三大认证工作原理简介
认证、权限、频率
源码分析:
from rest_framework.views import APIView
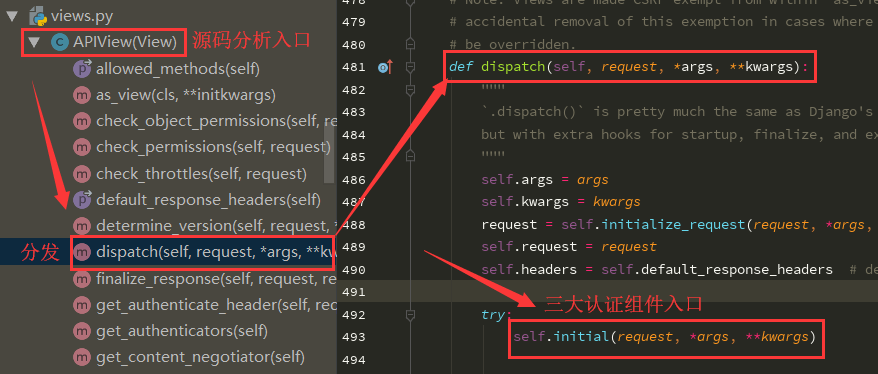
源码分析入口:

内部的三大认证方法封装:
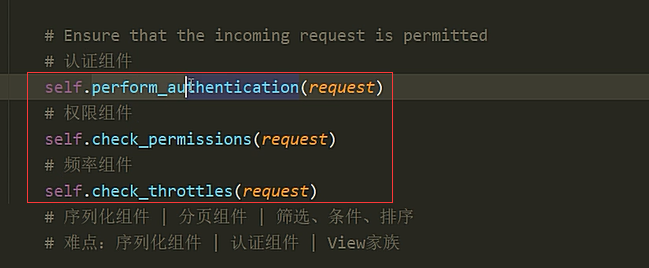
三大组件的原理分析:

权限六表分析
基于用户权限访问控制的认证(RBAC):Role-Based-Access-Control;基于auth的认证规则(了解)。
Django框架采用的是RBAC认证规则:通常分为:三表规则、五表规则、Django采用的是六表规则。
三表:用户表、角色表、权限表
五表:用户表、角色表、权限表、用户角色关系表、角色权限关系表、用户权限关系表
六表:用户表、角色表、权限表、用户角色关系表、角色权限关系表、用户权限关系表
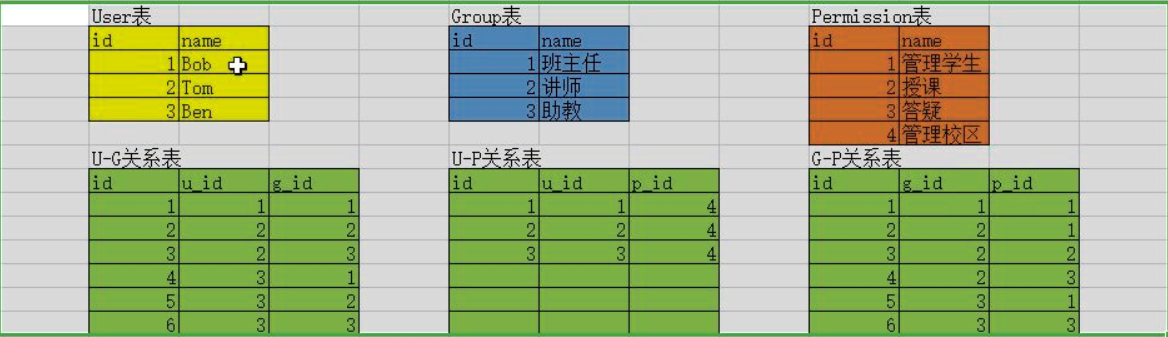
源码分析三者的关系
用户表:角色groups,权限user_permissions
角色表:用户user_set,权限permissions
权限表:用户user_set,角色group_set
重点:如果自定义User表后,再另一个项目中采用原生User表,完成数据库迁移时,可能失败。
解决的办法:
(1)、卸载Django,重新安装(源码问题)
(2)、将django.contrib下面的admin、auth下的数据迁移记录文件全部清空
from django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUser,User
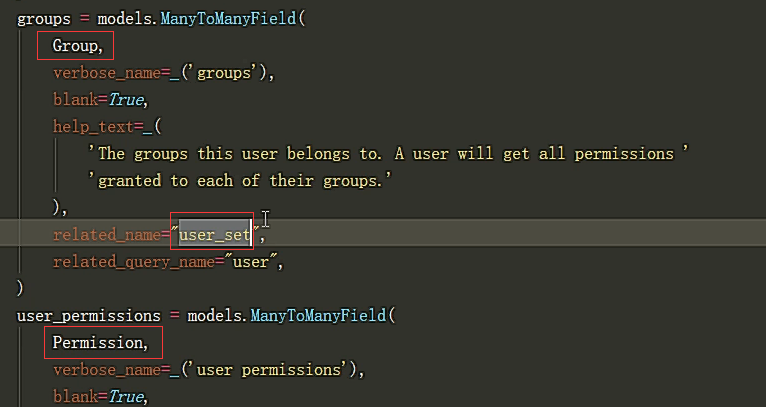
创建自定义User表
models.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUser class User(AbstractUser): mobile = models.CharField(max_length=11, unique=True)#设置成唯一的
class Meta: db_table = 'api_user' verbose_name = '用户表' verbose_name_plural = verbose_name def __str__(self): return self.username
数据库迁移:
>> python3 manage.py makemigrations >> python3 manage.py migrate >> #创建超级用户 >>> python3 manage.py createsuperuser >> admin admin123
配置自定义user表
在settings.py下面输入,告诉django系统自己创建自定义的用户表。
AUTH_USER_MODEL = "api/User"
创建好的三表结构
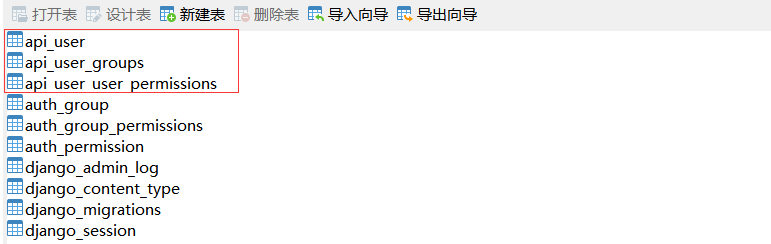
脚本启动测试查询数据
# django脚本话启动 import os, django os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "dg_proj.settings") django.setup() from api import models user = models.User.objects.first() # type: models.User print(user.username) print(user.groups.first().name) print(user.user_permissions.first().name)
from django.contrib.auth.models import Group
group = Group.objects.first()
# print(group.name)
# print(group.user_set.first().username)
# print(group.permissions.first().name)
认证组件的源码分析

点击进去,逐一分析,第一个分析的是,认证组件,
def perform_authentication(self, request):

需要点击定位到request下面的user方法继续往下查看其内部的封装原理。
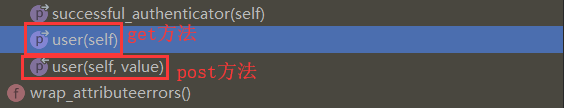
内部user的方法:调用了self._authenticare()封装的方法。

点击 self._authenticate查看认证源码的精髓实现认证的部分。
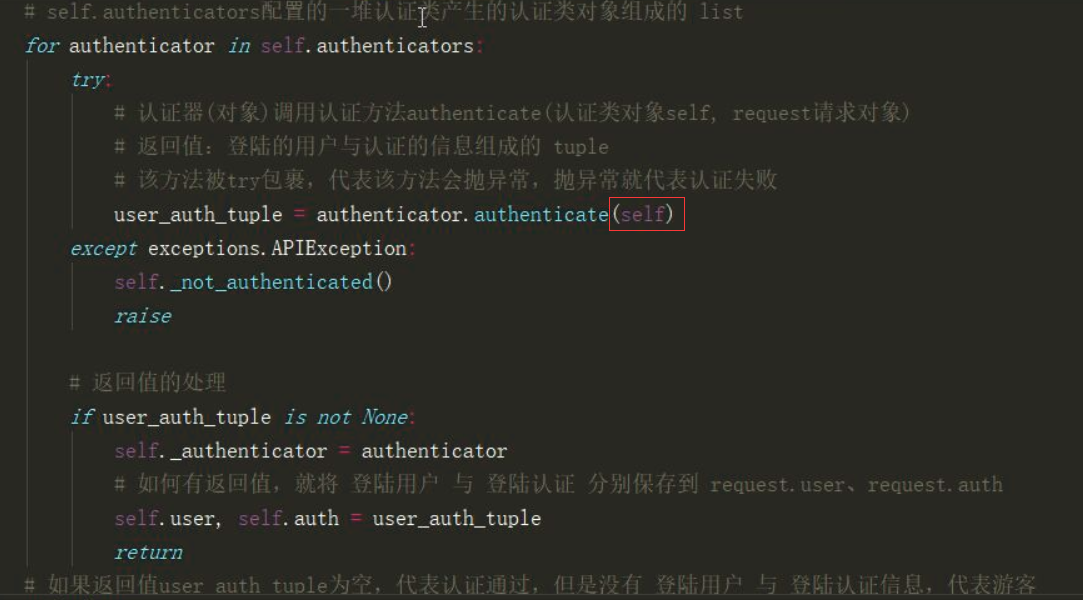
最后分析得出认证类的配置文件

再通过导入模块,查看内部封装认证的原理
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication
分析BaseAuthentication 和 SessionAuthentication。


自定义认证模块
新建一个文件夹,来写自定义的认证模块,authentications.py
分析以上源码后,总结该如何书写自定义认证模块的功能
# 自定义认证类 # 1)继承BaseAuthentication类
# 2)重新authenticate(self, request)方法,自定义认证规则
# 3)认证规则基于的条件: # 没有认证信息返回None(游客) # 有认证信息认证失败抛异常(非法用户) # 有认证信息认证成功返回用户与认证信息元组(合法用户)
# 4)完全视图类的全局(settings文件中)或局部(确切的视图类)配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = { 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication', # 基本认证 'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication', # session认证 ) }
也可以在每个视图views,py中通过设置authencation_classess属性来配置
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication, BasicAuthentication from rest_framework.views import APIView class ExampleView(APIView): authentication_classes = (SessionAuthentication, BasicAuthentication) ...
认证失败会有两种可能的返回值:
>>> 401 Unauthorized 未认证
>>> 403 Permission Denied 权限被禁止
书写自定义的认证组件
api/authentications.py
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed from . import models class MyAuthentication(BaseAuthentication): def authenticate(self, request): # 前台在请求头携带认证信息, # 且默认规范用 Authorization 字段携带认证信息, # 后台固定在请求对象的META字段中 HTTP_AUTHORIZATION 获取 auth = request.META.get('HTTP_AUTHORIZATION', None) # 处理游客 if auth is None: return None # 设置一下认证字段小规则(两段式):"auth 认证字符串" auth_list = auth.split() # 校验合法还是非法用户 if not (len(auth_list) == 2 and auth_list[0].lower() == 'auth'): raise AuthenticationFailed('认证信息有误,非法用户') # 合法的用户还需要从auth_list[1]中解析出来 # 注:假设一种情况,信息为abc.123.xyz,就可以解析出admin用户;实际开发,该逻辑一定是校验用户的正常逻辑 if auth_list[1] != 'abc.123.xyz': # 校验失败 raise AuthenticationFailed('用户校验失败,非法用户') user = models.User.objects.filter(username='admin').first() if not user: raise AuthenticationFailed('用户数据有误,非法用户') return (user, None)
# 登录:账号密码 => token(账号密码对应的用户) # 访问需要登录的接口:携带token发送请求 => 校验token,得到用户
views.py
from rest_framework.views import APIView class TestAPIView(APIView): def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): # 如果通过了认证组件,request.user就一定有值 # 游客:AnonymousUser # 用户:User表中的具体用户对象 print(request.user) return APIResponse(0, 'test get ok')
postman测试时需要注意的点
用post请求在Headers的key:Authoriaztion,内携带认证数据返送个后端。

系统权限类
权限Permissions
权限控制可以限制用户对于视图的访问和对于具体数据对象的访问
-
-
在通过get_object()获取具体对象时,会进行模型对象访问权限的判断
源码解析
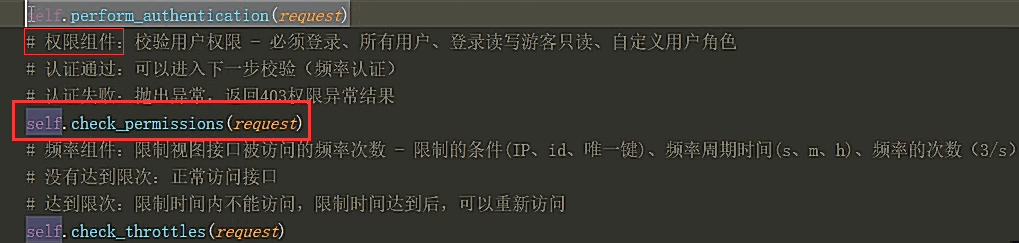
源码分析:
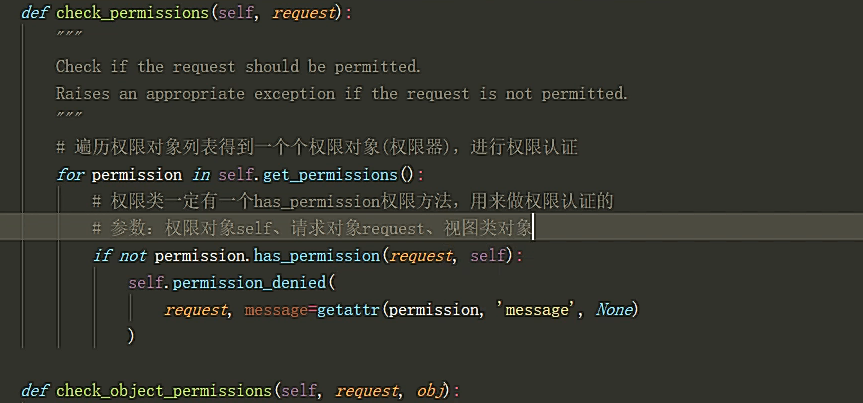
得出权限配置的settings
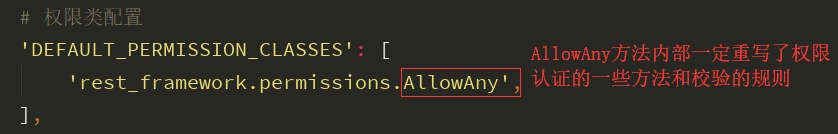
AllowAny内部封装
内部权限校验的其他方法
""" 1)AllowAny: 认证规则全部返还True:return True 游客与登陆用户都有所有权限 2) IsAuthenticated: 认证规则必须有登陆的合法用户:return bool(request.user and request.user.is_authenticated) 游客没有任何权限,登陆用户才有权限 3) IsAdminUser: 认证规则必须是后台管理用户:return bool(request.user and request.user.is_staff) 游客没有任何权限,登陆用户才有权限 4) IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly 认证规则必须是只读请求或是合法用户: return bool( request.method in SAFE_METHODS or request.user and request.user.is_authenticated ) 游客只读,合法用户无限制 """
api/views.py 举例校验
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated class TestAuthenticatedAPIView(APIView): permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated] def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return APIResponse(0, 'test 登录才能访问的接口 ok') # 因为默认全局配置的权限类是AllowAny # settings.py REST_FRAMEWORK = { # 权限类配置 'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [ 'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny', ], }
自定义的权限类
分析:
""" 1) 创建继承BasePermission的权限类 2) 实现has_permission方法 3) 实现体根据权限规则 确定有无权限 4) 进行全局或局部配置 认证规则 i.满足设置的用户条件,代表有权限,返回True ii.不满足设置的用户条件,代表有权限,返回False """
utils/permissions.py
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission from django.contrib.auth.models import Group class MyPermission(BasePermission): def has_permission(self, request, view): # 只读接口判断 r1 = request.method in ('GET', 'HEAD', 'OPTIONS') # group为有权限的分组 group = Group.objects.filter(name='管理员').first() # groups为当前用户所属的所有分组 groups = request.user.groups.all() r2 = group and groups r3 = group in groups # 读接口大家都有权限,写接口必须为指定分组下的登陆用户 return r1 or (r2 and r3)
views.py
# 游客只读,登录用户只读,只有登录用户属于 管理员 分组,才可以增删改 from utils.permissions import MyPermission class TestAdminOrReadOnlyAPIView(APIView): permission_classes = [MyPermission] # 所有用户都可以访问 def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return APIResponse(0, '自定义读 OK') # 必须是 自定义“管理员”分组 下的用户 def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return APIResponse(0, '自定义写 OK')
使用权限认证配置
可以在配置文件中设置默认的权限管理类,如:
REST_FRAMEWORK = { 'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated', ) }
如果为指明,则采用如下默认配置
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny', )
也可以在具体的视图中通过permissions_classes属性来设置,如
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated from rest_framework.views import APIView class ExampleView(APIView): permission_classes = (IsAuthenticated,) ...
提供的权限有一下几种
""" - AllowAny 允许所有用户
- IsAuthenticated 仅通过认证的用户
- IsAdminUser 仅管理员用户
- IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly 已经登陆认证的用户可以对数据进行增删改操作,没有登陆认证的只能查看数据。 """
举例
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated from rest_framework.generics import RetrieveAPIView class BookDetailView(RetrieveAPIView): queryset = BookInfo.objects.all() serializer_class = BookInfoSerializer authentication_classes = [SessionAuthentication] permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated]
