接口
1、多个无关的类可以实现同一个接口
2、一个类可以实现多个无关的接口
3、与继承关系类似,接口与实现类之间存在多态性
4、定义java类的语法格式
< modifier> class < name>[extends< superclass>][implements< interface>[, interface]*]{
<declarations>*
}
附:
1、接口(interface)是抽象方法和常亮值的定义的结合。
2、从本质上讲,接口是一种特殊的抽象类,这种抽象类中只包含常亮和方法的定义,而没有变量和方法的实现。
3、接口定义举例:
public interface Runner{ public static final int id = 1; public void strrt(); public void run(); public void stop(); }
接口特性:
1、接口可以实现多重继承
2、接口声明的属性默认为public static final 的;也只能是public static final 的;
3、接口中只能定义抽象方法,而且这些方法默认为public 的、也只能是public的;
4、接口可以继承其他接口,并添加新的属性和抽象方法;
接口的使用以及接口实现多态:
public class TestInterface{ public static void main(String args[]){ Singer student = new Student("studentName"); student.sing(); student.sleep(); Teacher teacher = new Teacher("TeacherName"); teacher.painter(); teacher.eat(); Painter painter = (Painter)teacher; painter.painter(); painter.eat(); //下面是实现多态的部分 TestInterface t1 = new TestInterface(); t1.f(student); t1.f(teacher); } public void f(Singer s){ s.sing(); } } interface Singer{ public void sing(); public void sleep(); } interface Painter{ public void painter(); public void eat(); } class Student implements Singer{ private String name; public Student(String name){ this.name = name; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void Study(){ System.out.println("studying..."); } public void sing(){ System.out.println("study is singing"); } public void sleep(){ System.out.println("study is sleeping"); } } class Teacher implements Singer,Painter{ private String name; public Teacher(String name){ this.name = name; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void sing(){ System.out.println("teacher is singing"); } public void sleep(){ System.out.println("teacher is sleeping"); } public void painter(){ System.out.println("teacher is paintering"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("teacher is eating"); } }
运行结果:
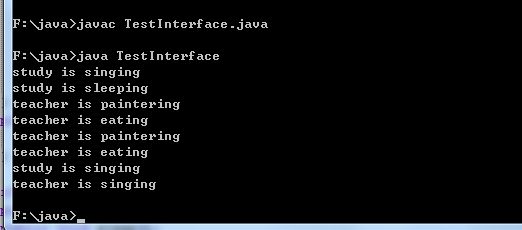
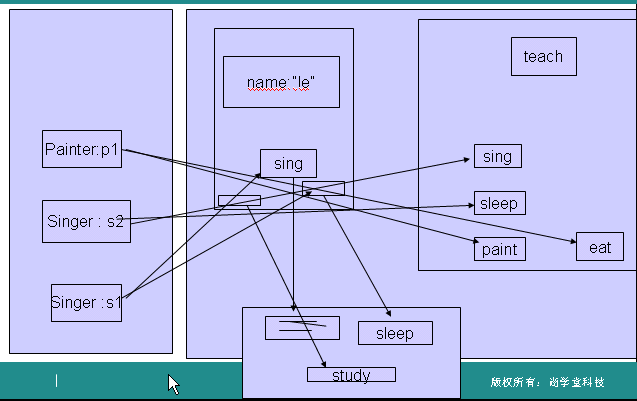
内存分析图:
示例:下面实现了一个三种不同的人给动物喂食和玩的多态,用接口实现。
public class TestDynamic{ public static void main(String args[]){ HelpAnimal farmer = new Farmer("farmer"); HelpAnimal worker = new Worker("worker"); HelpAnimal goverment = new Goverment("goverment"); TestDynamic test = new TestDynamic(); test.f(farmer); test.f(worker); test.f(goverment); } public void f(HelpAnimal animal){ animal.play(); animal.eat(); } } interface HelpAnimal{ public void eat(); public void play(); } class Farmer implements HelpAnimal{ private String name; public Farmer(String name){ this.name = name; } public void eat(){ System.out.println("Farmer eat"); } public void play(){ System.out.println("Farmer play"); } } class Worker implements HelpAnimal{ private String name; public Worker(String name){ this.name = name; } public void eat(){ System.out.println("Worker eat"); } public void play(){ System.out.println("Worker play"); } } class Goverment implements HelpAnimal{ private String name; public Goverment(String name){ this.name = name; } public void eat(){ System.out.println("Goverment eat"); } public void play(){ System.out.println("Goverment play"); } }