概述(Motivation)
netty总的内存池是一个数组,数组每一个成员是一个独立的内存池。相当于一个国家(netty)有多个省(poolArena)分别自治管理不同的地区。
实现细节(Modification)
分配总述
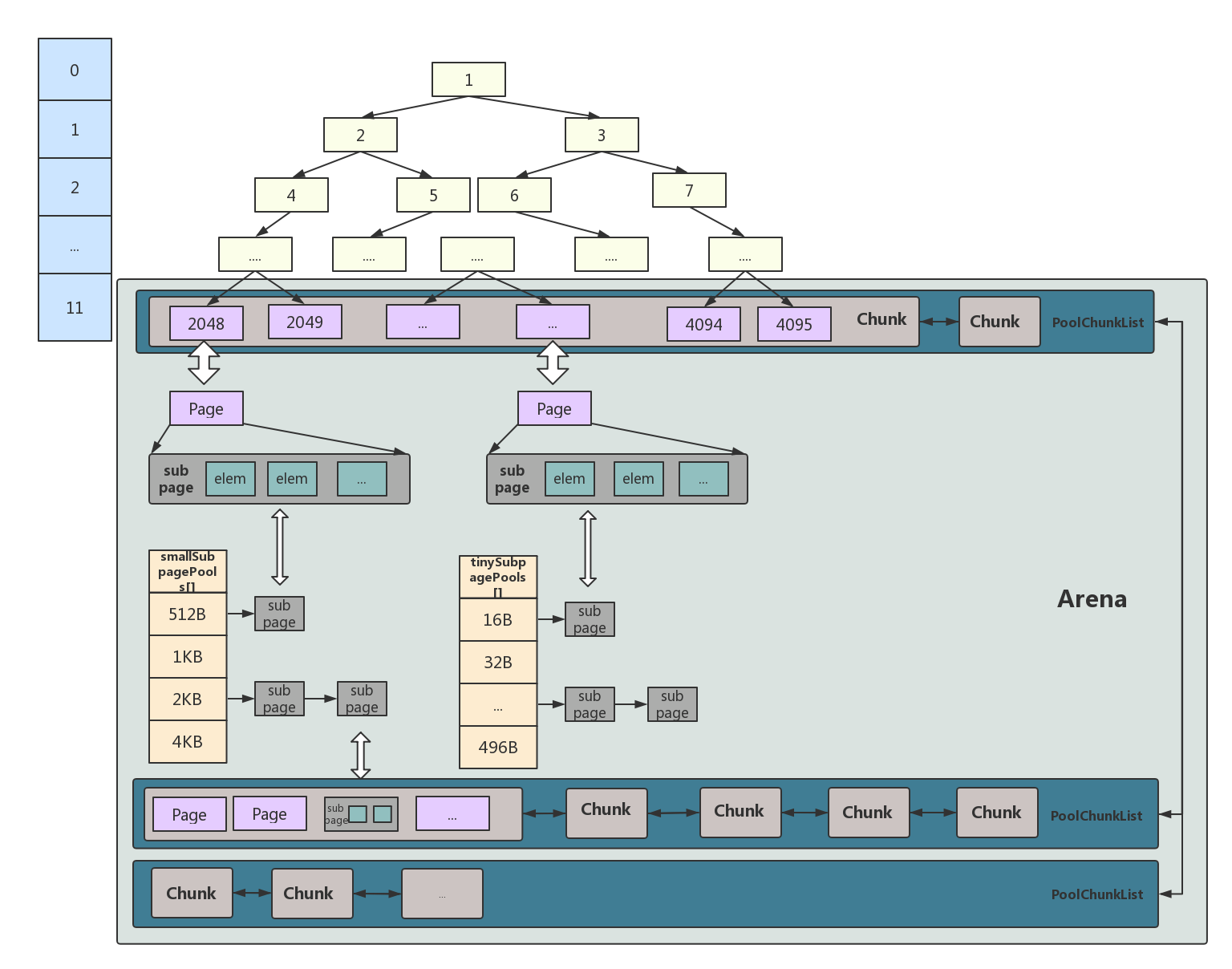
先不看树形,单纯从arena框住的地方来看,有几个chunk的链表,还有两个xxSubpagePools数组。是的,其实如果从实际的内存地址来讲,只有那几个chunk链表指向的空间,这两个数组所存储的空间从示意图中也可看出是从chunk中获得的。
chunk有2048个page,一个page默认是8k,那肯定有分配更小内存的存在,所以就有小内存的集装箱。假如分配1k,那么会把那个page拆成8个1k的subpage放到数组中来管理。那么下次想分配1k的会从小内存的集装箱数组中获取。
构造函数
protected PoolArena(PooledByteBufAllocator parent, int pageSize,
int maxOrder, int pageShifts, int chunkSize, int cacheAlignment) {
// 参数初始化
this.parent = parent; // 归属于哪个chunklist
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.maxOrder = maxOrder;
this.pageShifts = pageShifts;
this.chunkSize = chunkSize;
directMemoryCacheAlignment = cacheAlignment;
directMemoryCacheAlignmentMask = cacheAlignment - 1;
subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize - 1);
// 两个Subpage数组
tinySubpagePools = newSubpagePoolArray(numTinySubpagePools);
for (int i = 0; i < tinySubpagePools.length; i ++) {
tinySubpagePools[i] = newSubpagePoolHead(pageSize);
}
numSmallSubpagePools = pageShifts - 9;
smallSubpagePools = newSubpagePoolArray(numSmallSubpagePools);
for (int i = 0; i < smallSubpagePools.length; i ++) {
smallSubpagePools[i] = newSubpagePoolHead(pageSize);
}
// 六条chunk内存链,数字代表的是使用率
q100 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, null, 100, Integer.MAX_VALUE, chunkSize);
q075 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q100, 75, 100, chunkSize);
q050 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q075, 50, 100, chunkSize);
q025 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q050, 25, 75, chunkSize);
q000 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q025, 1, 50, chunkSize);
qInit = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q000, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 25, chunkSize);
q100.prevList(q075);
q075.prevList(q050);
q050.prevList(q025);
q025.prevList(q000);
q000.prevList(null);
qInit.prevList(qInit);
// 相关属性链
List<PoolChunkListMetric> metrics = new ArrayList<PoolChunkListMetric>(6);
metrics.add(qInit);
metrics.add(q000);
metrics.add(q025);
metrics.add(q050);
metrics.add(q075);
metrics.add(q100);
chunkListMetrics = Collections.unmodifiableList(metrics);
}
xxSubpagePools
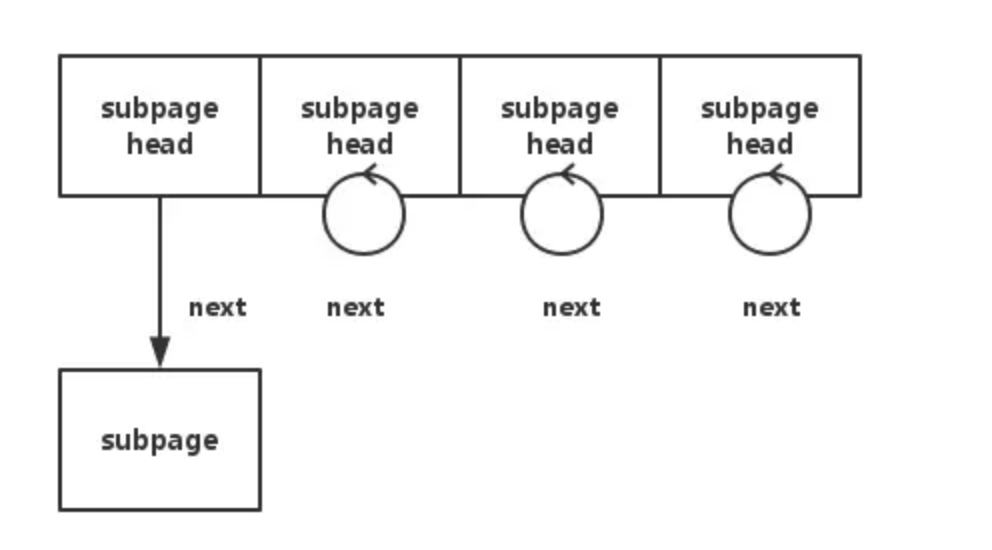
private PoolSubpage<T>[] newSubpagePoolArray(int size) {
return new PoolSubpage[size];
}
private PoolSubpage<T> newSubpagePoolHead(int pageSize) {
// 这个构造函数是专门给Head使用的,poolSubpage其他变量均为null
PoolSubpage<T> head = new PoolSubpage<T>(pageSize);
// head形成回环可以判断这是一个空链
head.prev = head;
head.next = head;
return head;
}
poolChunkList
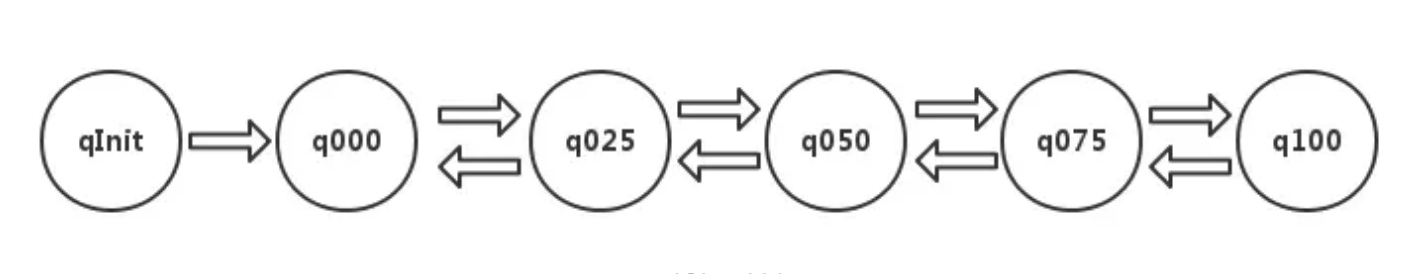
qInit:存储内存利用率0-25%的chunk
q000:存储内存利用率1-50%的chunk
q025:存储内存利用率25-75%的chunk
q050:存储内存利用率50-100%的chunk
q075:存储内存利用率75-100%的chunk
q100:存储内存利用率100%的chunk
分配函数
// 核心分配的流程
private void allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf<T> buf, final int reqCapacity) {
// 2的倍数向上取整,减一,将首位1后面所有位都置为1,然后加1
final int normCapacity = normalizeCapacity(reqCapacity);
if (isTinyOrSmall(normCapacity)) { // capacity < pageSize
int tableIdx;
PoolSubpage<T>[] table;
boolean tiny = isTiny(normCapacity);
if (tiny) { // < 512
// 线程缓存分配
if (cache.allocateTiny(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
tableIdx = tinyIdx(normCapacity); // normCapacity >>> 4; 因为tiny分为32组,最小的是16kb
table = tinySubpagePools;
} else {
if (cache.allocateSmall(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
tableIdx = smallIdx(normCapacity);
table = smallSubpagePools;
}
// 线程缓存已经没有办法分配,那么调用全局的
// arena中的两个subpage分配
final PoolSubpage<T> head = table[tableIdx];
/**
* Synchronize on the head. This is needed as {@link PoolChunk#allocateSubpage(int)} and
* {@link PoolChunk#free(long)} may modify the doubly linked list as well.
*/
synchronized (head) {
final PoolSubpage<T> s = head.next;
// head不是指向自己,那么数组非空,有分配的空间
if (s != head) {
assert s.doNotDestroy && s.elemSize == normCapacity;
long handle = s.allocate();
assert handle >= 0;
s.chunk.initBufWithSubpage(buf, handle, reqCapacity);
incTinySmallAllocation(tiny);
return;
}
}
// 没有可利用的小的空间了,全局找chunk分配拆成小份的
synchronized (this) {
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
}
incTinySmallAllocation(tiny);
return;
}
// 分配大块的page
if (normCapacity <= chunkSize) {
if (cache.allocateNormal(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
synchronized (this) {
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
++allocationsNormal;
}
} else {
// Huge allocations are never served via the cache so just call allocateHuge
// 分配的空间过大直接堆内存
allocateHuge(buf, reqCapacity);
}
}
整体的思路是小空间->大空间,threadcache->chunk->heap,看代码很好理解
// Method must be called inside synchronized(this) { ... } block
private void allocateNormal(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {
// 50->25->00->init->75这个顺序有讲究,后面看list来理解
if (q050.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || q025.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) ||
q000.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || qInit.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) ||
q075.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
return;
}
// Add a new chunk.
// chunk直接分配,类伙伴算法
PoolChunk<T> c = newChunk(pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize);
long handle = c.allocate(normCapacity);
assert handle > 0;
c.initBuf(buf, handle, reqCapacity);
qInit.add(c);
}
private void allocateHuge(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity) {
// 这个构造函数是专门给该类型的,有一个成员参数unpooled = true;
PoolChunk<T> chunk = newUnpooledChunk(reqCapacity);
// 所以这些chunk不进行独立的碎片化管理,直接大块的记录分配的大小统计,最后也是大块独立释放
activeBytesHuge.add(chunk.chunkSize());
buf.initUnpooled(chunk, reqCapacity);
allocationsHuge.increment();
}
综述(Result)
类似于linux中的伙伴算法和slab算法。