使用系统调用的时候用文件描述符(file descriptor,简称fd)的时候比较多,但是操作比较原始。C库函数在I/O上提供了一些方便的包装(比如格式化I/O、重定向),但是对细节的控制不够。
如果过度依赖其中的一种只会徒增麻烦,所以知道两者的转换是很有必要的。FILE*是对fd的封装
当然,有人会说知道文件路径的话重新打开就是了,但是这会产生竞争条件(Race Conditions),首先重新打开文件,相当于是2个fd指向同一文件,然后如果在打开的期间文件被删除了又被新建了一个同名文件,2个fd指向的便是不同的文件。
glibc库提供了两个转换函数fdopen(3)和fileno(3),都是<stdio.h>中的
FILE *fdopen(int fd, const char *mode);
int fileno(FILE *stream);
PS:为了节省篇幅,还是继续忽略返回值的检查。
来看看测试吧,是不是我们想的那样。
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main() { const char* filename = "new.txt"; int fd = open(filename, O_RDWR | O_CREAT, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR); FILE* fp = fdopen(fd, "w+"); int fd2 = fileno(fp); printf("fd=%d | fd2=%d ", fd, fd2); fclose(fp); close(fd); return 0; }
$ gcc test.c $ ./a.out fd=3 | fd2=3
参考fileno手册:The function fileno() examines the argument stream and returns its integer descriptor.
FILE是对fd的封装,fileno()是直接取得被封装的fd,因此并未创建新的fd指向该文件。
参考fdopen手册:
The fdopen() function associates a stream with the existing file descriptor, fd. The mode of
the stream (one of the values "r", "r+", "w", "w+", "a", "a+") must be compatible with the
mode of the file descriptor.
fdopen()是讲流(FILE对象)与已存在的文件描述符fd进行关联,因此也是未创建新的fd。值得注意的是,FILE指针的模式(mode)必须与文件描述符的模式兼容。
关于mode参数先搁置会儿,目前我们知道的是,使用fileno和fdopen进行转换,都是在原有的fd上进行操作,并未产生新的fd。那么,再次审视刚才的代码,是否发现了问题?
我们来检查下close(fd)的返回值,把close(fd)改成下列代码
if (-1 == close(fd)) { perror("close"); exit(1); }
$ gcc test.c $ ./a.out close: Bad file descriptor
没错,fclose在关闭文件指针的时候,内部其实也关闭了文件描述符(否则资源就泄露了),既然这里fp内部的文件描述符和fd是同一个,当fp被关闭时,fd也被关闭了,再次关闭fd就会出现“损坏的文件描述符”错误。
OK,现在回顾下fopen的第2个参数,又r/r+/w/w+/a/a+一共6种设置(windows平台的rb/rb+/wb/wb+暂且不谈),对比Linux手册我将对应的open设置列出来
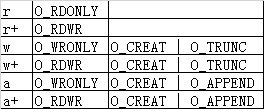
依然是进行测试,修改fd_mode和fp_mode,看看实验结果
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> const int security = S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR; const int fd_mode = O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC; const char* fp_mode = "r"; int main() { int fd = open("new.txt", fd_mode, security); FILE* fp = fdopen(fd, fp_mode); if (fp == NULL) { perror("fdopen"); exit(1); } close(fd); return 0; }
在fd_mode等价于"w+"时,fp_mode的6种设置(r/r+/w/w+/a/a+)均返回非空指针。
在fd_mode等价于"w"时,fp_mode6种设置只有"a"和"w"返回非空指针。
继续尝试"r"/"r+"/"a"/"a+"的设置,可以发现所谓“兼容”只与读写权限有关,O_RDWR兼容O_RDONLY和O_WRONLY,而后两者则只与自身兼容。
有意思的是O_APPEND(在末尾添加)和O_TRUNC(截断文件从头添加)也兼容。
The file position indicator of the new stream is set to that
belonging to fd, and the error and end-of-file indicators are cleared. Modes "w" or "w+" do
not cause truncation of the file. The file descriptor is not dup'ed, and will be closed when
the stream created by fdopen() is closed.
继续查看fdopen的手册内容,可以看到"w"和"w+"在这里不会导致文件截断。
后一句也印证了我们前面的实验结果:文件描述符不会被复制,文件指针被关闭时文件描述符也会被关闭。
PS:其实fdopen的手册上还有最后一句:The result of applying fdopen() to a shared memory object is undefined.
将fdopen用于共享内存对象的结果是未定义的。