1.写在前面
Android提供了丰富的Dialog函数,本文介绍最常用的8种对话框的使用方法,包括普通(包含提示消息和按钮)、列表、单选、多选、等待、进度条、编辑、自定义等多种形式,将在第2部分介绍。
有时,我们希望在对话框创建或关闭时完成一些特定的功能,这需要复写Dialog的create()、show()、dismiss()等方法,将在第3部分介绍。
2.代码示例
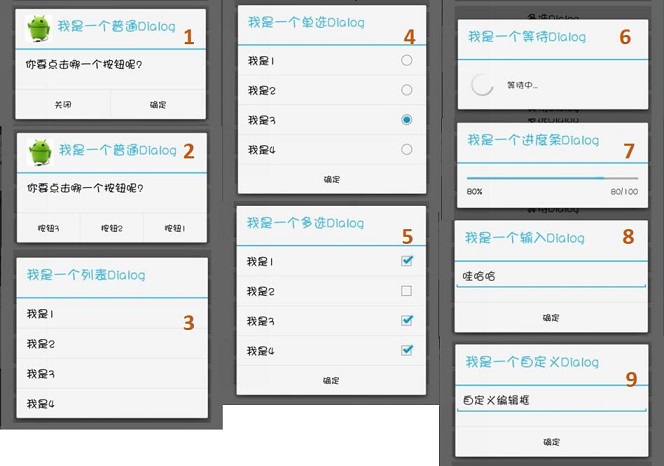
2.1 普通Dialog(图1和图2)
2个按钮
public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Button buttonNormal = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_normal); buttonNormal.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { showNormalDialog(); } }); } private void showNormalDialog(){ /* @setIcon 设置对话框图标 * @setTitle 设置对话框标题 * @setMessage 设置对话框消息提示 * setXXX方法返回Dialog对象,因此可以链式设置属性 */ final AlertDialog.Builder normalDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this); normalDialog.setIcon(R.drawable.icon_dialog); normalDialog.setTitle("我是一个普通Dialog") normalDialog.setMessage("你要点击哪一个按钮呢?"); normalDialog.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { //...To-do } }); normalDialog.setNegativeButton("关闭", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { //...To-do } }); // 显示 normalDialog.show(); } }
3个按钮
/* @setNeutralButton 设置中间的按钮 * 若只需一个按钮,仅设置 setPositiveButton 即可 */ private void showMultiBtnDialog(){ AlertDialog.Builder normalDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this); normalDialog.setIcon(R.drawable.icon_dialog); normalDialog.setTitle("我是一个普通Dialog").setMessage("你要点击哪一个按钮呢?"); normalDialog.setPositiveButton("按钮1", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // ...To-do } }); normalDialog.setNeutralButton("按钮2", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // ...To-do } }); normalDialog.setNegativeButton("按钮3", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // ...To-do } }); // 创建实例并显示 normalDialog.show(); }
2.2 列表Dialog(图3)
private void showListDialog() { final String[] items = { "我是1","我是2","我是3","我是4" }; AlertDialog.Builder listDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this); listDialog.setTitle("我是一个列表Dialog"); listDialog.setItems(items, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // which 下标从0开始 // ...To-do Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你点击了" + items[which], Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }); listDialog.show(); }
2.3 单选Dialog(图4)
int yourChoice; private void showSingleChoiceDialog(){ final String[] items = { "我是1","我是2","我是3","我是4" }; yourChoice = -1; AlertDialog.Builder singleChoiceDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this); singleChoiceDialog.setTitle("我是一个单选Dialog"); // 第二个参数是默认选项,此处设置为0 singleChoiceDialog.setSingleChoiceItems(items, 0, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { yourChoice = which; } }); singleChoiceDialog.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { if (yourChoice != -1) { Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你选择了" + items[yourChoice], Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } } }); singleChoiceDialog.show(); }
2.4 多选Dialog(图5)
ArrayList<Integer> yourChoices = new ArrayList<>(); private void showMultiChoiceDialog() { final String[] items = { "我是1","我是2","我是3","我是4" }; // 设置默认选中的选项,全为false默认均未选中 final boolean initChoiceSets[]={false,false,false,false}; yourChoices.clear(); AlertDialog.Builder multiChoiceDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this); multiChoiceDialog.setTitle("我是一个多选Dialog"); multiChoiceDialog.setMultiChoiceItems(items, initChoiceSets, new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which, boolean isChecked) { if (isChecked) { yourChoices.add(which); } else { yourChoices.remove(which); } } }); multiChoiceDialog.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { int size = yourChoices.size(); String str = ""; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { str += items[yourChoices.get(i)] + " "; } Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你选中了" + str, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }); multiChoiceDialog.show(); }
2.5 等待Dialog(图6)
private void showWaitingDialog() { /* 等待Dialog具有屏蔽其他控件的交互能力 * @setCancelable 为使屏幕不可点击,设置为不可取消(false) * 下载等事件完成后,主动调用函数关闭该Dialog */ ProgressDialog waitingDialog= new ProgressDialog(MainActivity.this); waitingDialog.setTitle("我是一个等待Dialog"); waitingDialog.setMessage("等待中..."); waitingDialog.setIndeterminate(true); waitingDialog.setCancelable(false); waitingDialog.show(); }
2.6 进度条Dialog(图7)
private void showProgressDialog() { /* @setProgress 设置初始进度 * @setProgressStyle 设置样式(水平进度条) * @setMax 设置进度最大值 */ final int MAX_PROGRESS = 100; final ProgressDialog progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainActivity.this); progressDialog.setProgress(0); progressDialog.setTitle("我是一个进度条Dialog"); progressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL); progressDialog.setMax(MAX_PROGRESS); progressDialog.show(); /* 模拟进度增加的过程 * 新开一个线程,每个100ms,进度增加1 */ new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { int progress= 0; while (progress < MAX_PROGRESS){ try { Thread.sleep(100); progress++; progressDialog.setProgress(progress); } catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } // 进度达到最大值后,窗口消失 progressDialog.cancel(); } }).start(); }
2.7 编辑Dialog(图8)
private void showInputDialog() { /*@setView 装入一个EditView */ final EditText editText = new EditText(MainActivity.this); AlertDialog.Builder inputDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this); inputDialog.setTitle("我是一个输入Dialog").setView(editText); inputDialog.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, editText.getText().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }).show(); }
2.8 自定义Dialog(图9)
<!-- res/layout/dialog_customize.xml--> <!-- 自定义View --> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <EditText android:id="@+id/edit_text" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
private void showCustomizeDialog() { /* @setView 装入自定义View ==> R.layout.dialog_customize * 由于dialog_customize.xml只放置了一个EditView,因此和图8一样 * dialog_customize.xml可自定义更复杂的View */ AlertDialog.Builder customizeDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this); final View dialogView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this) .inflate(R.layout.dialog_customize,null); customizeDialog.setTitle("我是一个自定义Dialog"); customizeDialog.setView(dialogView); customizeDialog.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // 获取EditView中的输入内容 EditText edit_text = (EditText) dialogView.findViewById(R.id.edit_text); Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, edit_text.getText().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }); customizeDialog.show(); }
我们经常需要进行自定义Dialog,使用上面的AlertDialog.Builder类在处理背景的时候,灵活性不强。笔者推荐使用Dialog类进行窗口定义:
Dialog dialog = new Dialog(getActivity()); dialog.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);//无标题 View dialogView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.dialog_customize,null); dialog.setContentView(dialogView); dialog.getWindow().setBackgroundDrawableResource(android.R.color.transparent);//设置背景透明 dialog.show();
上面使用了setBackgroundDrawableResource设置透明背景,如果是通过AlertDialog.Builder实例的getWindow().setBackgroundDrawableResource()设置的话是没有效果的。
inflate()方法的第二个参数是ViewGroup类型,如果这个参数传入的是空的话,那么dialogView的rootView将会是你自己的XML文件中定义的rootView。但是笔者发现,即使我的XML的root view是RelativeLayout,但是却会出现布局错误的现象,如果在inflate中传入RelativeLayout的话,就正常了:
View dialogView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.dialog_customize,new RelativeLayout(context));
3 复写回调函数
/* 复写Builder的create和show函数,可以在Dialog显示前实现必要设置 * 例如初始化列表、默认选项等 * @create 第一次创建时调用 * @show 每次显示时调用 */ private void showListDialog() { final String[] items = { "我是1","我是2","我是3","我是4" }; AlertDialog.Builder listDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this){ @Override public AlertDialog create() { items[0] = "我是No.1"; return super.create(); } @Override public AlertDialog show() { items[1] = "我是No.2"; return super.show(); } }; listDialog.setTitle("我是一个列表Dialog"); listDialog.setItems(items, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // ...To-do } }); /* @setOnDismissListener Dialog销毁时调用 * @setOnCancelListener Dialog关闭时调用 */ listDialog.setOnDismissListener(new DialogInterface.OnDismissListener() { public void onDismiss(DialogInterface dialog) { Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Dialog被销毁了", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }); listDialog.show(); }
4 方法介绍
dismiss()
AlertDialog.Builder对话框没有类似finish()或者dismiss()这样的关闭窗口方法,,但是他的父类具有这样的方法。可以通过他的父类,关闭对话框
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this); AlertDialog dialog = builder.show(); dialog.dismiss();
原文连接:Android的8种对话框