目录结构:
在这篇文章中,笔者会详细介绍Android的动画。安卓中的动画大致分为tweened animation(补间动画)、frame-by-frame animation(逐帧动画)、Property Animation(属性动画),这个三个概念之间有点重合,下面介绍三种属性动画的产生时间顺序,其中补间动画和逐帧动画是Android1.0中被加入的,随着时间的推移简单的动画已经不能满足需求了,在Android4.0之后就加入了属性动画。本文还会介绍View、surfaceView和GLSurfaceView之间的比较。
1.补间动画
补间动画(tweened animation)都继承自android.view.animation.Animation抽象类,android.view.animation.Animation有五个直接实现子类:AlphaAnimation,AnimationSet,RotateAnimation,ScaleAnimation,TranslateAnimation。
其中AlphaAnimation,RotateAnimation,ScaleAnimation,TranslateAnimation是效果动画类,而AnimationSet是用于完成一系列组合动画的。
1.1 使用java代码实现Alpha、Rotate、Scale、Translate动画
下面这个栗子,演示了Alpha(淡入淡出)、Rotate(旋转)、Scale(缩放)、Translate(移动)的效果:
xml文件布局如下:
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:id="@+id/rotateButton" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="旋转" /> <Button android:id="@+id/scaleButton" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="缩放" /> <Button android:id="@+id/alphaButton" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="淡入淡出" /> <Button android:id="@+id/translateButton" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="移动" /> </LinearLayout> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
java代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity { private Button rotateButton = null; private Button scaleButton = null; private Button alphaButton = null; private Button translateButton = null; private ImageView image = null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); rotateButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.rotateButton); scaleButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.scaleButton); alphaButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.alphaButton); translateButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.translateButton); image = (ImageView)findViewById(R.id.image); rotateButton.setOnClickListener(new RotateButtonListener()); scaleButton.setOnClickListener(new ScaleButtonListener()); alphaButton.setOnClickListener(new AlphaButtonListener()); translateButton.setOnClickListener(new TranslateButtonListener()); } class AlphaButtonListener implements OnClickListener{ public void onClick(View v) { //创建一个AnimationSet对象,参数为Boolean型, //true表示使用Animation的interpolator,false则是使用自己的 AnimationSet animationSet = new AnimationSet(true); //创建一个AlphaAnimation对象,参数从完全的透明度,到完全的不透明 AlphaAnimation alphaAnimation = new AlphaAnimation(1, 0); //设置动画执行的时间 alphaAnimation.setDuration(2000); //将alphaAnimation对象添加到AnimationSet当中 animationSet.addAnimation(alphaAnimation); //使用ImageView的startAnimation方法执行动画 image.startAnimation(animationSet); } } class RotateButtonListener implements OnClickListener{ public void onClick(View v) { AnimationSet animationSet = new AnimationSet(true); //参数1:从哪个旋转角度开始 //参数2:转到什么角度 //后4个参数用于设置围绕着旋转的圆的圆心在哪里 //参数3:确定x轴坐标的类型,有ABSOLUT绝对坐标、RELATIVE_TO_SELF相对于自身坐标、RELATIVE_TO_PARENT相对于父控件的坐标 //参数4:x轴的值,0.5f表明是以自身这个控件的一半长度为x轴 //参数5:确定y轴坐标的类型 //参数6:y轴的值,0.5f表明是以自身这个控件的一半长度为x轴 RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 360, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(2000); animationSet.addAnimation(rotateAnimation); image.startAnimation(animationSet); } } class ScaleButtonListener implements OnClickListener{ public void onClick(View v) { AnimationSet animationSet = new AnimationSet(true); //0f从相对0点开始(若x和y的开始点都是0,那么就是从一个点开始),1f表示目前一个控件长度的位置(若x和y的结束点都是1f,那么就是缩放到原本大小。) //参数1:x轴的初始值 //参数2:x轴收缩后的值 //参数3:y轴的初始值 //参数4:y轴收缩后的值 //参数5:确定x轴坐标的类型 //参数6:x轴的值,0.5f表明是以自身这个控件的一半长度为x轴 //参数7:确定y轴坐标的类型 //参数8:y轴的值,0.5f表明是以自身这个控件的一半长度为x轴 ScaleAnimation scaleAnimation = new ScaleAnimation( 0f, 1f,0f,1f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5f); scaleAnimation.setDuration(2000); animationSet.addAnimation(scaleAnimation); image.startAnimation(animationSet); } } class TranslateButtonListener implements OnClickListener{ public void onClick(View v) { AnimationSet animationSet = new AnimationSet(true); //参数1~2:x轴的开始位置,0f代表从当前x轴点移动,1f代表以右移当前控件长度开始 //参数3~4:y轴的开始位置,0f代表从当前y轴点移动,1f代表下移当前控件长度开始 //参数5~6:x轴的结束位置 //参数7~8:y轴的结束位置 TranslateAnimation translateAnimation = new TranslateAnimation( Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,2f); translateAnimation.setDuration(2000); animationSet.addAnimation(translateAnimation); image.startAnimation(animationSet); } } }
效果图如下:
1.2 通过xml文件实现Alpha、Rotate、Scale、Translate动画
上面是在java代码中使用的使用Animation,这样的方式方便调试、运行,但是代码的重用性却不好,下面通过xml来实现Animation。
1.2.1 步骤
1) 在res文件夹下面建立anim文件夹
2) 创建xml文件,并加入set标签
3) 向set标签中加入rotate,alpha,scale或者translate标签
4) 使用AnimationUtils类加载xml文件
1.2.2 xml实现Animation案例
建立如下图的文件格式
alpha.xml 文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"> <!-- fromAlpha和toAlpha是起始透明度和结束时透明度 --> <alpha android:fromAlpha="1.0" android:toAlpha="0.0" android:duration="2000"/> </set>
rotate.xml 文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"> <!-- fromDegrees:开始的角度 toDegrees:结束的角度,+表示是正的 pivotX:用于设置旋转时的x轴坐标 例 1)当值为"50",表示使用绝对位置定位 2)当值为"50%",表示使用相对于控件本身定位 3)当值为"50%p",表示使用相对于控件的父控件定位 pivotY:用于设置旋转时的y轴坐标 --> <rotate android:fromDegrees="0" android:toDegrees="+360" android:pivotX="50%" android:pivotY="50%" android:duration="2000"/> </set>
scale.xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"> <!-- 起始x轴坐标 止x轴坐标 始y轴坐标 止y轴坐标 轴的坐标 轴的坐标 --> <scale android:fromXScale="1.0" android:toXScale="0.0" android:fromYScale="1.0" android:toYScale="0.0" android:pivotX="50%" android:pivotY="50%" android:duration="1000"/> </set>
translate.xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"> <!-- 始x轴坐标 止x轴坐标 始y轴坐标 止y轴坐标 --> <translate android:fromXDelta="0%" android:toXDelta="100%" android:fromYDelta="0%" android:toYDelta="100%" android:duration="2000"/> </set>
java调用代码如下:

public class MainActivity extends Activity { private Button rotateButton = null; private Button scaleButton = null; private Button alphaButton = null; private Button translateButton = null; private ImageView image = null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Interpolator t; rotateButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.rotateButton); scaleButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.scaleButton); alphaButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.alphaButton); translateButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.translateButton); image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image); rotateButton.setOnClickListener(new RotateButtonListener()); scaleButton.setOnClickListener(new ScaleButtonListener()); alphaButton.setOnClickListener(new AlphaButtonListener()); translateButton.setOnClickListener(new TranslateButtonListener()); } class AlphaButtonListener implements OnClickListener { public void onClick(View v) { // 使用AnimationUtils装载动画配置文件 Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation( MainActivity.this, R.anim.alpha); // 启动动画 image.startAnimation(animation); } } class RotateButtonListener implements OnClickListener { public void onClick(View v) { Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation( MainActivity.this, R.anim.rotate); image.startAnimation(animation); } } class ScaleButtonListener implements OnClickListener { public void onClick(View v) { Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation( MainActivity.this, R.anim.scale); image.startAnimation(animation); } } class TranslateButtonListener implements OnClickListener { public void onClick(View v) { Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation( MainActivity.this, R.anim.translate); image.startAnimation(animation); } } }
1.3 动画叠加
在上面我们介绍了AlphaAnimation,RotateAnimation,ScaleAnimation,TranslateAnimation,但这些只能是单独表现的动画。如果想把这些动画融合到一起,那么应该使用AnimationSet类,AnimationSet是Animation的派生类,它主要用于将多个动画效果融合在一起。
融合的代码如下:
//定义AnimationSet对象 AnimationSet animationSet = new AnimationSet(true); //定义淡入淡出动画 AlphaAnimation alphaAnimation = new AlphaAnimation(1, 0); //定义旋转动画 RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 360, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(1000);//设置旋转动画的结束时间 //将rotateAnimation添加到animationSet中 animationSet.addAnimation(rotateAnimation); //将alphaAnimation添加到animationSet中 animationSet.addAnimation(alphaAnimation); //开始动画 image.startAnimation(animationSet);
如果想通过配置xml文件的方式来实现的话,只需要在<set></set>中多定义一组动画即可
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator" android:shareInterpolator="true"> <!-- fromAlpha和toAlpha是起始透明度和结束时透明度 --> <alpha android:fromAlpha="1.0" android:toAlpha="0.0" android:startOffset="500" android:duration="500"/> <translate android:fromXDelta="0%" android:toXDelta="100%" android:fromYDelta="0%" android:toYDelta="100%" android:duration="2000"/> </set>
1.4 动画速率
上面我们使用的所有动画速率都是默认的,
Interpolator定义了动画变化的速率,在Animations框架当中定义了一下几种Interpolator
AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator:在动画开始与结束的地方速率改变比较慢,在中间的时候速率快。
AccelerateInterpolator:在动画开始的地方速率改变比较慢,然后开始加速
CycleInterpolator:动画循环播放特定的次数,速率改变沿着正弦曲线
DecelerateInterpolator:在动画开始的地方速率改变比较慢,然后开始减速
LinearInterpolator:动画以均匀的速率改变
Interpolator在xml文件中的使用主要分为以下几种情况:
a)在set标签中
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"/>
b)如果在一个set标签中包含多个动画效果,如果想让这些动画效果共享一个Interpolator。
android:shareInterpolator="true"
c)如果不想共享一个interpolator,则设置android:shareInterpolator="true",并且需要在每一个动画效果处添加interpolator。
<alpha android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_decelerate_interpolator" android:fromAlpha="1.0" android:toAlpha="0.0" android:startOffset="500" android:duration="500"/>
Interpolator在java代码中的使用,又可以分为以下几种情况:
a)如果是在代码上设置共享一个interpolator,则可以在AnimationSet设置interpolator。
AnimationSet animationSet = new AnimationSet(true); animationSet.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());
b)如果不设置共享一个interpolator则可以在每一个Animation对象上面设置interpolator。
//false不使用默认的AnimationSet AnimationSet animationSet = new AnimationSet(false); alphaAnimation.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator()); rotateAnimation.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
2.逐帧动画
Frame-By-Frame Animations(逐帧动画)是一帧一帧的格式显示动画效果。类似于电影胶片拍摄的手法。
逐帧动画依靠AnimationDrawable类,AnimationDrawable对ImageView进行动画时,原来的ImageView中是不能设置初始图片的。
2.1 实现小熊快跑动画效果
下面使用小熊快跑这个动画来讲解AnimationDrawable的使用
bear.xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <animation-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:oneshot="false"> <item android:drawable="@drawable/littlebear1" android:duration="50"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/littlebear2" android:duration="50"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/littlebear3" android:duration="50"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/littlebear4" android:duration="50"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/littlebear5" android:duration="50"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/littlebear6" android:duration="50"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/littlebear7" android:duration="50"/> </animation-list>
activity_main.xml文件

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <Button android:id="@+id/startbutton" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="开始"/> <Button android:id="@+id/endbutton" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_toEndOf="@+id/startbutton" android:text="停止" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true"/> </RelativeLayout>
java代码:

public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button startbutton=null;
Button endbutton=null;
ImageView imageView=null;
AnimationDrawable animationDrawable=null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
startbutton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startbutton);
imageView = (ImageView)findViewById(R.id.image);
startbutton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
imageView.setBackgroundResource(R.anim.bear);
animationDrawable = (AnimationDrawable)
imageView.getBackground();
animationDrawable.start();
}
});
endbutton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.endbutton);
endbutton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View paramView) {
if(animationDrawable!=null){
animationDrawable.stop();
}
}
});
}
}
效果图:
2.2 Movie 类的使用(GIF动图)
说起逐帧动画,肯定大家会想到的就是GIF动图,上面我们使用AnimationDrawable来绘制逐帧动画,但这样未免太过于麻烦,在Android API中还提供了另外一个类就是android.graphics.Movie。接下来看看这个案例:
customGifView文件

import java.io.InputStream; import android.content.Context; import android.graphics.Canvas; import android.graphics.Movie; import android.util.AttributeSet; import android.view.View; public class CustomGifView extends View { private InputStream gifInputStream; private Movie gifMovie; private int movieWidth, movieHeight; private long movieDuration; private long mMovieStart; public CustomGifView(Context context) { super(context); init(context); } public CustomGifView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); init(context); } public CustomGifView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); init(context); } private void init(Context context){ setFocusable(true); gifInputStream = context.getResources() .openRawResource(R.drawable.YOUR_GIF); /** * Movie 提供了三个decodeXXX方法,分别是 * decodeByteArray(byte[] data, int offset, int length) * decodeFile(String pathName) * decodeStream(InputStream is) */ gifMovie = Movie.decodeStream(gifInputStream); movieWidth = gifMovie.width(); movieHeight = gifMovie.height(); //持续获得持续时间 movieDuration = gifMovie.duration(); } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { setMeasuredDimension(movieWidth, movieHeight); } public int getMovieWidth(){ return movieWidth; } public int getMovieHeight(){ return movieHeight; } public long getMovieDuration(){ return movieDuration; } @Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { long now = android.os.SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); if (mMovieStart == 0) { // first time mMovieStart = now; } if (gifMovie != null) { int dur = gifMovie.duration(); if (dur == 0) { dur = 1000; } int relTime = (int)((now - mMovieStart) % dur);//设置要被显示的帧 gifMovie.setTime(relTime); gifMovie.draw(canvas, 0, 0); invalidate(); } } }
可以在XML中使用:
<Your_PackageName.CustomGifView android:id="@+id/gifview" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
修改硬件加速关闭:
android:hardwareAccelerated="false"
或
View.setLayerType(View.LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
然后就可以看到GIF动图了。
3.LayoutAnimationController
LayoutAnimationController用于对layout中或View Group中的子元素进行动画的,每个子元素使用的都是相同的动画,但是每个子元素的启动时间不一样。如果想要定义自己的延迟启动时间,那么可以重写LayoutAnimationController类的getDelayForView(android.view.View)方法。
下面是使用对ListView使用LayoutAnimationController的案例,通过这个案例我们来讲解一下LayoutAnimationController是如何工作的:
list_anim.xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator" android:shareInterpolator="true"> <alpha android:fromAlpha="0.0" android:toAlpha="1.0" android:duration="2000"/> </set>
list_anim_layout.xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layoutAnimation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:delay="0.5" android:animationOrder="normal" android:animation="@anim/list_anim"/>
activity_main.xml文件

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <ListView android:id="@+id/list" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:scrollbars="vertical" android:layoutAnimation="@anim/list_anim_layout" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="测试"/> </LinearLayout> </RelativeLayout>
activity_item.xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" android:paddingLeft="10dip" android:paddingRight="10dip" android:paddingTop="1dip" android:paddingBottom="1dip"> <TextView android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="180dip" android:layout_height="30dip" android:textSize="5pt" android:singleLine="true" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/sex" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:textSize="5pt" android:singleLine="true"/> </LinearLayout>
mainActivity.java文件

public class MainActivity extends Activity { private Button button = null; private ListView listView = null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); listView = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.list); button=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button); button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { listView.setAdapter(createListAdapter()); } }); } private ListAdapter createListAdapter() { List<HashMap<String,String>> list = new ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>>(); HashMap<String,String> m1 = new HashMap<String,String>(); m1.put("name", "bauble"); m1.put("sex", "male"); HashMap<String,String> m2 = new HashMap<String,String>(); m2.put("name", "Allorry"); m2.put("sex", "male"); HashMap<String,String> m3 = new HashMap<String,String>(); m3.put("name", "Allotory"); m3.put("sex", "male"); HashMap<String,String> m4 = new HashMap<String,String>(); m4.put("name", "boolbe"); m4.put("sex", "male"); list.add(m1); list.add(m2); list.add(m3); list.add(m4); SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter( this,list,R.layout.activty_item,new String[]{"name","sex"}, new int[]{R.id.name,R.id.sex}); return simpleAdapter; } }
效果图: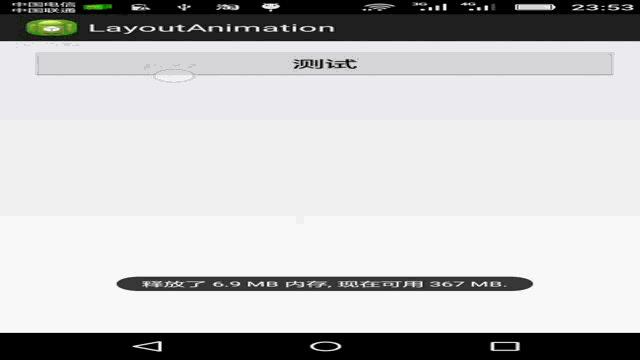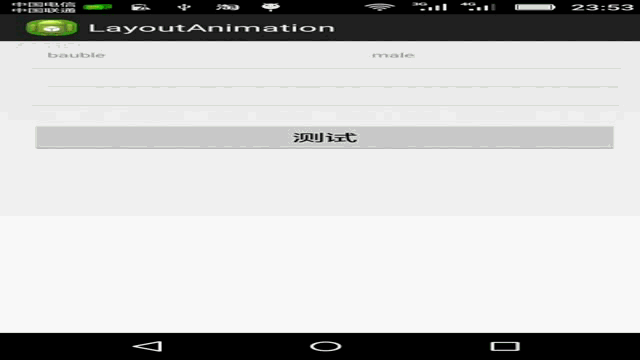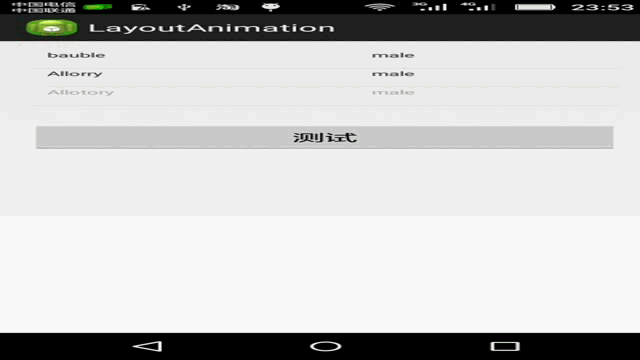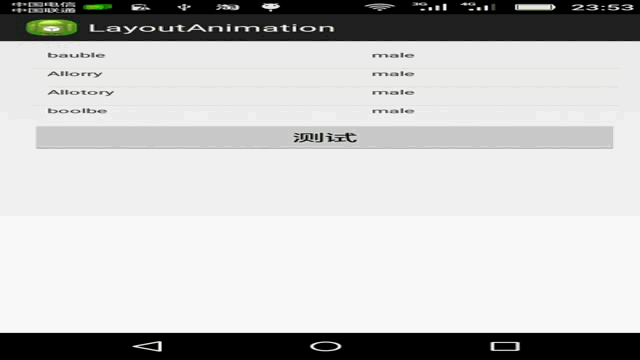
4.属性动画
4.1 基本简介
属性动画是在Android3.0之后加入的,在一定时间间隔内,通过不断对值进行改变,并不断将该值赋给对象的属性,从而实现该对象在该属性上的动画效果。
ValueAnimator是属性动画机制中最核心的一个类,除了ValueAnimator类,AnimatorSet、ObjectAnimator类也是属性动画机制中的核心类,其中ObjectAnimator是ValueAnimator的派生类。下面笔者会详细介绍这个三个类。
4.2 ValueAnimator类
现在开始介绍ValueAnimator类的使用,ValueAnimator提供了一种简单的定时引擎,它可以计算动画的属性值,然后通过手动将变化的值设置到对象属性上。默认情况下,ValueAnimator使用的是非线性的Interpolation(AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator),AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator类对象的Interpolator在开始的时候加速,在动画结束的时候减速。也可以通过setInterpolator(TimeInterpolator)方法来设置自己的Interpolator。
valueAnimator有如下几个比较常用的方法:
//将开始值以浮点数值的形式过度到结束值 public static ValueAnimator ofFloat (float... values) //将开始值以整数的形式过度到结束值 public static ValueAnimator ofInt (int... values) //使用指定的TypeEvaluator对象,将 开始值以对象的形式过度到结束值。 public static ValueAnimator ofObject (TypeEvaluator evaluator, Object... values) //开始动画 public void start(); //结束动画 public void end(); //取消动画 public void cancle(); //添加更新监听器 public void addUpdateListener (ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener listener) //设置自定义的TimerInterpolator public void setInterpolator (TimeInterpolator value) //设置执行时间 public ValueAnimator setDuration (long duration) //设置启动的延迟时间 public void setStartDelay (long startDelay)
下面通过改变按钮的宽度来展示ValueAnimator的用法,
xml布局如下:
<Button android:id="@+id/button1" style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall" android:layout_width="200px" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:text="属性动画" />
java代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity { Button button=null; ValueAnimator valueAnimator=null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); button=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1); //对指定Button对象的with属性创建ValueAnimator对象 valueAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofInt(button.getLayoutParams().width, 500); //设置持续时间 valueAnimator.setDuration(2000); //添加AnimatorUpdateListener监听器,每当属性值改变就会调用onAnimationUpdate方法 valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener() { @Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animator) { //获得变化的值 int currentValue = (Integer) animator.getAnimatedValue(); Log.i("info", currentValue+""); //重新设置属性值 button.getLayoutParams().width=currentValue; //重新显示 button.requestLayout(); } }); button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View paramView) { valueAnimator.start(); } }); } }
效果图:
观察上面的代码我们知道,ValueAnimator只是负责值的改变,若想要把改变后的值重新赋给对象,那么这个过程应该由程序员应该手动来完成。幸好官方提供了ObjectAnimator类,来帮我们实现这个过程。
4.3 ObjectAnimator类
ObjectAnimator是ValueAnimator的派生类,它对ValueAnimator进行了改进,它可以直接对对象的属性进行动画设置,但是被动画的属性必须要提供set/get方法。
由于ObjectAnimator派生自ValueAnimator,ObjectAnimator能使用ValueAnimator中的大部分方法(除private外)。
下面这个案例展示了利用ObjectAnimator来实现旋转、平移、缩放、淡入淡出
xml文件布局如下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"> <Button android:id="@+id/move" android:text="平移" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content"/> <Button android:id="@+id/rotate" android:text="旋转" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <Button android:id="@+id/scale" android:text="缩放" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <Button android:id="@+id/alpha" android:text="淡入淡出" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" /> </RelativeLayout>
java的调用代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity { Button move=null; Button rotate=null; Button scale=null; Button alpha=null; ImageView image=null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); move= (Button)findViewById(R.id.move); rotate=(Button)findViewById(R.id.rotate); scale=(Button)findViewById(R.id.scale); alpha=(Button)findViewById(R.id.alpha); image=(ImageView)findViewById(R.id.image); move.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { ObjectAnimator objectAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(image,"TranslationX",0,100,0);//移动 objectAnimator.setDuration(2000); objectAnimator.start(); } }); rotate.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { ObjectAnimator objectAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(image,"Rotation",0,360);//旋转 objectAnimator.setDuration(2000); objectAnimator.start(); } }); scale.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { ObjectAnimator objectAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(image,"ScaleX",1,2,1);//缩放 objectAnimator.setDuration(2000); objectAnimator.start(); } }); alpha.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { ObjectAnimator objectAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(image,"Alpha",1,0,1);//淡入淡出 objectAnimator.setDuration(2000); objectAnimator.start(); } }); } }
效果图:
下面介绍一些常用的属性的名:
| 属性 | 作用 | 数值类型 |
| Alpha | 控制View的透明度 | float |
| TranslationX | 控制X方向的位移 | float |
| TranslationY | 控制Y方向的位移 | float |
| ScaleX | 控制X方向的缩放倍数 | float |
| ScaleY | 控制Y方向的缩放倍数 | float |
| Rotation | 控制以屏幕方向为轴的旋转度数 | float |
| RotationX | 控制以x轴为轴的旋转度数 | float |
| RotationY | 控制以Y轴为轴的旋转度数 | float |
4.4 AnimatorSet类
AnimatorSet类可以实现Animation的组合动画,其中的Animation可以按照指定的顺序或交叉方式进行显示。
该类有一些常用方法:
AnimatorSet.play(Animator anim) :播放当前动画 AnimatorSet.after(long delay) :将现有动画延迟x毫秒后执行 AnimatorSet.with(Animator anim) :将现有动画和传入的动画同时执行 AnimatorSet.after(Animator anim) :将现有动画插入到传入的动画之后执行 AnimatorSet.before(Animator anim) :将现有动画插入到传入的动画之前执行
下面是一个混合旋转和移动动画案例:
xml布局文件:
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="开始" android:id="@+id/start"/> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
java代码:
public class MainActivity extends Activity { ImageView image=null; Button start=null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); image=(ImageView)findViewById(R.id.image); start=(Button)findViewById(R.id.start); start.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { ObjectAnimator transX=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(image, "TranslationX", 0,100,0); ObjectAnimator transY=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(image, "TranslationY", 0,100,0); ObjectAnimator rotate=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(image, "Rotation", 0,360); AnimatorSet animatorSet=new AnimatorSet(); Builder builder= animatorSet.play(transX).with(transY);//移动 builder.before(rotate);//旋转 animatorSet.setDuration(2000); //启动 animatorSet.start(); } }); } }
效果图:
4.5 估值器(TypeEvaluator)
接下来我们继续讲解估值器,估值器(TypeEvaluator)是一个接口,该接口允许开发人员自定义动画中的属性值。
TypeEvaluator有一些已知的实现类,例如ArgbEvaluator、FloatEvaluator、IntEvaluator、RectEvaluator、PointEvaluator等等。其中Argb是在用于计算Argb之间的值时使用的,RectEvaluator是在用于计算Rect之间的值时使用的,FloatEvaluator是在用于计算Float之间值使用的,IntEvaluator是在用于计算Int之间值时使用的。
TypeEvaluator接口只有一个抽象方法:
public abstract T evaluate (float fraction, T startValue, T endValue);
TypeEvaluator只有一个抽象方法evaluate。evaluate中包含三个形参,其中startValue形参表示动画的结束值,endValue形参表示动画的结束值。由于startValue,endValue以及方法的返回值都是泛型类型,所以我们可以在TypeEvaluator的实现类中为泛型指定任何类型,比如Integer,Double,或者自定义的类型,显然该类型必须和属性动画中的动画属性保持一致。
evaluate方法中有一个形参比较特殊,它就是fraction,fraction形参是float类型。fraction表示单个动画的完成比例(重复动画可以认为是单个动画的多次运行),它的值是[0~1],当fraction = 0时表示单个动画还未开始,fraction = 1表示单个动画的已经完成。当我们使用属性动画类(ValueAnimator或ObjectAnimator类)运行动画时,属性动画类会根据当前动画的运行时间(Elapsed time)和当前动画的运行速率(Interpolator),得出动画的完成比例,在调用我们的TypeEvaluator的实现类时把它传给fraction参数。因此在我们使用fraction参数计算时,无需额外考虑运行速率。
有了这些概念后,我们来自定义一个CircleEvaluator:
Circle.java文件

package com.bean; public class Circle { /** * 圆心的横坐标 */ private float x; /** * 圆心的纵坐标 */ private float y; /** * 圆的半径 */ private float radius; public Circle(float x,float y,float radius) { this.x=x; this.y=y; this.radius=radius; } public float getX() { return x; } public void setX(float x) { this.x = x; } public float getY() { return y; } public void setY(float y) { this.y = y; } public float getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(float radius) { this.radius = radius; } }
CircleEvaluator.java 文件

package com.evaluator; import com.bean.Circle; import android.animation.TypeEvaluator; public class CircleEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator<Circle>{ @Override public Circle evaluate(float fraction, Circle startValue, Circle endValue) { //圆心的横坐标 float x=startValue.getX()+fraction*(endValue.getX()-startValue.getX()); //圆心的纵坐标 float y=startValue.getY()+fraction*(endValue.getY()-startValue.getY()); //圆的半径 float radius=startValue.getRadius()+fraction*(endValue.getRadius()-startValue.getRadius()); return new Circle(x, y, radius); } }
CircleView.java 文件

package com.entry; import com.bean.Circle; import android.content.Context; import android.graphics.Canvas; import android.graphics.Paint; import android.graphics.Paint.Style; import android.view.View; public class CircleView extends View { private Circle circle=null; public CircleView(Context context,Circle circle) { super(context); this.circle=circle; } @Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { Paint paint=new Paint(); paint.setStyle(Style.STROKE); canvas.drawCircle(circle.getX(), circle.getY(), circle.getRadius(),paint); super.onDraw(canvas); } public Circle getCircle() { return circle; } public void setCircle(Circle circle) { this.circle = circle; } }
MainActivity.java 文件

package com.entry; import com.bean.Circle; import com.evaluator.CircleEvaluator; import android.os.Bundle; import android.animation.ObjectAnimator; import android.animation.ValueAnimator; import android.animation.ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener; import android.app.Activity; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.RelativeLayout; public class MainActivity extends Activity { RelativeLayout layout=null; Button button=null; CircleView circleView=null; Circle startCircle=null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); startCircle=new Circle(200,200,60); circleView=new CircleView(this,startCircle); layout=(RelativeLayout)findViewById(R.id.main); layout.addView(circleView); button=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1); button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { CircleEvaluator circleEvaluator= new CircleEvaluator(); Circle endCircle=new Circle(250, 300, 100); ObjectAnimator objectAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofObject(circleView,"circle",circleEvaluator,startCircle,endCircle); objectAnimator.setDuration(2000);//两秒内完成 objectAnimator.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener() { @Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) { circleView.invalidate(); } }); objectAnimator.start(); } }); } }
效果图:
4.6 实现贝塞尔曲线动画
在开始之前,介绍一下Path类,Path类中提供了一个quadTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2)方法,该方法可以用于绘制二阶贝塞尔曲线。
笔者介绍三个贝塞尔曲线的网站:The Bezier Game,Canvas Bezier Curve Example,Bezier Curve
贝塞尔曲线的应用非常广泛,栗如:
QQ小红点拖拽效果
360火箭发射
加入购物车动画
一些炫酷的下拉刷新控件
阅读软件的翻书效果
一些平滑的折线图的制作
很多炫酷的动画效果
这里对贝塞尔曲线不做过多的解释,关于贝塞尔曲线读者可以自行度娘。
下面介绍实现贝塞尔曲线动画的思想:
a)自定义估值器(TypeEvaluator),在public abstract T evaluate (float fraction, T startValue, T endValue);方法中利用贝塞尔公式计算出下一个图形的属性的值。
b)对组件动画对象设置新的值,如果是ObjectValuator的话,这一步可以省略,在上面的分析中已经知道ObjectValuator会自动帮我们完成这一步。
c)调用invalidate()重新刷新组件。
接下来我们要利用贝塞尔曲线,实现如下这样的功能: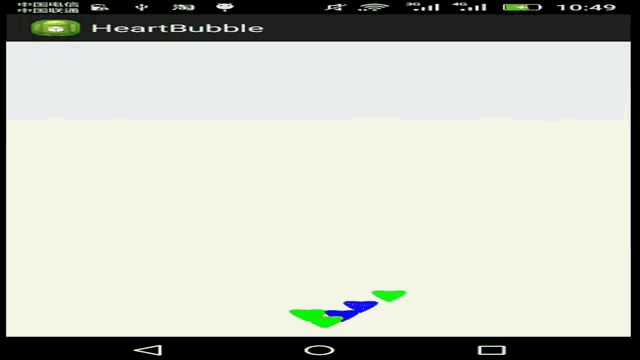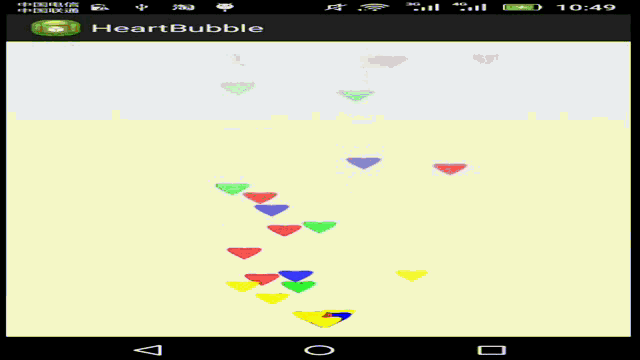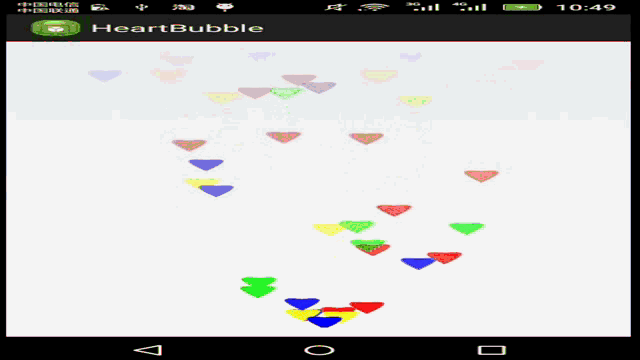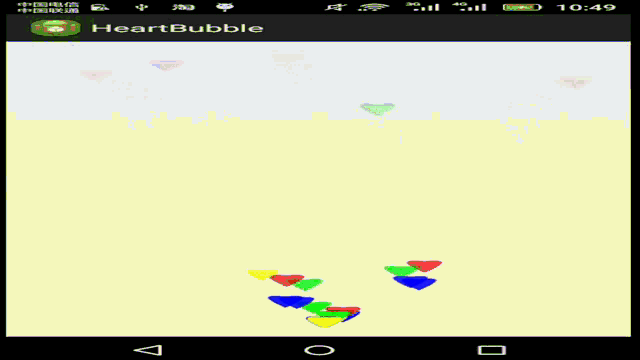
结构图:
Heart.java 文件

package heart.model; public class Heart { /** * 横坐标 */ private float x=0; /** * 纵坐标 */ private float y=0; /** * 颜色值 */ private int color=0; public Heart(float x,float y,int color){ this.x=x; this.y=y; this.color=color; } public int getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(int color) { this.color = color; } public float getX() { return x; } public void setX(float x) { this.x = x; } public float getY() { return y; } public void setY(float y) { this.y = y; } }
HeartView.java 文件

package heart.model; import android.content.Context; import android.graphics.Canvas; import android.graphics.Paint; import android.graphics.Paint.Style; import android.graphics.Path; import android.view.View; public class HeartView extends View{ private Heart heart=null; public float getAlpha() { return super.getAlpha(); } public void setAlpha(float alpha) { super.setAlpha(alpha); } public Heart getHeart() { return heart; } public void setHeart(Heart heart) { this.heart = heart; } private final float h=40; public HeartView(Context context,Heart heart){ super(context); this.heart=heart; } @Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); Paint p=new Paint(); //设置透明度 p.setAlpha((int) getAlpha()); //设置样式 p.setStyle(Style.FILL); //设置画笔颜色 p.setColor(heart.getColor()); //使用二阶贝塞尔曲线绘制心形图案 Path path=new Path(); float x=heart.getX();//获得起始点的横坐标 float y=heart.getY();//获得起始点的纵坐标 path.moveTo(x,y); path.quadTo(x+h,y-0.268f*h,x,y+h); path.moveTo(x,y+h); path.quadTo(x-h,y-0.268f*h,x,y); canvas.drawPath(path,p); } }
HeartEvaluator.java 文件

package heart.model; import java.util.Random; import android.animation.TypeEvaluator; public class HeartEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator<Heart>{ private int orientation=1; private static Random r=new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); public HeartEvaluator(){ orientation=getOrientation(); } /** * 利用三阶贝塞尔曲线公式,得出位置。 */ @Override public Heart evaluate(float t, Heart startValue, Heart endValue) { Heart[] points=createPoints(startValue,endValue); Heart p0=points[0];//开始点 Heart p1=points[1];//第一个辅佐点 Heart p2=points[2];//第二个辅佐点 Heart p3=points[3];//终点 //使用三阶贝塞尔曲线算出横坐标 Double dx= p0.getX()*Math.pow((1-t),3)+ 3*p1.getX()*t*Math.pow((1-t), 2)+ 3*p2.getX()*Math.pow(t, 2)*(1-t)+ p3.getX()*Math.pow(t, 3); float x=Float.parseFloat(dx.toString()); //使用三阶贝塞尔曲线算出纵坐标 Double dy= p0.getY()*Math.pow((1-t),3)+ 3*p1.getY()*t*Math.pow((1-t), 2)+ 3*p2.getY()*Math.pow(t, 2)*(1-t)+ p3.getY()*Math.pow(t, 3); float y=Float.parseFloat(dy.toString()); return new Heart(x,y,startValue.getColor()); } /** * 根据起始点和终点 算出其余两个辅佐点, * 算法自定义 * @param heart0 开始点 * @param heart3 终点 * @return */ public Heart[] createPoints(Heart heart0,Heart heart3){ float wx=Math.abs(heart0.getX()-heart3.getX()); Heart heart1=new Heart(heart3.getX(), heart0.getY()-wx, heart0.getColor()); Heart heart2=new Heart(heart0.getX(),wx,heart3.getColor()); return new Heart[]{heart0,heart1,heart2,heart3}; } /** * 获得飘动的方向 * @return 一个Int类型的数据,数字为1或是-1。 */ private int getOrientation(){ if(r.nextFloat()>=0.5){ return 1; } return -1; } }
在这个HeartEvaluator估值器中,我们使用三阶贝塞尔曲线公式,实现单个图形按如下路径移动:
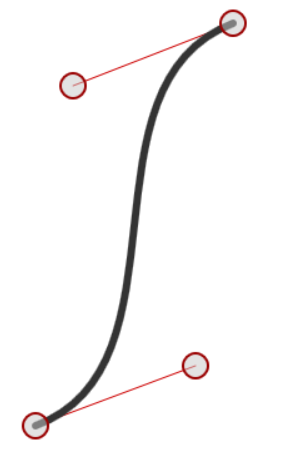
三阶贝塞尔曲线的公式为:
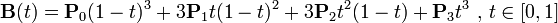
HeartAnimation.java 文件

package heart.model; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; import android.animation.Animator; import android.animation.Animator.AnimatorListener; import android.animation.AnimatorSet; import android.animation.ObjectAnimator; import android.animation.ValueAnimator; import android.animation.ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener; import android.content.Context; import android.graphics.Color; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.Message; import android.view.ViewGroup; public class HeartAnimation { private int width; private int height; private List<HeartView> heartViews=null; private static Random random=new Random(); private ViewGroup parent=null; private Context context=null; private static final int COLOR_LIMIT=4; /** * 有参数构造器 * @param width 宽度 * @param height 高度 * @param parent 容器组件 * @param context 上下文对象 */ public HeartAnimation(int width,int height,ViewGroup parent,Context context){ this.width=width; this.height=height; this.parent=parent; this.context=context; heartViews=new ArrayList<HeartView>(); } /** * 设置需要显示图形的个数 * @param count 图形的个数 * @return 返回一个HeartAnimation类型的数据,当前对象。 */ public HeartAnimation setCount(int count){ if(heartViews!=null) heartViews.clear(); for(int i=0;i<count;i++){ HeartView heartView=new HeartView(context, new Heart(width/2-25, height-100,getColor())); heartViews.add(heartView); addAnimation(heartView);//添加动画 } return this; } public HeartAnimation addAnimation(final HeartView heartView){ //创建一个估值器 HeartEvaluator heartEvaluator=new HeartEvaluator(); //获得起点的图形 Heart startHeart=heartView.getHeart(); //获得终点的图形 Heart endHeart=new Heart(getXPosition(),0,startHeart.getColor()); ValueAnimator animator=ValueAnimator.ofObject(heartEvaluator, startHeart,endHeart); ObjectAnimator alphaAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(heartView, "alpha", 1,0); animator.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener() { @Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) { //获得改变后的值 heartView.setHeart((Heart)animation.getAnimatedValue()); //重新设置新值 heartView.invalidate(); } }); animator.addListener(new AnimatorListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { parent.removeView(heartView);//移除 HeartView fHeartView= new HeartView(context, new Heart(width/2-25, height-100,getColor())); addAnimation(fHeartView);//重新开始动画 parent.addView(fHeartView);//将该新图形添加到容器中 } @Override public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) { } }); AnimatorSet animatorSet=new AnimatorSet(); animatorSet.play(animator).with(alphaAnimator); animatorSet.setDuration(getDuration()); animatorSet.setStartDelay(getStartDelay()); //开始 animatorSet.start(); return this; } /** * 开始 */ public void start(){ for(HeartView heartView : heartViews){ parent.addView(heartView);//将心图形对象依次添加到容器中 } } /** * 终点横坐标的随机数 * @return 终点的横坐标 */ private int getXPosition(){ return random.nextInt(width); } /** * @return 一个long类型的整数,表示延迟的毫秒数。 */ public static long getStartDelay(){ return (random.nextInt(5)+1)*1000; } /** * @return 一个long类型的数据,表示持续毫秒时间,返回值在[3000,5000)之间; */ public long getDuration(){ return (random.nextInt(2)+3)*1000; } /** * @return 一个int类型的数据,表示颜色值。 */ public int getColor(){ int colorType= random.nextInt(COLOR_LIMIT); int color=0; switch (colorType) { case 0: color=Color.RED; break; case 1: color=Color.BLUE; break; case 2: color=Color.YELLOW; break; default: color=Color.GREEN; break; } return color; } }
笔者在addAnimation方法中,同时播放alpha和Heart的动画,然后监听addUpdateListener,在有新值后,重新设置新值。
Mainctivity.java 文件

package heart.entry; import heart.model.HeartAnimation; import cn.heart.R; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.RelativeLayout; public class MainActivity extends BaseActivity { RelativeLayout relativeLayout=null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ViewShowListen(R.id.layout, 10001); } @Override public void ViewAfterShow(final int width,final int height) { relativeLayout=(RelativeLayout)findViewById(R.id.layout); HeartAnimation heartAnimation=new HeartAnimation(width, height,relativeLayout,MainActivity.this); heartAnimation.setCount(20).start(); } }
5.View、surfaceView和GLSurfaceView的区别
5.1 View、surfaceView和GLSurfaceView的区别
Android游戏当中主要的除了控制类外就是显示类View。SurfaceView是从View基类中派生出来的显示类。android游戏开发中常用的三种视图是:
view、SurfaceView和GLSurfaceView的区别如下:
View:显示视图,内置画布,提供图形绘制函数、触屏事件、按键事件函数等;必须在UI主线程内更新画面,速度较慢
SurfaceView:基于view视图进行拓展的视图类,更适合2D游戏的开发;是view的子类,类似使用双缓机制,在新的线程中更新画面所以刷新界面速度比view快。
GLSurfaceView:基于SurfaceView视图再次进行拓展的视图类,专用于3D游戏开发的视图;是SurfaceView的子类,openGL专用。
在2D游戏开发中,大致可以分为两种游戏框架,View和SurfaceView。
View和SurfaceView区别:
View:必须在UI的主线程中更新画面,用于被动更新画面。
surfaceView:UI线程和子线程中都可以。在一个新启动的线程中重新绘制画面,主动更新画面。
UI的主线程中更新画面 可能会引发问题,比如你更新画面的时间过长,那么你的主UI线程会被你正在画的函数阻塞。那么将无法响应按键,触屏等消息。
当使用surfaceView 由于是在新的线程中更新画面所以不会阻塞你的UI主线程。但这也带来了另外一个问题,就是事件同步,涉及到线程同步。
所以基于以上,根据游戏特点,一般分成两类。
1 被动更新画面的。比如棋类,这种用view就好了。因为画面的更新是依赖于 onTouch 来更新,可以直接使用 invalidate。 因为这种情况下,这一次Touch和下一次的Touch需要的时间比较长些,不会产生影响。
2 主动更新。比如一个人在一直跑动。这就需要一个单独的thread不停的重绘人的状态,避免阻塞main UI thread。所以显然view不合适,需要surfaceView来控制
上面的所有的案例的,笔者都是用的View来实现的(这并不是最理想的选择,尤其是最后一个贝塞尔曲线动画),在知道了这一节的知识后,读者可以尝试使用SurfaceView来实现那些2D动画。
5.2 SurfaceView
5.2.1 SurfaceView的使用
1.创建SurfaceView,需要创建一个新的扩展了SurfaceView的类,并实现SurfaceHolder.Callback
2.需要重写的方法
(1)public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder,int format,int width,int height){}
//在surface的大小发生改变时激发
(2)public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder){}
//在创建时激发,一般在这里调用画图的线程。
(3)public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {}
//销毁时激发,一般在这里将画图的线程停止、释放。
整个过程:继承SurfaceView并实现SurfaceHolder.Callback接口 ----> SurfaceView.getHolder()获得SurfaceHolder对象 ---->SurfaceHolder.addCallback(callback)添加回调函数---->SurfaceHolder.lockCanvas()获得Canvas对象并锁定画布----> Canvas绘画 ---->SurfaceHolder.unlockCanvasAndPost(Canvas canvas)结束锁定画图,并提交改变,将图形显示。
3、SurfaceHolder
这里用到了一个类SurfaceHolder,可以把它当成surface的控制器,用来操纵surface。处理它的Canvas上画的效果和动画,控制表面,大小,像素等。
几个需要注意的方法:
(1)、abstract void addCallback(SurfaceHolder.Callback callback);
// 给SurfaceView当前的持有者一个回调对象。
(2)、abstract Canvas lockCanvas();
// 锁定画布,一般在锁定后就可以通过其返回的画布对象Canvas,在其上面画图等操作了。
(3)、abstract Canvas lockCanvas(Rect dirty);
// 锁定画布的某个区域进行画图等..因为画完图后,会调用下面的unlockCanvasAndPost来改变显示内容。
// 相对部分内存要求比较高的游戏来说,可以不用重画dirty外的其它区域的像素,可以提高速度。
(4)、abstract void unlockCanvasAndPost(Canvas canvas);
// 结束锁定画图,并提交改变。
栗子:
public class MainActivity extends Activity { public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(new MyView(this)); } class MyView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback,Runnable{ boolean mRunning=false; SurfaceHolder holder=null; Thread td=null; public MyView(Context context) { super(context); holder=getHolder(); holder.addCallback(this); setFocusable(true); setFocusableInTouchMode(true); this.setKeepScreenOn(true); } @Override public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) { mRunning=true;//允许开始绘制 td=new Thread(this); td.start();//开始线程 } @Override public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width, int height) { } @Override public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) { mRunning=false;//停止 } @Override public void run() { Canvas c = null; int count=0; while(mRunning){ try{ c = holder.lockCanvas();//锁定画布,一般在锁定后就可以通过其返回的画布对象Canvas,在其上面画图等操作了。 c.drawColor(Color.BLACK);//设置画布背景颜色,如何背景是透明的话,那么建议设置成c.drawColor(Color.TRANSPARENT);如果需要在设置画布之前,清楚画布上的所有东西,那么建议设置成c.drawColor(Color.TEANSPARENT,Mode.CLEAR) Paint p = new Paint(); //创建画笔 p.setColor(Color.WHITE); Rect r = new Rect(100, 50, 300, 250); c.drawRect(r, p); c.drawText("这是第"+(count++)+"秒", 100, 310, p); Thread.sleep(1000);//睡眠时间为1秒 }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(c!= null) holder.unlockCanvasAndPost(c);//结束锁定画图,并提交改变。 } } } } }
5.2.2 SurfaceView的分层
在使用Surface类开发时,常常需要使绘制出来的图案背景色透明,以实现背景图片和绘制出来的图案融为一体,具体操作方法如下:
首先继承surfaceview类的子类(即你写的类)的构造方法中设置背景图片:
setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.background);
再加入下面这两行:
setZOrderOnTop(true);//使surfaceview放到最顶层 getHolder().setFormat(PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT);//使窗口支持透明度
然后在绘制方法(一般为onDraw())中加入:
canvas.drawColor(Color.TRANSPARENT,Mode.CLEAR);//绘制透明色
在Surface开发中,是常常需要进行分层开发的,这时候可能需要在界面上加入好几个的Surface的实现类。
比如:
RelativeLayout rl=(RelativeLayout)findViewById(R.id.idVal);
rl.addView(SurfaceSubClass1);
rl.addView(SurfaceSubClass2);
如果SurfaceSubClass2覆盖了SurfaceSubClass1的图案,那么这显然不是我们希望的,所以应该把SurfaceSubClass2设置为背景透明。
上面讨论是进行两层的开发,那么如果是需要进行三层或是三层以上分层开发,那么应该怎么办呢?
例如:
RelativeLayout rl=(RelativeLayout)findViewById(R.id.idVal); rl.addView(SurfaceSubClass1);//1 rl.addView(SurfaceSubClass2);//2 rl.addView(SurfaceSubClass3);//3
上面的代码中,读者知道1,2,3条语句的哪一个SurfaceSubClass最先被加载到RelativeLayout(三个SurfaceSubClass都没有设置setZOrderOnTop(true))中吗?答案是SurfaceSubClass3,注意这里的三个SurfaceSubClass被加载到RelativeLayout中的顺序是3-2-1。知道了这一点后,进行多层开发就简单了,比如上面的三个SurfaceSubClass中,SurfaceSubClass3应该是最底层的图案(不需要设置透明),再上面一层应该是SurfaceSubClass2的图案(需要设置为透明,否则看不到底层图案),最上面一层是SurfaceSubClass1的图案(需要设置为透明),注意:这三个SurfaceSubClass都没有设置setZOrderOnTop(true)。
