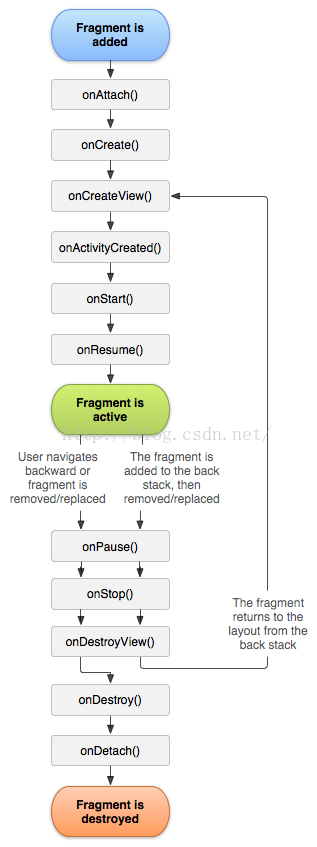
4.3 Fragment的生命周期
4.3.1 Fragment的状态和回调
1.运行状态
当一个Fragment是可见的,并且它关联的活动正处于运行状态是,该Fragment也处于运行状态
2.暂停状态
当一个活动进入了暂停状态时(由于另一个未占满屏幕的活动被添加到了栈顶),与它相关的可见Fragment就会进入暂停状态
3.停止状态
当一个活动进入了停止状态,与它相关联的Fragment就会进入到停止状态,或者通过调用FragmentTransaction的remove()、replace()方法将Fragment从活动中移除。
总的来说,进入停止状态的Fragment对用户来说时完全不可见的。
4.销毁状态
当活动被销毁时,与它相关联的Fragment就会进入到销毁状态。或者调用FragmentTransaction的remove()、replace()方法将Fragmet从活动中移除。
在事务提交之前没有调用addToBackStack()方法,也会使Fragment进入到销毁状态。
Fragment的几个回调方法
onAttach() 当Fragment和活动建立关联的时候调用。
onCreateView() 当Fragment创建视图(加载布局)时调用。
onActivityCreated() 确保与Fragment相关联的活动一定已经创建完毕的时候调用。
onDestroyView() 当与Fragment相关联的视图被移除的时候调用。
onDetach() 当Fragment与活动解除关联的时候调用。
Fragment完整的生命周期示意图:
4.4 动态加载布局的技巧
4.4.1 使用限定符
运行程序判断应该使用单页模式还是双页模式,需要借助限定符(Qualifiers)来实现
Eg:
1.修改FragmentTest中的activity_main.xml文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <fragment android:id="@+id/left_fragment" android:name="com.example.song.fragmenttest.LeftFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </LinearLayout>
只留下一个左侧Fragment并让它充满父布局。
2.在res目录下新建layout-large文件夹,并新建一个布局也为activity-main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <fragment android:id="@+id/left_fragment" android:name="com.example.song.fragmenttest.LeftFragment" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="1"/> <fragment android:id="@+id/right_fragment" android:name="com.example.song.fragmenttest.RightFragment" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="3"/> </LinearLayout>
3.layout/activity_main布局只包含一个Fragment,即单页模式。layout-large/activity_main布局包含了两个Fragment,即双页模式。
large即为一个限定符,屏幕被认为是large的设备就会自动加载layout-large文件夹下的布局
小屏幕设备则还是会加载layout文件夹下的布局
注释掉MainActivity中replaceFragment()方法里的代码
运行程序:
平板和手机显示的分别为双页模式和单页模式
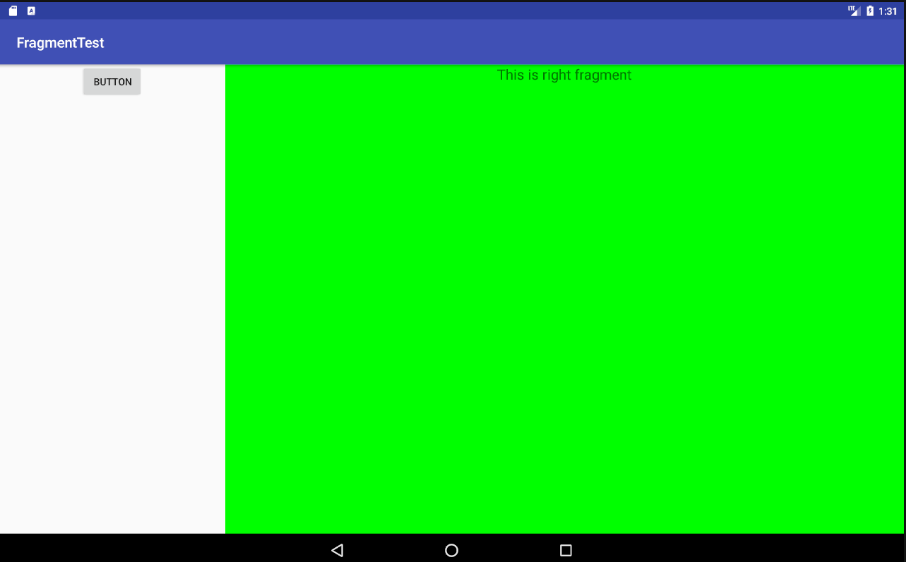

4.4.2 使用最小宽度限定符
最小宽度限定符(Smallest-width-Qualifier)允许对屏幕的宽度指定一个最小值(以dp为单位),然后以这个最小值为临界点,屏幕宽度大于这个值就加载一个布局,小于这个值的设备就加载另一个布局。
res目录下新建layout-sw600dp文件夹,然后新建activity_layout.xml布局
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <fragment android:id="@+id/left_fragment" android:name="com.example.song.fragmenttest.LeftFragment" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="1"/> <fragment android:id="@+id/right_fragment" android:name="com.example.song.fragmenttest.RightFragment" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="3" /> </LinearLayout>
当程序运行的屏幕大于等于600dp时,会加载layout-600dp/activity-main.xml
当程序运行的屏幕小于600dp时,会加载默认的layout/activity-main.xml