ThreadLocal
使用场景
使用场景是在于同一个类,但是会开多个线程执行,但是每一个线程可以保持不同的变量状态。
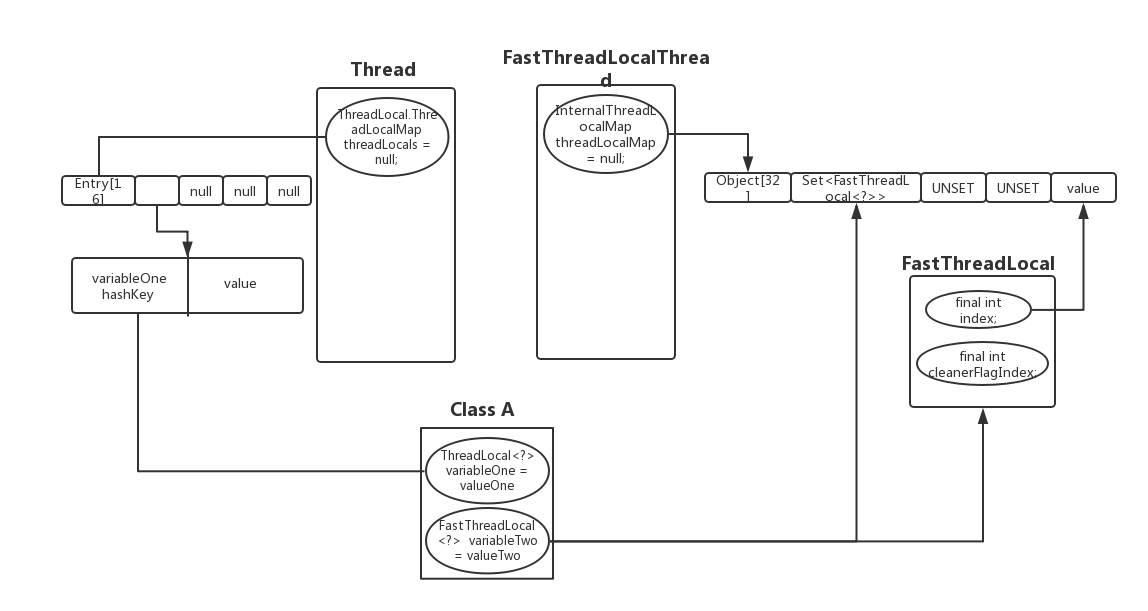
做法如上图,线程类Thread有成员变量ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap,用来存储该线程中的所有的ThreadLocal变量,初始化是一个Entry数组。
内存泄漏
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
Entry继承于WeakReference,简单说一下四种引用。强引用,就是我们常规使用的new出来一个对象,这时候会有变量建立具体的对象联系。软引用,适用于cache类型的变量,当jvm内存不够时会释放该引用。弱引用,只要发生gc就会回收。虚引用,没有很深刻的体会。
SoftReference<Dog> softReference = new SoftReference<Dog>(new Dog("dd"));
while (true){
if(softReference.get() == null){
System.out.println("null");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("ok");
}
System.gc();
}
ok
ok
ok
...
WeakReference<Dog> weakReference = new WeakReference<Dog>(new Dog("dd"));
while (true){
if(weakReference.get() == null){
System.out.println("null");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("ok");
}
System.gc();
}
ok
null
Entry中的key设置为虚引用,那么gc时候会被回收,此时ThreadLocal进行清理的时候可以根据key是否为null进行判断清除,防止内存泄漏。
但是还是要调用remove函数,这个在线程池中如果不执行的话会造成内存泄漏,因为线程不进行回收,那么ThreadLocalMap中会一直存在这些Entry,同时不进行remove的话就会一直占用内存。
Hash原理
获取线程对应的ThreadLocal,是应用hashcode在Map中定位,如果发生hash冲突使用的是线性寻地址法,即往下一位找,这种冲突方法有概率会导致死循环。所以如果变量过多,冲突很多,定位较慢。
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
FastThreadLocal
使用场景
不同于JDK自带的ThreadLocal,如果Thread是使用的FastThreadLocalThread,那么自带有private InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap,那么如果类中有用到FastThreadLocal会从threadLocalMap中获取,netty中每一个FastThreadLocal都有全局唯一的index,所以是常数级从数组中定位获取内容,并且在set的同时会将该FastThreadLocal放到threadLocalMap中index为0的Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>上,这样垃圾清理会比较简单和快捷。
构造函数
public FastThreadLocal() {
index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
cleanerFlagIndex = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
}
由该函数保证了index的全局唯一性
public static int nextVariableIndex() {
int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement();
if (index < 0) {
nextIndex.decrementAndGet();
throw new IllegalStateException("too many thread-local indexed variables");
}
return index;
}
set方法
public final void set(V value) {
// 如果设置的非“空”
if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
// 获取存储的Map对象
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
// 如果当前设置的index上是unset(即我们已经开始污染使用这个Map了),进行注册清理操作(保证内存清理)
if (setKnownNotUnset(threadLocalMap, value)) {
registerCleaner(threadLocalMap);
}
} else {
// 如果设置UNSET,则进行清理操作
remove();
}
}
UNSET是一个new Object()对象,一方面用来填充整个空的Map,另一方面也是一个判断是否使用的标志。
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
// 直接会从FastThreadLocalThread中的成员变量中获取InternalThreadLocalMap
return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
} else {
// ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>,用JDK的ThreadLocal代存InternalThreadLocalMap
return slowGet();
}
}
private boolean setKnownNotUnset(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, V value) {
// 数组定位进行替换,判断原来的位置是否没用过,即是否为unset
if (threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, value)) {
// 存放到数组[0]上的set中,方便回收
addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean setIndexedVariable(int index, Object value) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
if (index < lookup.length) {
Object oldValue = lookup[index];
lookup[index] = value;
return oldValue == UNSET;
} else {
expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(index, value);
return true;
}
}
private static void addToVariablesToRemove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal<?> variable) {
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);
Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove;
// 判断v有没有设置为set,一般是首次会执行这个
if (v == InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET || v == null) {
variablesToRemove = Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<FastThreadLocal<?>, Boolean>());
threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex, variablesToRemove);
} else {
// 已经设置过了
variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;
}
// 直接在set中加入当前的FastThreadLocal
variablesToRemove.add(variable);
}
注册到ObjectClean中,保证会被清理内存
private void registerCleaner(final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (FastThreadLocalThread.willCleanupFastThreadLocals(current) ||
threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(cleanerFlagIndex) != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
return;
}
// removeIndexedVariable(cleanerFlagIndex) isn't necessary because the finally cleanup is tied to the lifetime
// of the thread, and this Object will be discarded if the associated thread is GCed.
threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(cleanerFlagIndex, Boolean.TRUE);
// We will need to ensure we will trigger remove(InternalThreadLocalMap) so everything will be released
// and FastThreadLocal.onRemoval(...) will be called.
ObjectCleaner.register(current, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
remove(threadLocalMap);
// It's fine to not call InternalThreadLocalMap.remove() here as this will only be triggered once
// the Thread is collected by GC. In this case the ThreadLocal will be gone away already.
}
});
}
ObjectCleaner
这个和ThreadDeathWatcher的监控大致原理是相似的,都是开启一个监控守护线程进行for循环拉取任务,只是该类没有取消任务,所以直接一个并发安全的set就足够。
注册函数将需要进行清理的object对象设为虚引用,并保存了清理任务,放入到任务集中,如果未开启监控线程就开启。
监控线程死循环拿出虚引用队列,如果有引用拿到,说明该对象已经被gc,此时执行清理任务,如果无任务了就关闭线程。反之继续。
这么做能保证内存释放,即使是使用JDK的ThreadLocal,因为也是对象Map。
/**
* Allows a way to register some {@link Runnable} that will executed once there are no references to an {@link Object}
* anymore.
*/
public final class eObjectCleaner {
private static final int REFERENCE_QUEUE_POLL_TIMEOUT_MS =
max(500, getInt("io.netty.util.internal.ObjectCleaner.refQueuePollTimeout", 10000));
// Package-private for testing
static final String CLEANER_THREAD_NAME = ObjectCleaner.class.getSimpleName() + "Thread";
// This will hold a reference to the AutomaticCleanerReference which will be removed once we called cleanup()
private static final Set<AutomaticCleanerReference> LIVE_SET = new ConcurrentSet<AutomaticCleanerReference>();
private static final ReferenceQueue<Object> REFERENCE_QUEUE = new ReferenceQueue<Object>();
private static final AtomicBoolean CLEANER_RUNNING = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private static final Runnable CLEANER_TASK = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
// Keep on processing as long as the LIVE_SET is not empty and once it becomes empty
// See if we can let this thread complete.
while (!LIVE_SET.isEmpty()) {
final AutomaticCleanerReference reference;
try {
// 从虚引用的队列中获取引用,这个是只有对象被回收才会放到这个队列中,能获取得到,说明该引用已经被gc
reference = (AutomaticCleanerReference) REFERENCE_QUEUE.remove(REFERENCE_QUEUE_POLL_TIMEOUT_MS);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
// Just consume and move on
interrupted = true;
continue;
}
if (reference != null) {
try {
// 执行引用的清理任务,从而保证gc后也能清理
reference.cleanup();
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
// ignore exceptions, and don't log in case the logger throws an exception, blocks, or has
// other unexpected side effects.
}
// 从任务集中去除引用
LIVE_SET.remove(reference);
}
}
CLEANER_RUNNING.set(false);
// Its important to first access the LIVE_SET and then CLEANER_RUNNING to ensure correct
// behavior in multi-threaded environments.
if (LIVE_SET.isEmpty() || !CLEANER_RUNNING.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// There was nothing added after we set STARTED to false or some other cleanup Thread
// was started already so its safe to let this Thread complete now.
break;
}
}
if (interrupted) {
// As we caught the InterruptedException above we should mark the Thread as interrupted.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
};
/**
* Register the given {@link Object} for which the {@link Runnable} will be executed once there are no references
* to the object anymore.
*
* This should only be used if there are no other ways to execute some cleanup once the Object is not reachable
* anymore because it is not a cheap way to handle the cleanup.
*/
public static void register(Object object, Runnable cleanupTask) {
AutomaticCleanerReference reference = new AutomaticCleanerReference(object,
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(cleanupTask, "cleanupTask"));
// Its important to add the reference to the LIVE_SET before we access CLEANER_RUNNING to ensure correct
// behavior in multi-threaded environments.
// 任务集内容,要保证并发安全
LIVE_SET.add(reference);
// Check if there is already a cleaner running.
// 如果running标志没开启,CAS操作进行开启一个守护线程执行
if (CLEANER_RUNNING.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
final Thread cleanupThread = new FastThreadLocalThread(CLEANER_TASK);
cleanupThread.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
// Set to null to ensure we not create classloader leaks by holding a strong reference to the inherited
// classloader.
// See:
// - https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/7290
// - https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-7008595
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
@Override
public Void run() {
cleanupThread.setContextClassLoader(null);
return null;
}
});
cleanupThread.setName(CLEANER_THREAD_NAME);
// Mark this as a daemon thread to ensure that we the JVM can exit if this is the only thread that is
// running.
cleanupThread.setDaemon(true);
cleanupThread.start();
}
}
public static int getLiveSetCount() {
return LIVE_SET.size();
}
private ObjectCleaner() {
// Only contains a static method.
}
// 继承软引用,这里Object是thread,用来判断thread是否被回收
private static final class AutomaticCleanerReference extends WeakReference<Object> {
// 存下任务
private final Runnable cleanupTask;
AutomaticCleanerReference(Object referent, Runnable cleanupTask) {
super(referent, REFERENCE_QUEUE);
this.cleanupTask = cleanupTask;
}
void cleanup() {
cleanupTask.run();
}
@Override
public Thread get() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
LIVE_SET.remove(this);
super.clear();
}
}
}
remove方法
public final void remove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
return;
}
// lookup[index] = UNSET;制定位置置为unset,去除value强引用
Object v = threadLocalMap.removeIndexedVariable(index);
// set.remove(this),去除FastTheadLocal的强引用
removeFromVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
try {
// 可以重写,做一些自己想做的事情。。
onRemoval((V) v);
} catch (Exception e) {
PlatformDependent.throwException(e);
}
}
}
// 从set中取出所有的FastThreadLocal执行remove,并且最后将Map置为空,all over
public static void removeAll() {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet();
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
return;
}
try {
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);
if (v != null && v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;
FastThreadLocal<?>[] variablesToRemoveArray =
variablesToRemove.toArray(new FastThreadLocal[variablesToRemove.size()]);
for (FastThreadLocal<?> tlv: variablesToRemoveArray) {
tlv.remove(threadLocalMap);
}
}
} finally {
InternalThreadLocalMap.remove();
}
}
get方法
public final V get() {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
return (V) v;
}
// 利用重写的初始化函数进行初始化
V value = initialize(threadLocalMap);
registerCleaner(threadLocalMap);
return value;
}
对比
- 都是Thead自己存储自己的TheadLocal
- JDK的存储使用线性探测法的Map,数量大容易造成冲突,性能下降很快,并且会有内存泄漏的风险。
- FastTheadLocal快的原因改进了存储方式,全局唯一index来标志一个ftl,当然这样如果全局ftl很多会造成空间浪费,这是一种空间换时间的方式。同时它会进行内存监控清理防止内存泄漏。
- 个人认为在TheadLocal不多的情况下其实两种性能差不多(因为JDK自身不会hash冲突),但是Ftl更能保证内存不泄漏,所以JDK调用的时候记得
remove
reference