1、LINQ(语言级集成查询)的作用就是提供一种统一且对称的方式,让程序员在广义的数据上获取和操作数据。广义的数据包括XML文档数据、元数据、System.Data.dll和System.Data.SqlClient.dll提供的DataSet和DataTable等数据、内存数据(Array、Collection)等.
2、Linq To Object是针对实现了IEnumerable<T>的对象操作或获取数据的功能,代码如下:
(1)、通过Enumerable的实例方法实现查询
string[] str = {"Tom", "Dick", "Harry"}; IEnumerable<string> filteredNames = Enumerable.Where(str, delegate(string s) { return s.Length > 2; }); foreach (var name in filteredNames) { Console.WriteLine(name); }
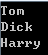
(2)、使用扩展方法
因为查询预算符是以扩展方法的形式实现的,所以如下代码也可以:
string[] str = {"Tom", "Dick", "Harry"}; var filteredNames = str.Where(n=>n.Length>4); foreach (var name in filteredNames) { Console.WriteLine(name); }
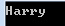
(3)、使用查询表达式语法
C#提供了一种类似sql语句的写法来操作集合数据,代码如下:
string[] str = {"Tom", "Dick", "Harry"}; var filteredNames =
from n in str where n.Length > 4 & n.Contains('a') select n; foreach (var name in filteredNames) { Console.WriteLine(name); }

3、扩展方法
Linq的大多数查询操作方法是扩展方法
what is expended method? 请参考
4、代码写法分析
当使用Linq对集合数据进行操作查询时,往往有很多种方法,这里主要分析的是传统委托方法和匿名方法和Lambda表达式.
举个例子查询一个List<int>()集合中的偶数项.
(1)、传统委托方法
static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> list=new List<int>(); list.AddRange(new int[]{6,66,1,2,3,45}); Predicate<int> pre = new Predicate<int>(IsNumber); var res = list.FindAll(pre);; foreach (var item in res) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadKey(); } static bool IsNumber(int i) { return i % 2 == 0; }

(2)、升级,匿名方法取代传统委托
List<int> list=new List<int>(); list.AddRange(new int[]{6,66,1,2,3,45}); Predicate<int> pre = new Predicate<int>(delegate(int i) { return i % 2 == 0; }); var res = list.FindAll(pre);; foreach (var item in res) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadKey();

(3)、最后,Lambda登场
List<int> list=new List<int>(); list.AddRange(new int[]{6,66,1,2,3,45}); var res = list.FindAll(n=>n%2==0);; foreach (var item in res) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadKey();
5、对象初始化
(1)、常规初始化
public class Test { public string A{ get; set; } public string B{ get; set; } } static void Main() { Test te=new Test{A='a',B='b'}; };
(2)、内部对象初始化
public class Rectangle { public Point TopLeft { get; set; } public Point BottomRight { get; set; } } static void CompareObjectInitMethods() { // 传统初始化方法 Rectangle r = new Rectangle(); Point p1 = new Point(); p1.X = 10; p1.Y = 10; r.TopLeft = p1; Point p2 = new Point(); p2.X = 20; p2.Y = 20; r.BottomRight = p2; // 对象初始化语法 Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle { TopLeft = new Point { X = 10, Y = 10 }, BottomRight = new Point { X = 20, Y = 20 } }; }
(3)、集合初始化
static void CollectionInitSyntax() { // 初始化标准数组 int[] numbers = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }; // 初始化一个ArrayList ArrayList list = new ArrayList { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }; // 初始化一个List<T>泛型容器 List<int> list2 = new List<int> { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }; // 如果容器存放的是非简单对象 List<Point> pointList = new List<Point> { new Point { X = 2, Y = 2}, new Point { X = 3, Y = 3} }; // 使用恰当的缩进和嵌套的大括号会使代码易于阅读,同时节省我们的输入时间 // 想想如果不使用初始化语法构造如下的List,将需要多少行代码 List<Rectangle> rectList = new List<Rectangle> { new Rectangle { TopLeft = new Point { X = 1, Y = 1}, BottomRight = new Point { X = 2, Y = 2}}, new Rectangle { TopLeft = new Point { X = 3, Y = 3}, BottomRight = new Point { X = 4, Y = 4}}, new Rectangle { TopLeft = new Point { X = 5, Y = 5}, BottomRight = new Point { X = 6, Y = 6}} }; }