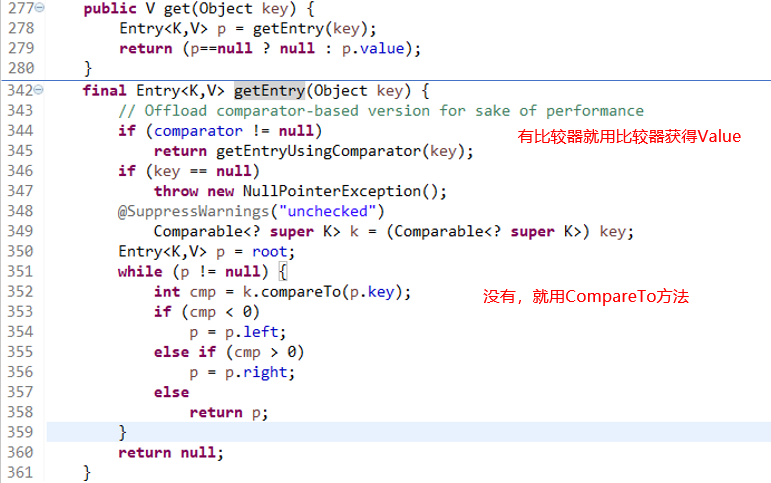
- remove
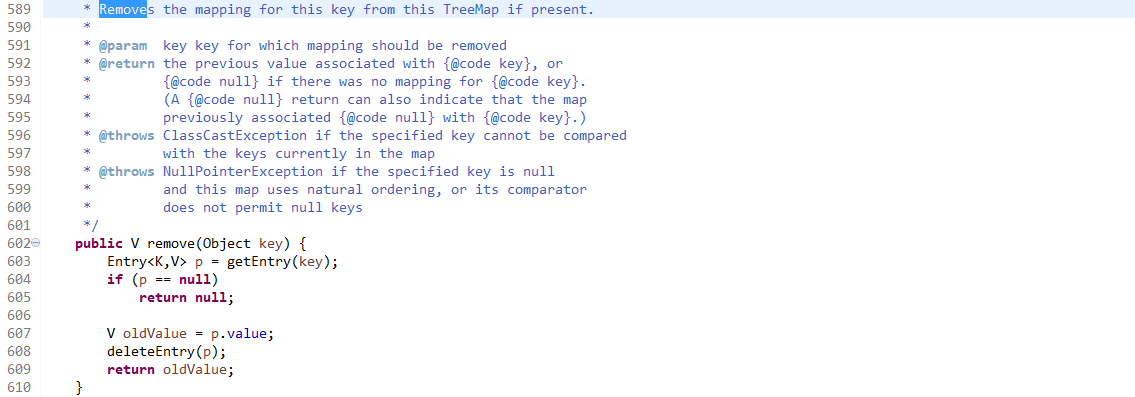
608行 删除结点还是要平衡结点,很难,有兴趣去看看二叉查找树,平衡树,红黑树
- 补充
构造方法
//默认构造没有比较器
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
//也可以传入比较器
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
继承关系
- 当时在Map接口下找TreeMap,找了好久没找到,结果是实现了AbstractMap接口
- 发现TreeMap是实现了NavigableMap接口,而后者又继承SortedMap接口,其中定义了下面方法使得有序
/**
* Returns the comparator used to order the keys in this map, or
* {@code null} if this map uses the {@linkplain Comparable
* natural ordering} of its keys.
*
* @return the comparator used to order the keys in this map,
* or {@code null} if this map uses the natural ordering
* of its keys
*/
Comparator<? super K> comparator();
遍历
利用父类的successor遍历树
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
三. Set——无序,不可重复
Set集合底层用的就是Map,所以看过Map集合后再来看Set集合简直太简单,下面看看怎么使用Map集合
1. HashSet
- 注意其构造函数,底层用的是HashMap,而Set集合存的不是键值对怎么办?
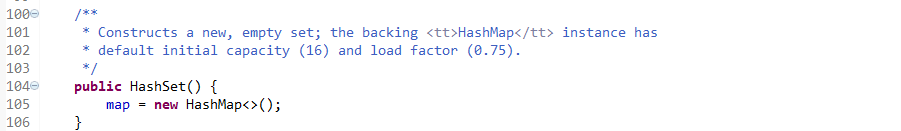
- Set的值存入Map的键里面,而Map的全部值存放同一个Object,开头变量就定义了一个空对象

其余都和HashMap一致,不再赘述
2. TreeSet
- 和TreeMap一致,懒得说了
3. LinkedHashMap
- 和LinkedHashMap一致,懒得说了
总结
Set集合和Map集合一样,那就没什么好说的了
-
源码基于JDK1.8