1.基本三层框架
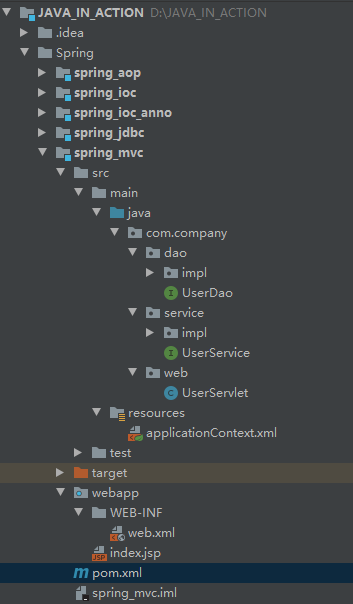
具体的创建web工程可以查看这篇文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/GumpYan/p/13711056.html
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.company.web.UserServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/userServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--配置userDao--> <bean id="userDao" class="com.company.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean> <!--配置userService--> <bean id="userService" class="com.company.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"> <property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property> </bean> </beans>
UserDao.java
package com.company.dao;
public interface UserDao {
void save();
}
UserDaoImpl.java
package com.company.dao.impl;
import com.company.dao.UserDao;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
public void save() {
System.out.println("save running...");
}
}
UserService.java
package com.company.service;
public interface UserService {
void save();
}
UserServlet.java
package com.company.web;
import com.company.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
}
开启Tomcat服务器
浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8080/spring_mvc_war/userServlet
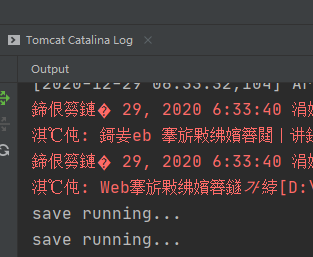
这就是web层调用service层,service层调用dao层,运行的结果
2.ApplicationContext应用上下文获取方式
应用上下文对象是通过newClasspathXmlApplicationContext(spring配置文件)方式获取的,但是每次从容器中获得Bean时都要编写newClasspathXmlApplicationContext(spring配置文件),这样的弊端是配置文件加载多次,应用上下文对象创建多次。
在web项目中,可以使用ServletContextListener监听web应用的启动,我们可以在web应用启动时,就加载Spring的配置文件,创建应用上下文对象ApplicationContext,在将其存储到最大的域servletContext域中,这样就可以在任意位置从域中获得应用上下文ApplicationContext对象了。
2.1 添加自定义监听器

ContextLoaderListener.java
package com.company.listener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
public class ContextLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
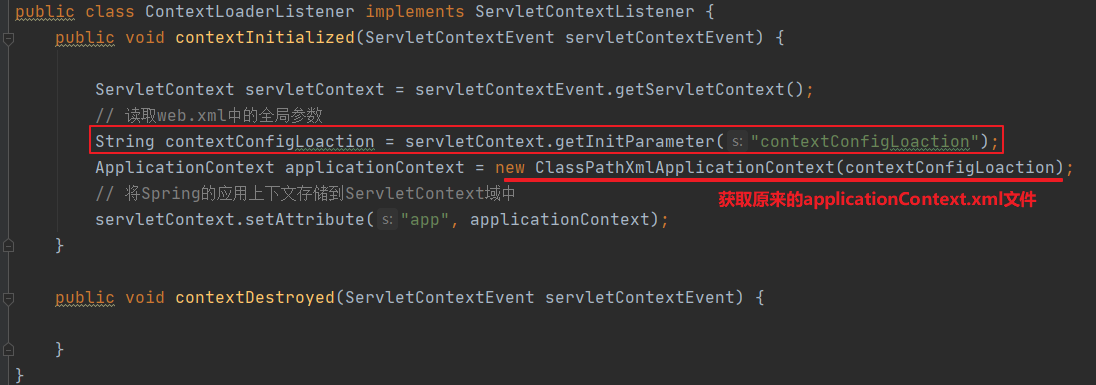
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 将Spring的应用上下文存储到ServletContext域中
ServletContext servletContext = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("app", applicationContext);
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
}
}
在web.xml中添加监听器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <!--配置监听器--> <listener> <listener-class>com.company.listener.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.company.web.UserServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/userServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
修改UserServlet.java中的,将原来从applicationContext.xml中获取对象,改成从应用上下文中获取
package com.company.web;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
ApplicationContext app = (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("app");
System.out.println("spring容器创建完毕....");
}
}
运行结果:
启动服务器:
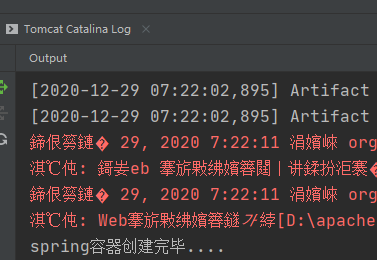
服务器刚启动,还没有访问,spring就创建完毕了,等于我在访问时,不用创建了,直接从容器中拿对象就可以了
对上面的代码优化
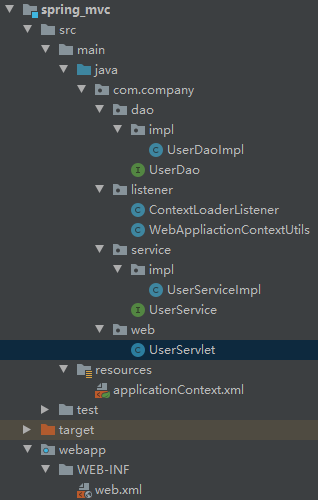
将applicationContext.xml放到配置文件web.xml中引用
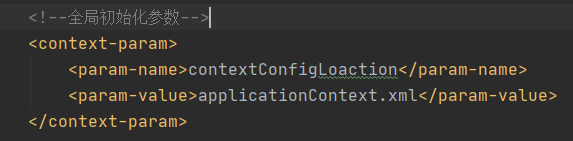
listener中添加WebApplicationContextUtils.java
package com.company.listener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
public class WebAppliactionContextUtils {
public static ApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext (ServletContext servletContext) {
return (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("app");
}
}
ContextLoaderListener.java
UserServlet.java中修改

完整版web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <!--全局初始化参数--> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLoaction</param-name> <param-value>applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!--配置监听器--> <listener> <listener-class>com.company.listener.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.company.web.UserServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/userServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
3.Spring提供获取应用上下文的工具
上面的分析不用手动实现,Spring提供了一个监听器ContextLoaderListener就是对上述功能的封装,该监听器内部加载Spring配置文件,创建应用上下文对象,并存储到ServletContext域中,提供了一个客户端工具WebApplicationContextUtils供使用者获得应用上下文对象。
所以我们只需要做两件事:
(1)在web.xml中配置ContextLoaderListener监听器(导入spring-web坐标)
(2)使用WebApplicationContextUtils获得应用上下文对象ApplicationContext
第一步主要是在web.xml中操作,在此之前需要在pom.xml中导入

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <!--全局初始化参数--> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!--配置监听器--> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.company.web.UserServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/userServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
第二步主要是在UserServlet.java中操作
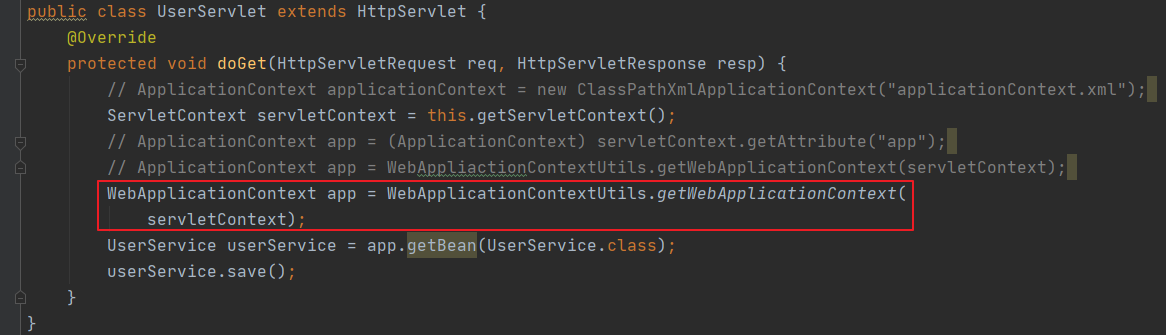
之前自定义的listener就可以不要了